The Laboratory of Multiscale Bioimaging (LMB) investigates the molecular structure and dynamics of complex molecular machines and cascades in the context of the living cell.
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
Hochauflösende Gehirnkartierung dank Röntgenlicht in Reichweite
Ein Durchbruch bei einem bildgebenden Verfahren könnte die Verbindungen innerhalb des Gehirns in bisher unerreichter 3D-Auflösung sichtbar machen.
Wie das Prinzip von Käsenudeln gegen Alzheimer hilft
Forschende des PSI haben zelluläre Mechanismen entdeckt, die helfen könnten, Krankheiten wie Alzheimer oder Parkinson einzudämmen.
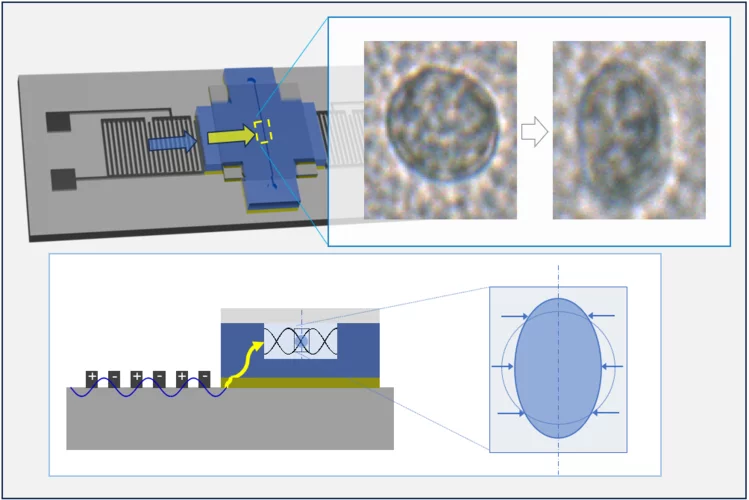
Manipulating microscopic object with sound
Manipulating microscopic objects with sound: hybrid acoustic tweezers with strong acoustic field were developed and successfully applied for transient mechanical deformation and capturing of biological cells.
Publications
-
Chen Y, Sun X, Tang Y, Tan Y, Guo C, Pan T, et al.
Pathogenic mutation ΔK280 promotes hydrophobic interactions involving microtubule-binding domain and enhances liquid-liquid phase separation of tau
Small. 2025; 21(6): 2406429 (12 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202406429
DORA PSI -
Aidukas T, Phillips NW, Diaz A, Poghosyan E, Müller E, Levi AFJ, et al.
High-performance 4-nm-resolution X-ray tomography using burst ptychography
Nature. 2024; 632(8023): 81-88. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07615-6
DORA PSI -
Asmara TC, Green RJ, Suter A, Wei Y, Zhang W, Knez D, et al.
Emergence of interfacial magnetism in strongly‐correlated nickelate‐titanate superlattices
Advanced Materials. 2024; 36(38): 2310668 (14 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202310668
DORA PSI -
Braunger JM, Cammarata LV, Sornapudi TR, Uhler C, Shivashankar GV
Transcriptional changes are tightly coupled to chromatin reorganization during cellular aging
Aging cell. 2024; 23(3): e14056 (18 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.14056
DORA PSI -
Cellini A, Shankar MK, Nimmrich A, Hunt LA, Monrroy L, Mutisya J, et al.
Directed ultrafast conformational changes accompany electron transfer in a photolyase as resolved by serial crystallography
Nature Chemistry. 2024; 16: 624-632. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01413-9
DORA PSI