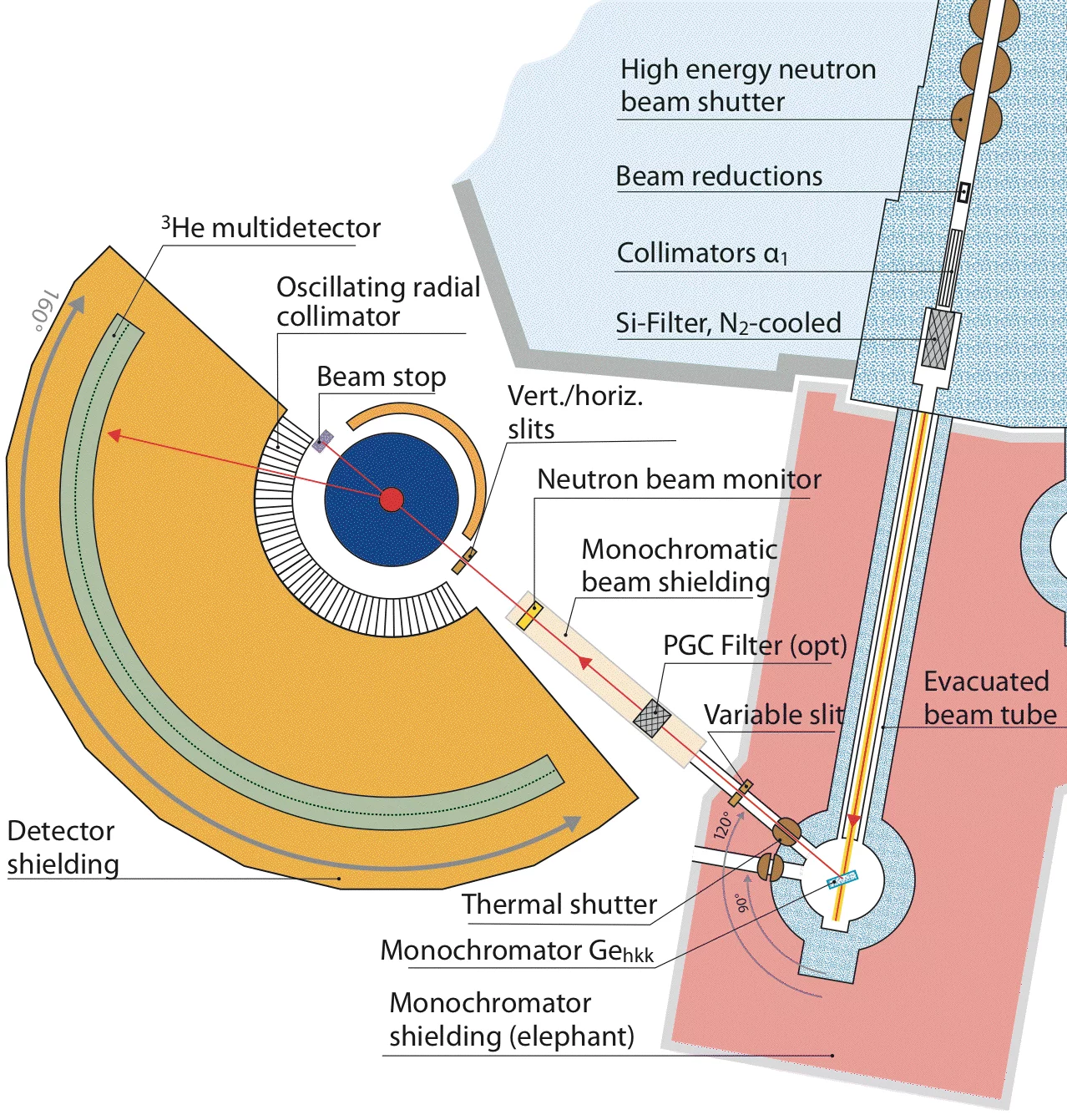
| Neutrons: | thermal (0.84-2.954Å) beam 1RNS41 from a water scatterer close to the SINQ target. |
| Primary collimation: | Gd-O Soller collimators with primary white beam collimations α1 = 6', 12', 24' (high resolution), - = approx. 40' (high intensity) |
| Liquid N2 cooled Si filter: | 20 cm length |
| Monochromator | Ge (hkk) of wafer type, 28 cm high, variable vertical focusing, total mosaic halfwidth 15' |
| Secondary collimation: | variable computer controlled slit system for monochromatic beam |
| Radial collimators: (from JJ X-Ray, Risø, Denmark) | Oscillating mylar-Gd-O collimators to eliminate Bragg peaks from sample environment such as from cryostat or furnace tails. FWFM are 14mm and 28mm. |
| PSD detector: (LCP1600 from Cerca, F-26104 Romans) (more pictures) | 3He (3.6 bar + 1.1 bar CF4), 25 x 64 = 1600 counters, step 0.1°, 15 cm high, radius 1.5 m, effective detection length 3.5 cm |
| Stroboscopic mode of operation | The maximal time resolution is 10ms: for instance a process started with the strobe signal each minute can be chopped by time interval of 10 milliseconds resulting in simultaneous collection of 3000 powder diffraction spectra corresponding to the different time from the strobe signal. Maximal number of histograms is about 100000. |
| HRPT gas mixture cleaning/adding system (more pictures) | cleaning of the gas mixture from (O2, H2O, etc) by a circulation of the gas mixture through the appropriate filters without pumping out the mixture. |
| Sample containers, beam size, sample space: | cylindrical, normally V tubes (also double cylinders), diameters 5 to 10 mm, usable height up to 50 mm (1cm3, 1.4cm3, 2.5cm3, 4.3cm3 for 5, 6, 8 and 10mm), sample under He gas atmosphere for air sensitive samples, sealed by In wire on the top flange of 25 mm diameter, M6 screw to fix the sample container; diameter of sample table = 40 cm, height sample table to neutron beam center = 270 (400) mm; |
| Sample temperature: | 50 mK - 1800 K |
| Magnetic field: | superconducting magnet MAO6, field H vertical to scattering plane, H up to 6 T. |
| Zero matrix pressure cells: | up to 8, 15 kbar for full scattering angle range. Example of pattern, |
| Sample changers: | Room temperature sample changer for eight (8) samples, low temperature sample changer for four (4) samples (more pictures) , low temperature sample changer for five (5) samples with sample rotation |
"Powder neutron diffraction at continuous spallation source SINQ (pdf)", Workshop "High-resolution Neutron Diffraction: Current and Future Perspectives", 7th-8th January 2020, The Cosener’s House, Abingdon, UK
