Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
Rezeptorproteinen beim Verbiegen zuschauen
G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren vermitteln unzählige Prozesse im Körper. Im Interview erzählt PSI-Forscher Ramon Guixà, wie er die Rezeptormoleküle auf dem Bildschirm lebendig werden lässt.
Neuer Bauplan für stabilere Quantencomputer
PSI-Forscher haben gezeigt, wie sich schnellere und genauere Quantenbits erschaffen liessen. Die zentralen Elemente sind dabei magnetische Atome aus der Klasse der sogenannten Seltenen Erden, die gezielt in das Kristallgitter eines Materials eingebracht würden.
Clocking the movement of electrons inside an atom
Scientists pioneer an approach called self-referenced streaking, clocking Auger electrons with sub-femtosecond resolution. The breakthrough will unlock the broader potential for attosecond time resolution at X-ray free-electron lasers
SLS 2.0 approved - TOMCAT 2.0 cleared for takeoff!
In December 2020 the Swiss parliament approved the Swiss Dispatch on Promotion of Education, Research and Innovation (ERI) for 2021 to 2024 which includes funding for the planned SLS 2.0 upgrade. The new machine will lead to significantly increased brightness, thus providing a firm basis for keeping the SLS and its beamlines state-of-the-art for the decades to come. The TOMCAT crew is very excited that the TOMCAT 2.0 plans (deployment of the S- and I-TOMCAT branches, see SLS 2.0 CDR, p. 353ff) have been included in the Phase-I beamline upgrade portfolio. These beamlines will receive first light right after the commissioning of the SLS 2.0 machine around mid 2025. A first milestone towards this goal has just been achieved, with the successful installation of the S-TOMCAT optics hutch during W1 of 2021. The TOMCAT scientific and technical staff would like to thank Mr. Nolte and his Innospec crew for delivering perfectly on schedule.
