News & Events
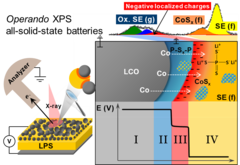
Reactivity and potential profile across the electrified LiCoO2-Li3PS4 interface probed by operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
All-solid-state lithium batteries are a promising alternative for next generation of safe energy storage devices, provided that parasitic side reactions and the resulting hindrances in ionic transport at the electrolyte-electrode interface can be overcome. Motivated by the need for a fundamental understanding of such interface, we present here real-time measurements of the (electro-)chemical reactivity and local surface potential at the electrified interface Li3PS4 and LiCoO2 using operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Deciphering the Mechanism of FEC-induced SEI Formation in Li-ion Batteries
Fluoroethylene-carbonate is often referred to as a film-forming electrolyte additive for Li-ion batteries, resulting in high quality Solid–Electrolyte-Interphase on negative electrode, however, the underlying mechanism, even if thought to be known, has been only clarified due to our targeted experimental design, combining systematic electrochemical, chemical and microscopy characterization techniques. We have shown that first the formation of inorganic LiF-rich particles appear and only later the carbonate-rich film is actually formed.
Towards in situ imaging of electrolyte physical and chemical changes in Li-ion batteries
The Lithium conducting electrolyte is a critical component of Li-ion batteries, as it has an important impact on performance and its durability, in particular in case of extreme environmental conditions. At low temperatures, a partial solidification can occur, while high temperatures can promote the degradation of the electrolyte. Using time-of-flight (ToF) neutron radiography, the possibility of imaging such changes in a fully non-invasive manner was demonstrated for the first time.
First direct observation of the oxygen transport in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis
PSI researchers have developed a new methodology for studying the complex transport processes in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE). Using advanced operando X-ray tomographic microscopy, we were able to observe for the first time the formation of oxygen pathways in the porous transport layer, in three dimensions. Understanding oxygen transport is crucial for improving PEWE technology and this work provides precious insights for the design of future, better-performing PEWE cells.
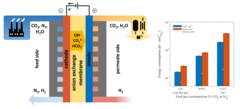
An electrochemical membrane processes for CO2 capture
CO2 capture from dilute gas mixtures (e.g., combustion flue gases, air) is increasingly recognized as a critical technological pathway towards stemming catastrophic climate change. Conventional thermal-based processes for removing CO2 from flue gas (e.g., amine scrubbing) are energy intensive and significantly reduce power plant efficiency. Electrochemical separation approaches have the potential to reduce these power requirements considerably by using electrons to transport CO2 as (bi)-carbonate ions across an alkaline membrane.
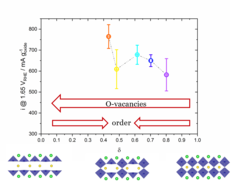
Correlation between Oxygen Vacancies and Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity for a Model Electrode: PrBaCo2O5+δ
The role of the oxygen stoichiometry of perovskite catalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is systematically studied in the PrBaCo2O5+δ family. The reduced number of physical/chemical variables combined with in-depth characterizations such as neutron diffraction, O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy(XAS), electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), magnetization and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) studies, helps investigating the complex correlation between OER activity and a single perovskite property, such as the oxygen content. Larger amount of oxygen vacancies appears to facilitate the OER, possibly contributing to the mechanism involving the oxidation of lattice oxygen, i.e., the lattice oxygen evolution reaction (LOER). Furthermore, not only the number of vacancies but also their local arrangement in the perovskite lattice influences the OER activity, with a clear drop for the more stable, ordered stoichiometry.
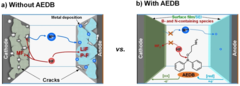
Cross-Talk–Suppressing Electrolyte Additive for Li-ion Batteries
Control of interfacial reactivity at high-voltage is a key to high-energy-density Li-ion batteries. 2-aminoethyldiphenyl borate was investigated as an electrolyte additive to stabilize surface and bulk of both NCM851005 and graphite in the cell with upper cut-off voltage of 4.4 V vs Li+/Li. AEDB almost completely eliminated the “cross-talk” in the cell, by significantly reducing metal leaching from the cathode, preventing their deposition at the anode, and further electrolyte decomposition.
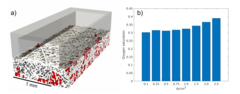
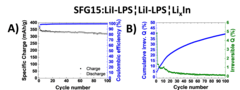
Excellent cycling stability of graphite in all-solid-state battery using sulfide solid electrolyte
All-solid-state lithium ion batteries represent a promising battery technology for boosting the volumetric energy density and promising a superior safety. In this study excellent cycling stability of graphite anode material have been demonstrated in combination with sulfide-based solid electrolyte. Furthermore we evaluated the stability of the graphite-electrolyte interface by analyzing the normalized cumulative irreversible charge during cycling experiments.
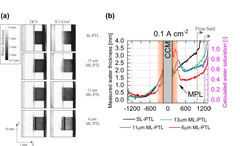
Impact of micro-porous layers (MPL) on two-phase flow in electrolyzers
Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolyzers (PEWE), due to their excellent dynamic characteristics, can provide an economical solution to the intermittent nature of new renewable sources, by converting the excess electricity into hydrogen. However, improvements in efficiency and in capital cost are still required for the large-scale deployment of this solution. In this context, we studied whether the efficiency improvements observed when using porous structures featuring a micro-porous layer (MPL) can be attributed to a better distribution of the water.