Neutron imaging as a non-destructive testing method can be used for a broad spectrum of industrial applications. It provides similar capabilities as industrial X-ray i.e. radiographic images or 3D tomographic views of samples with a size of a few centimeters up to tens of centimeters. Due to the quite different attenuation characteristics of neutrons and X-ray, neutrons are most useful if small amounts of hydrogenous material has to be detected within a metallic or ceramics sample.
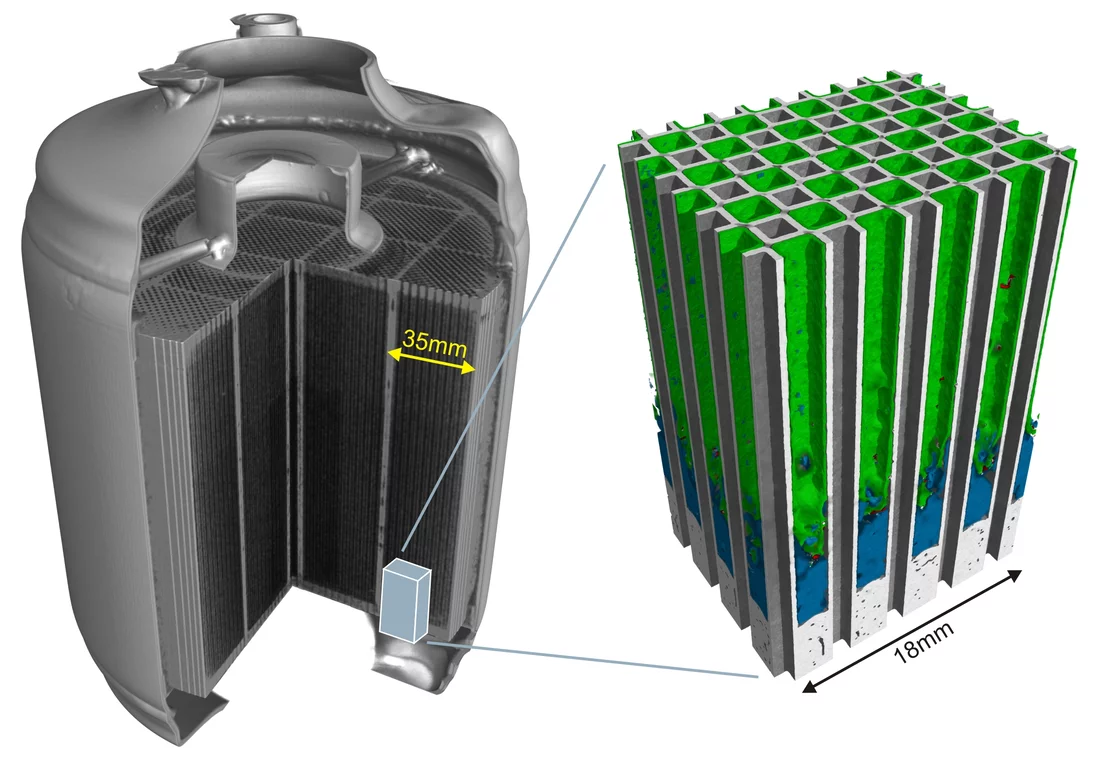
Neutron tomography is presently the only possibility to obtain information about the three-dimensional distribution of soot and ash in a filter monolith. The estimation of the soot distribution in a diesel particulate filter with neutron imaging is possible because neutrons are highly sensitive to the element hydrogen, which is content of soot.
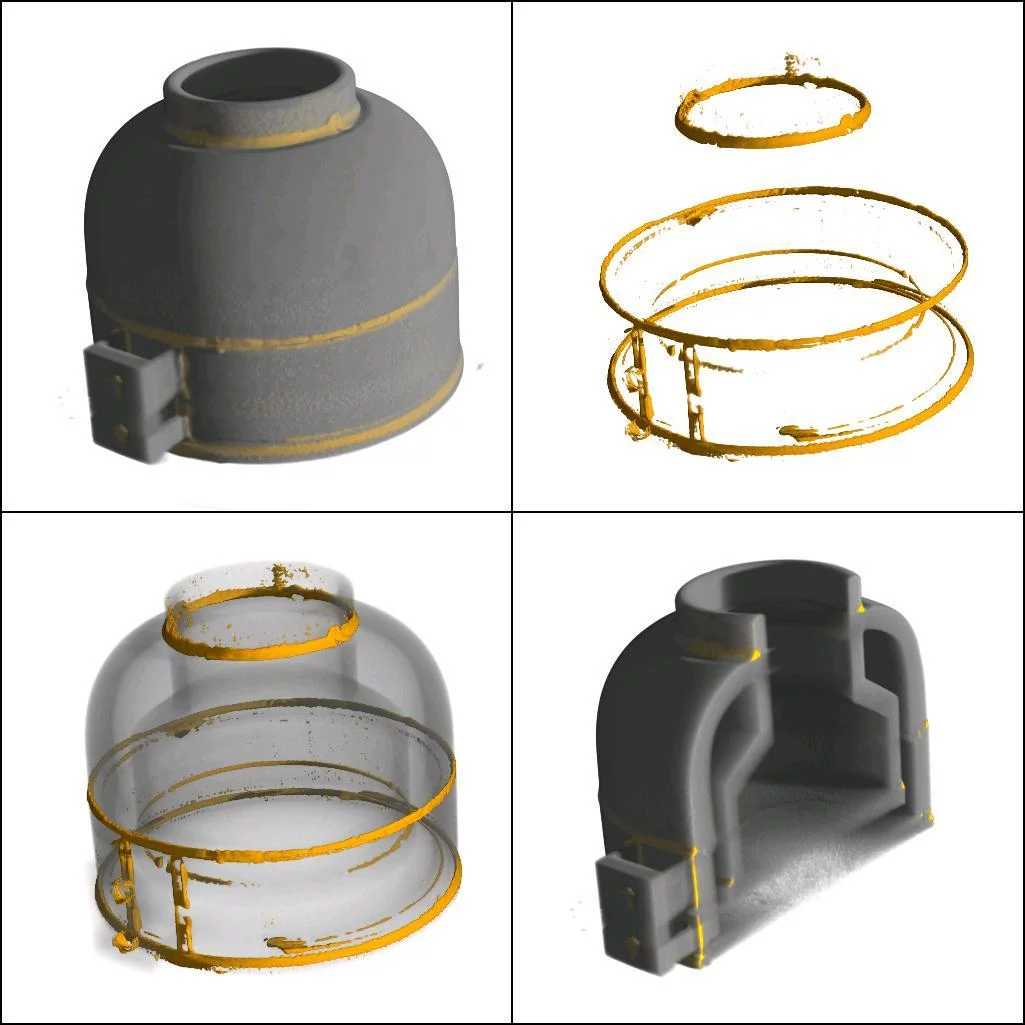
Boron containing brazing solder shows with high contrast in a steel sample. This is due to the high neutron absorption coefficient of boron for thermal neutrons.
In a collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut experts from the company quattro GmbH (Neckarsulm, Germany) were investigatig the fluid dynamics of car shock absorber systems using neutron imaging. The aim of this project was the comparison of digital simulation results with experimental dynamic vehicle-behaviour.
Applied Materials Group - Industry Contact
AMG responsible
Dr. David Mannes
Paul Scherrer Institut
LNS WBBA/108
5232 Villigen PSI