PSI rüstet die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS für die Zukunft
Grünes Licht für die SLS 2.0: Das geplante Upgrade der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS kann stattfinden, die Finanzierung ist im Rahmen der BFI-Botschaft 2021-2024 zugesichert, die Mitte Dezember verabschiedet wurde.
Dreidimensionaler Blick in aktive Katalysatoren
Die operando-Röntgenspektroskopie erlaubt einen Blick ins Innere laufender Chemiereaktoren. Forschende des Karlsruher Instituts für Technologie (KIT), am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI und an der European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Frankreich setzen die Methode erfolgreich ein.
Der Bibliothekar der Petabytes
Das geplante Upgrade der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS muss schon jetzt vorbereitet werden. Um der künftigen Forschung gerecht zu werden, schätzt Alun Ashton die Datenmenge ab, die die kommenden Experimente produzieren werden.
Meilenstein für zweite Strahllinie des SwissFEL
Am Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI wird zurzeit die zweite Strahllinie in Betrieb genommen. Mittels «Athos» wollen Forschende verstehen, wie Katalysatoren funktionieren oder Biomoleküle Erbkrankheiten verursachen.
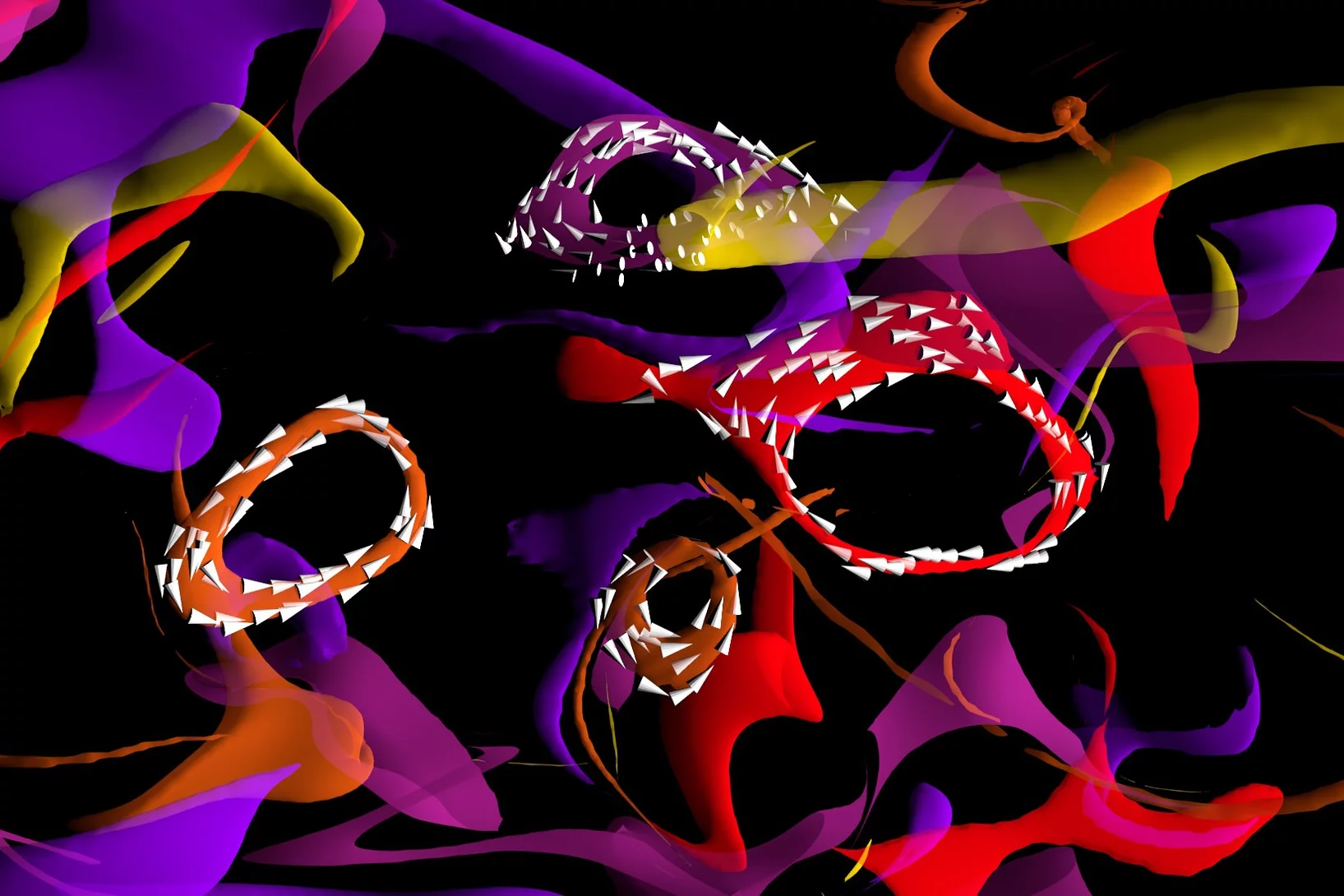
Magnetic vortices come full circle
The first experimental observation of three-dimensional magnetic ‘vortex rings’ provides fundamental insight into intricate nanoscale structures inside bulk magnets, and offers fresh perspectives for magnetic devices.
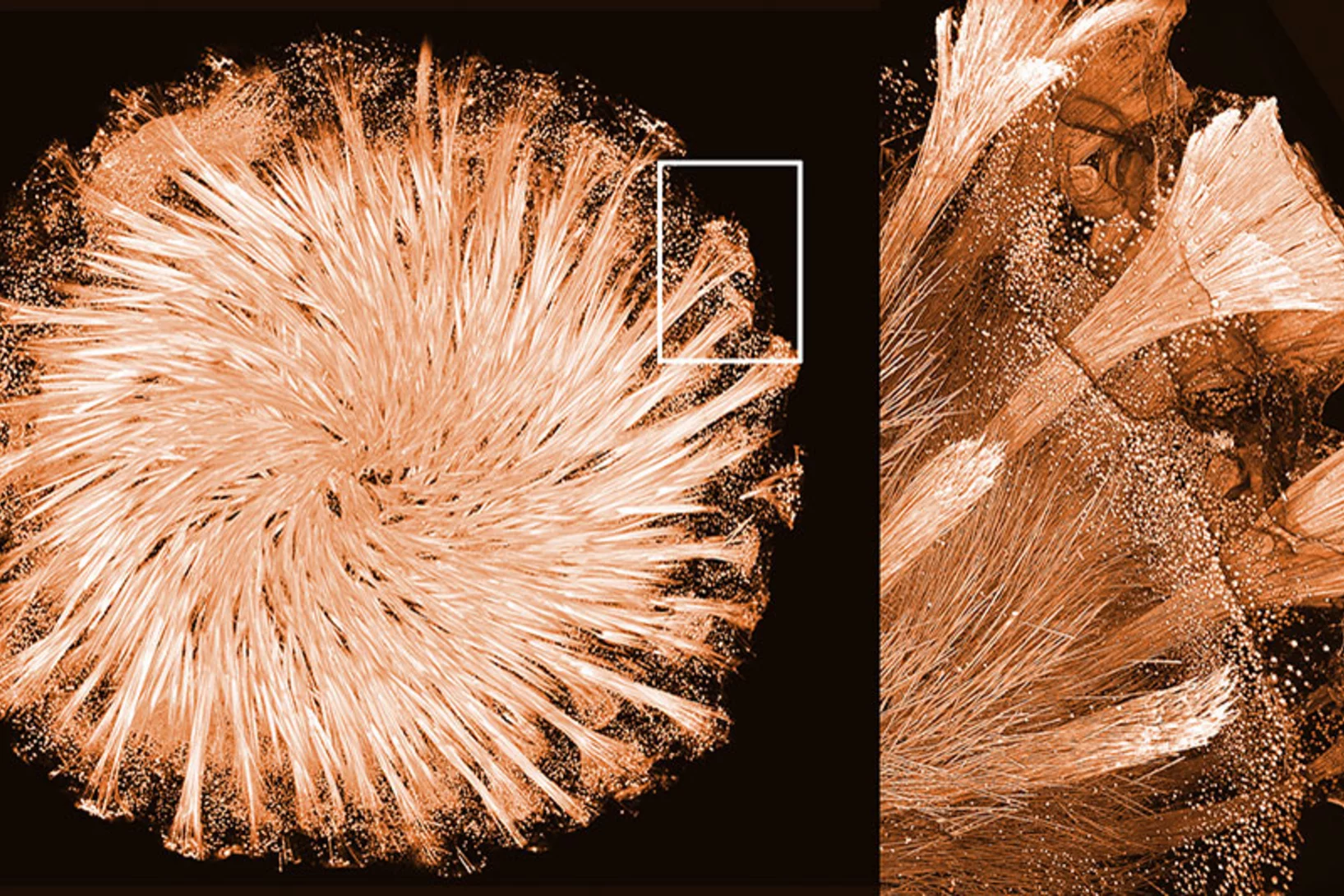
Struktur von glasbildenden Proteinen in Schwämmen aufgeklärt
Messungen an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS haben dabei geholfen zu verstehen, wie der bisher einzige bekannte natürliche Protein-Mineral-Kristall gebildet wird. Er ist Teil des faszinierenden Glasgerüsts von tierischen Schwämmen.