V. Pomjakushin, "High Resolution Powder Diffractometer for Thermal Neutrons." (pdf 31 Mb).
Talk given at the AIC Information Day on "Large Facilities for Crystallography Studies: Synchrotron and Neutron sources" October 19th, 2009 , Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen, Switzerland.
"Experimental powder diffraction using HRPT as an example" as it is (pdf 41 Mb).
Master class, October 26th, 2013, Paul Scherrer Institut
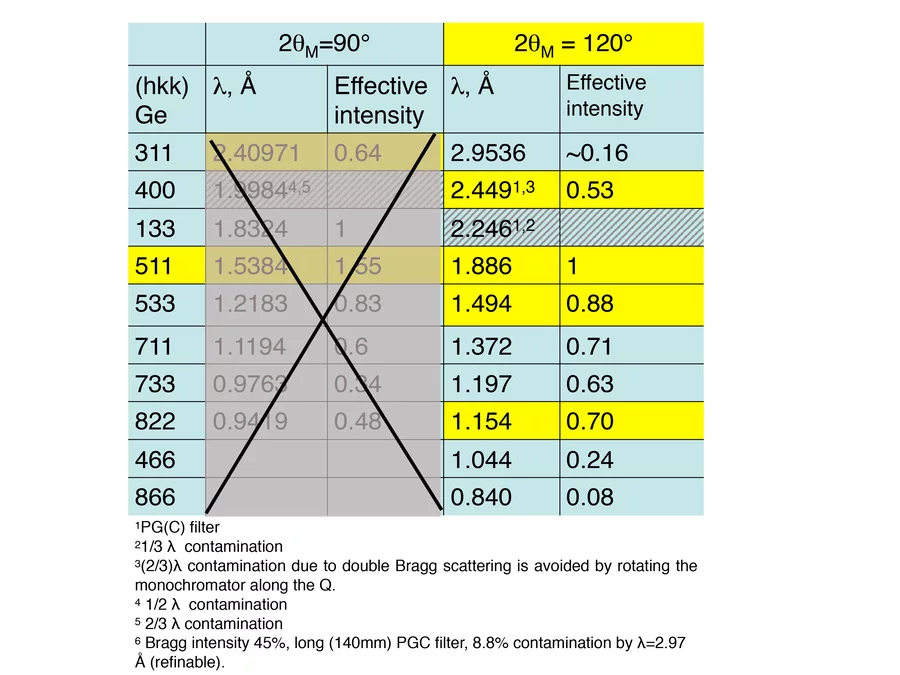
Choice of wavelength and resolution
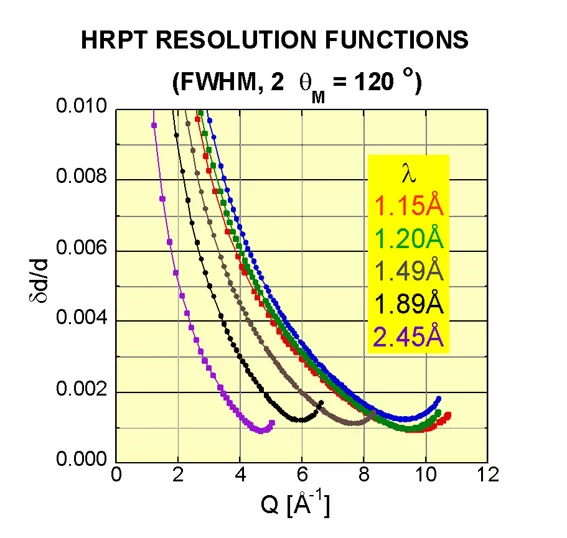
Possible choice of neutron wavelength and corresponding effective counting rates (calibrated by V) of the HRPT detector relative to the choice of λ = 1.886 Å in HI mode with 40’- collimation. Typical modes of HRPT are HI:40’-, MR:12’-24’, HR:6’-12’. Counting rates are decreased by the factor of ~3 and ~(8-10) for MR and HR, respectively. Typical resolution parameters.
Comparison of resolution for different modes of operation
Comparison of HRPT resolutions for 1.5A:
Comparison of resolutions as a function of Q:
- Comparison of low Q for 1.5A HI and 2.45A HR, HI ,
- Comparison of low Q for 1.5A HR and 2.45A HR, HI ,
- high Q for HR1.5, HI HR 2.5,HR 1.15 ,
- high Q zoom for HR1.5, HI HR 2.5,HR 1.15
Comparison of resolutions for different diameters of V-containers