Ruzicka Prize
The Ružička Prize 2020 goes to Dr. Patrick Hemberger (PSI) for his research on understanding the mechanisms of catalytic fast pyrolysis by unveiling reactive intermediates in heterogeneous catalysts.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
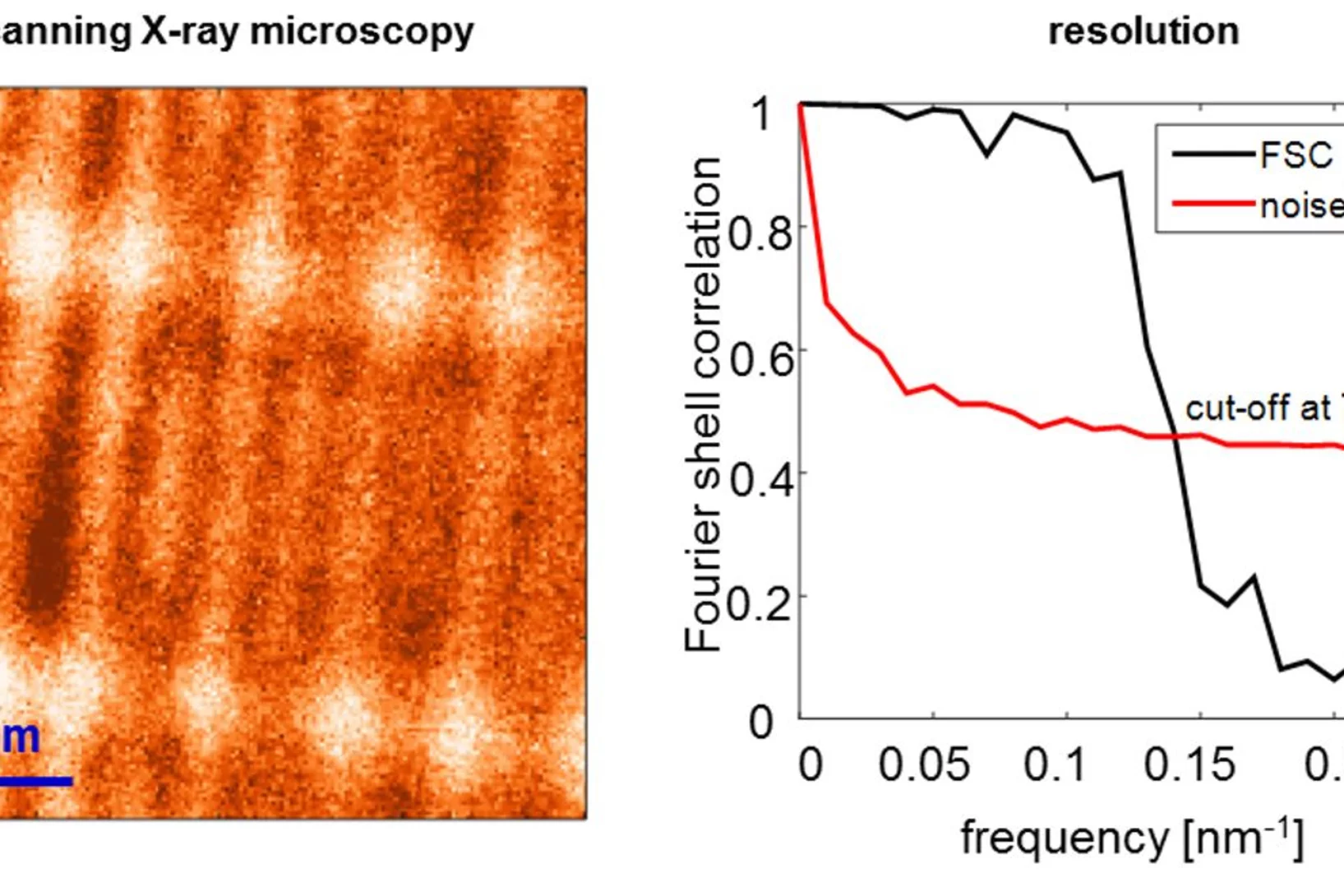
World Record: 7 nm Resolution in Scanning Soft X-ray Microscopy
During the past decade, scientists have put high effort to achieve sub-10 nm resolution in X-ray microscopy. Recent developments in high-resolution lithography-based diffractive optics, combined with the extreme stability and precision of the PolLux and HERMES scanning X-ray microscopes, resulted now in a so far unreached resolution of seven nanometers in scanning soft X-ray microscopy. Utilizing this highly precise microscopy technique with the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism effect, dimensionality effects in an ensemble of interacting magnetic nanoparticles can be revealed.
BEATS Project
Mirjam van Daalen, chair of the BEATS Steering Committee
COVID-19 - travel assistance websites launched
The Bio Nano spinout of Prof. Aeppli has launched new travel assistance websites that provide continually updated information on restrictions such as multi-day quarantines imposed on travel between countries, together with the latest pandemic predictions so that travellers can make informed decisions.
SwissFEL: Die Schwarze Mörtelbiene fühlt sich hier pudelwohl
Für den Bau des SwissFEL wurden 2013 rund fünf Hektar Wald gerodet und zu neuem Lebensraum für Flora und Fauna umgestaltet. Jetzt haben Biologen und Forstingenieure Zwischenbilanz zum Erfolg des Renaturierungsprojekts gezogen – und sind begeistert.
Abwarten und Kristalle züchten
Am PSI entschlüsseln Forschende die Struktur der Proteine von Bakterien und Viren. Mit diesem Wissen lassen sich beispielsweise Medikamente gegen Infektionskrankheiten entwickeln. Doch zuallererst muss ein äusserst kniffliges Problem gelöst werden: die Kristallisation der Moleküle.
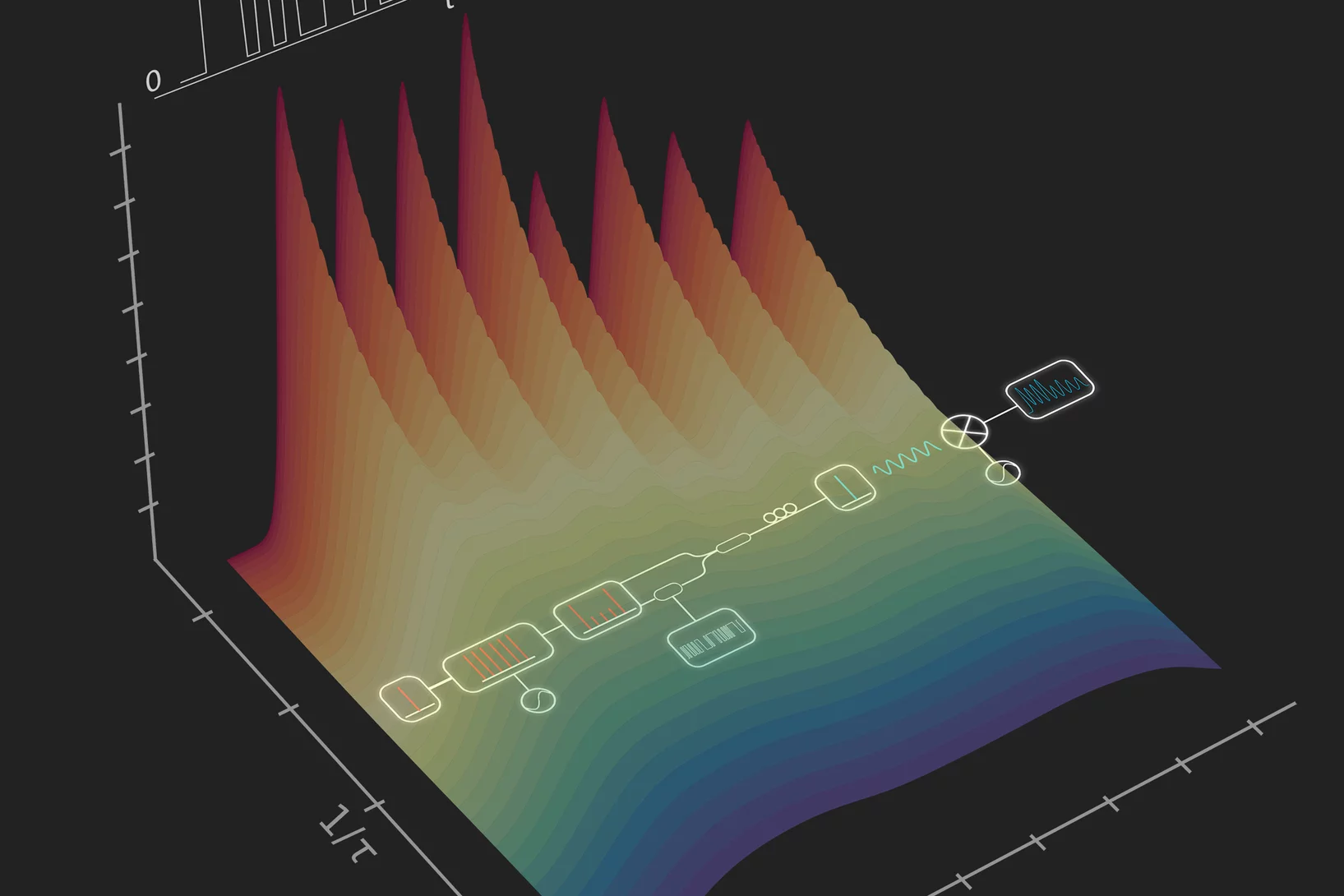
Harnessing components from the optical internet for programmable spectroscopy
A novel concept for extracting information from spectra where traditional post-processing procedures fail, dubbed ‘software-defined spectroscopy’, offers a fresh approach to high-resolution terahertz spectroscopy. The new method implements an ‘optical comb’ and combines it with a programmable modulator, all using components from the optical internet.
Messungen am PSI ermöglichten detailliertes Verständnis der Gen-Schere
Das PSI gratuliert Emmanuelle Charpentier und Jennifer Doudna zum diesjährigen Nobelpreis für Chemie. Experimente an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS im Jahr 2013 ermöglichten es, die Struktur des Proteinkomplexes CRISPR-Cas9 aufzuklären.
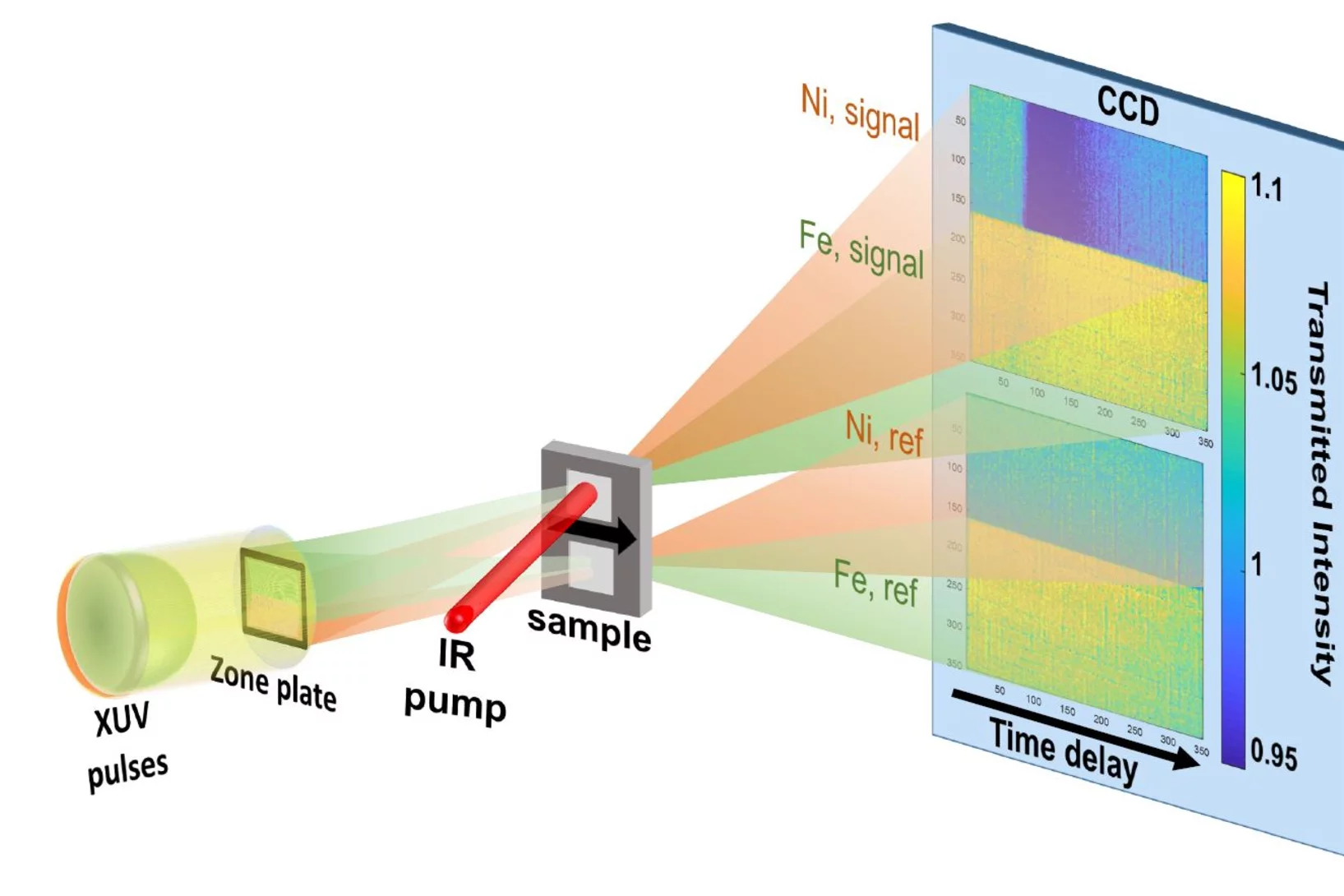
Two-color snapshots of ultrafast charge and spin dynamics
In a joint research effort, an international team of scientists lead by Emmanuelle Jal (Sorbonne Université) performed a time-resolved experiment at the FERMI free-electron laser to disclose the dynamic behavior of two magnetic element of a compount material in only one snapshot. The X-ray Optics and Applications group developed a dedicated optical element for this experiment that is usable with two different photon energies (colors) simultaneously.
PSI - member of the Microsoft Quantum Network
The PSD is a research partner in the Microsoft Quantum Network, which is a broad community of individuals and organizations collaborating with Microsoft to advance a comprehensive quantum ecosystem, develop practical solutions, and build a robust quantum workforce.
The institutions of scientific excellence are partnering collaboratively with Microsoft to pursue the advancement of quantum computing research, development, and education. The large scale facilities at PSI, in particular the Swiss Light Source, offers unique characterizations techniques to shed light on the secrets of functional materials.
First light in the SwissFEL Maloja endstation
The first endstation at the SwissFEL Athos soft X-ray branch is rapidly developing and on track for first experiments in 2021.
Ein elektronisches Material massschneidern
Forschende am PSI haben ein Material untersucht, das sich für zukünftige Anwendungen in der Datenspeicherung eignen könnte. Mit einem Trick haben sie die Kristallstruktur ihrer Probe gezielt verzerrt und dabei vermessen, wie dies die magnetischen und elektronischen Eigenschaften beeinflusst.
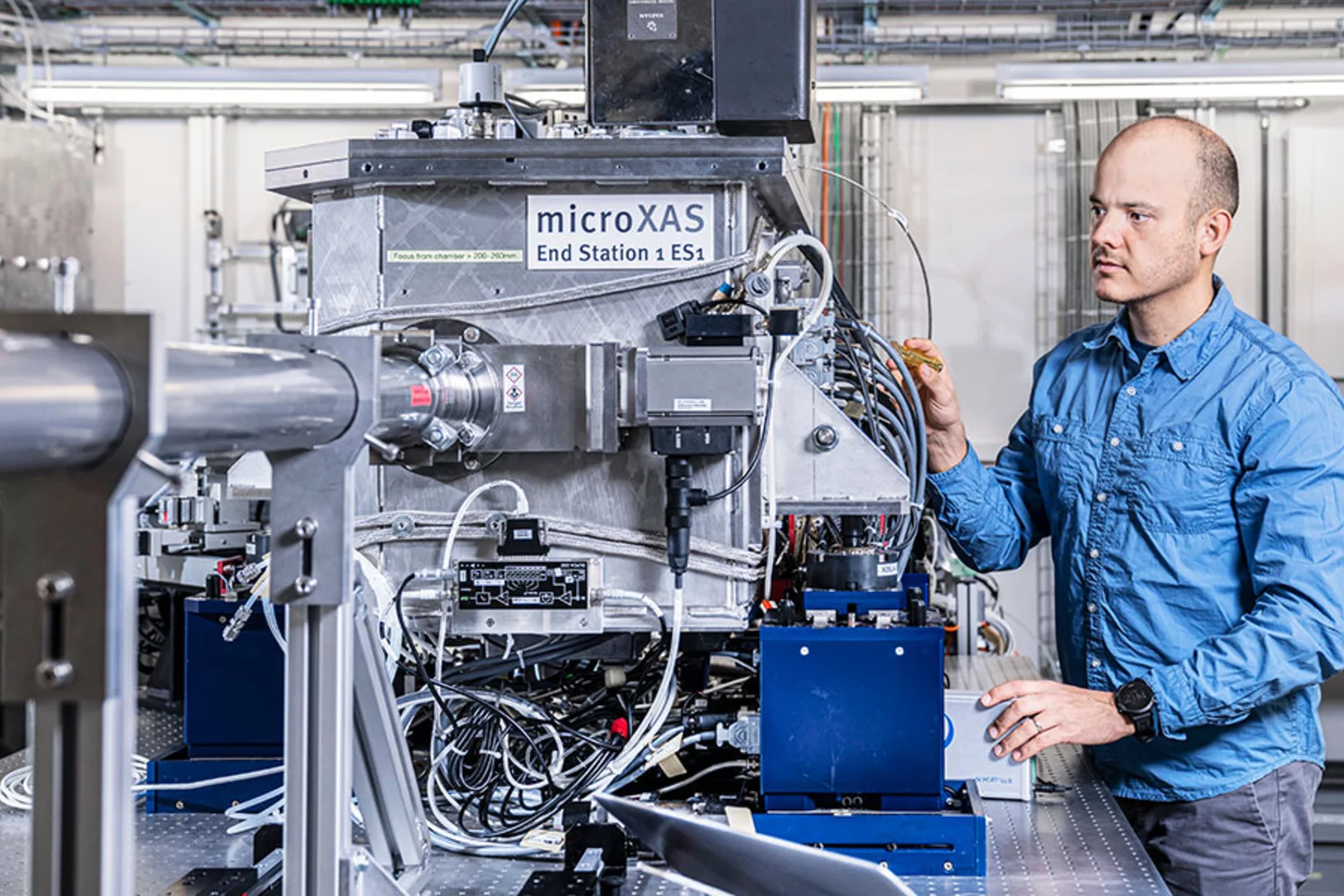
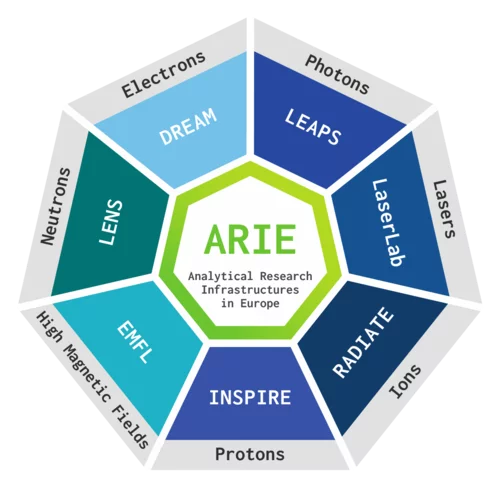
Analytical Research Infrastructures of Europe (ARIE) join forces to face COVID-19 and other viral and microbial threats
After the joint position paper published as a pre-release in July, in which the Analytical Research Infrastructures of Europe (ARIE) presented their plan to tackle HE Missions, the ARIE enhanced its cross-border, multidisciplinary collaboration to offer Europe a strong and valid weapon against the present COVID-19 challenge and other potential viral and microbial threats.
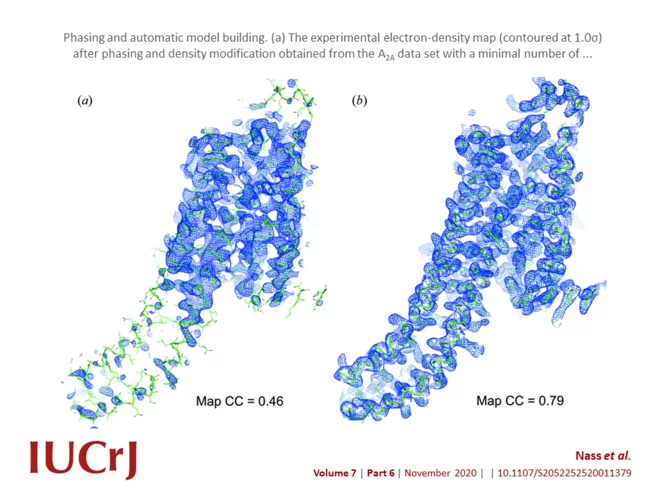
Advances in long-wavelength native phasing at X-ray free-electron lasers
Long-wavelength pulses from the Swiss X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) have been used for de novo protein structure determination by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) phasing of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) data.
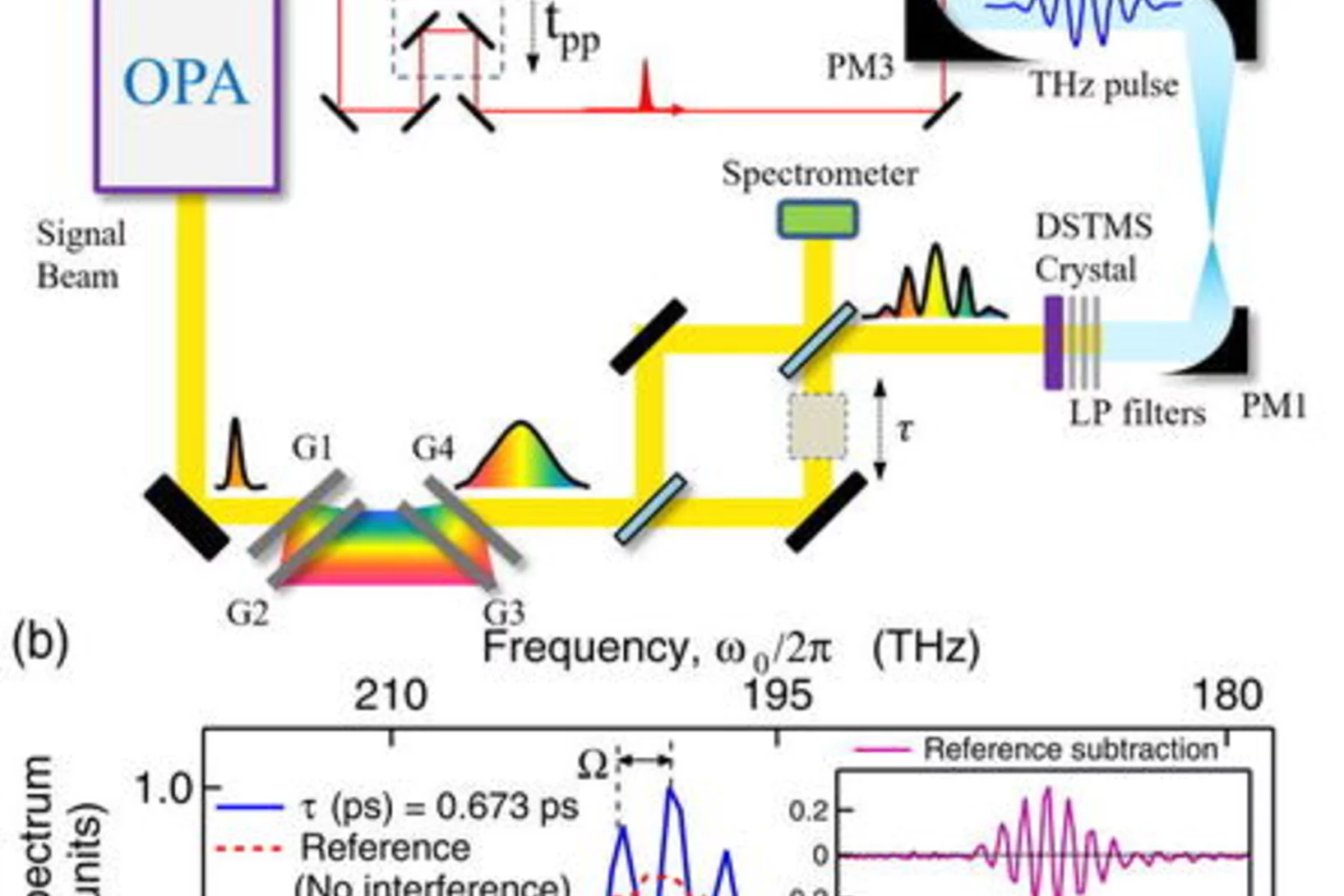
Narrow-band and tunable intense terahertz pulses for mode-selective coherent phonon excitation
We generate frequency-tunable narrow-band intense fields in the terahertz (THz) range by optical rectification of a temporally modulated near-infrared laser pumping a nonlinear organic crystal.
«Forschung online erleben»: Mittendrin statt nur dabei
Erstmals Live-Rundgang durch eine Grossforschungsanlage per Video-Stream. Am 9. September haben Interessierte exklusiv die Möglichkeit, sich von Experten des PSI durch den neuen Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL führen zu lassen und zu erfahren, welche Rätsel der Materie und der Natur sich damit lösen lassen.
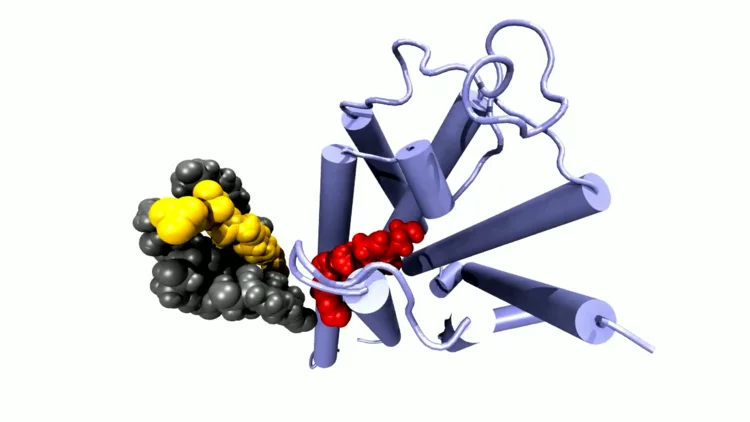
Eine Frage der Bindung
Am PSI screenen Forschende Molekülfragmente darauf, ob diese an wichtige Proteine des Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 binden und dieses so möglicherweise lahmlegen können. Aus den vielen Einzelinformationen erhoffen sie sich eine Antwort darauf, wie ein wirkungsvolles Medikament aussehen kann.
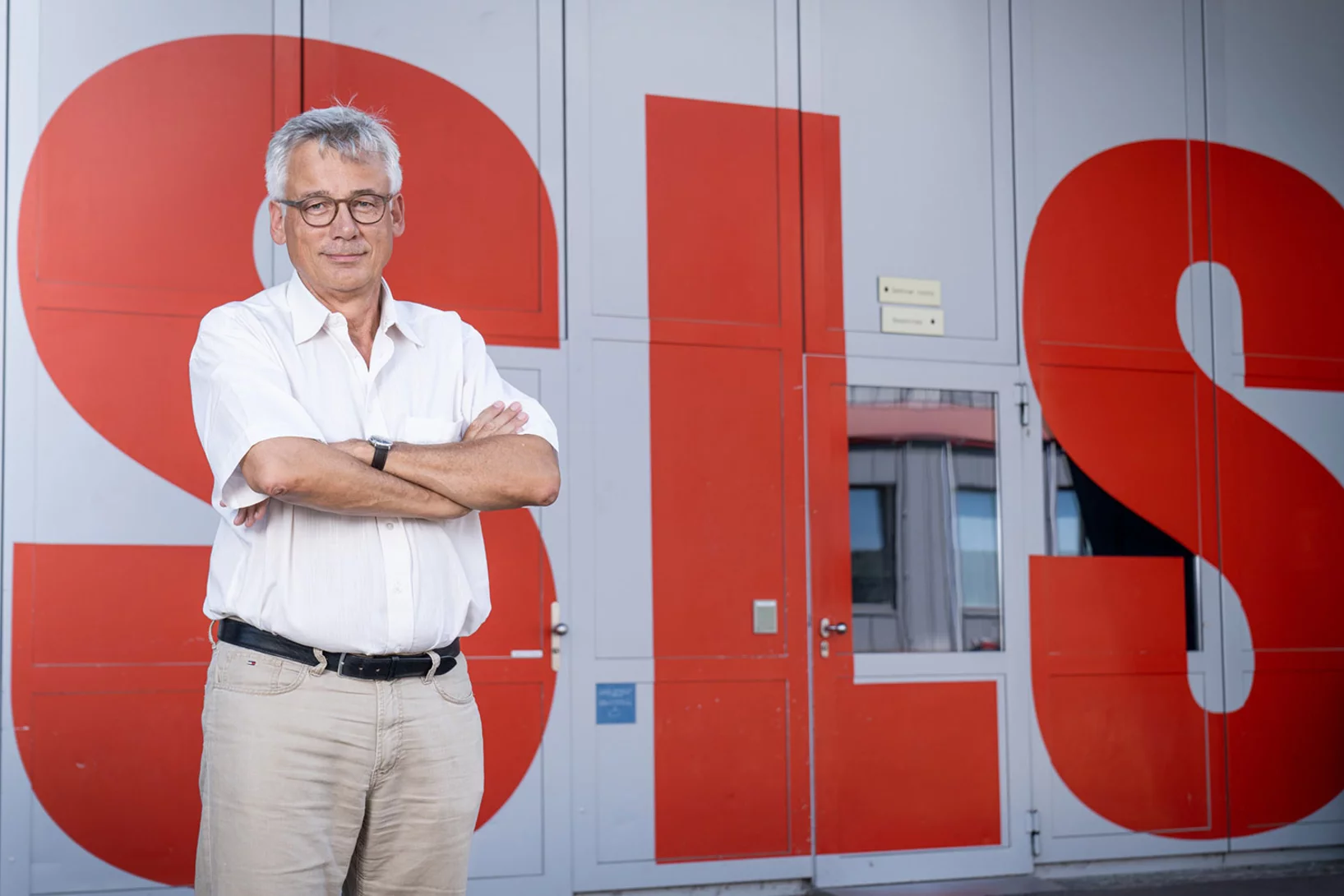
«Wir machen die SLS zukunftsfähig»
Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS soll ein Upgrade erhalten, um auch in den kommenden Jahrzehnten exzellente Forschung möglich zu machen. Hans Braun, Projektleiter SLS 2.0, spricht im Interview über das Vorhaben.