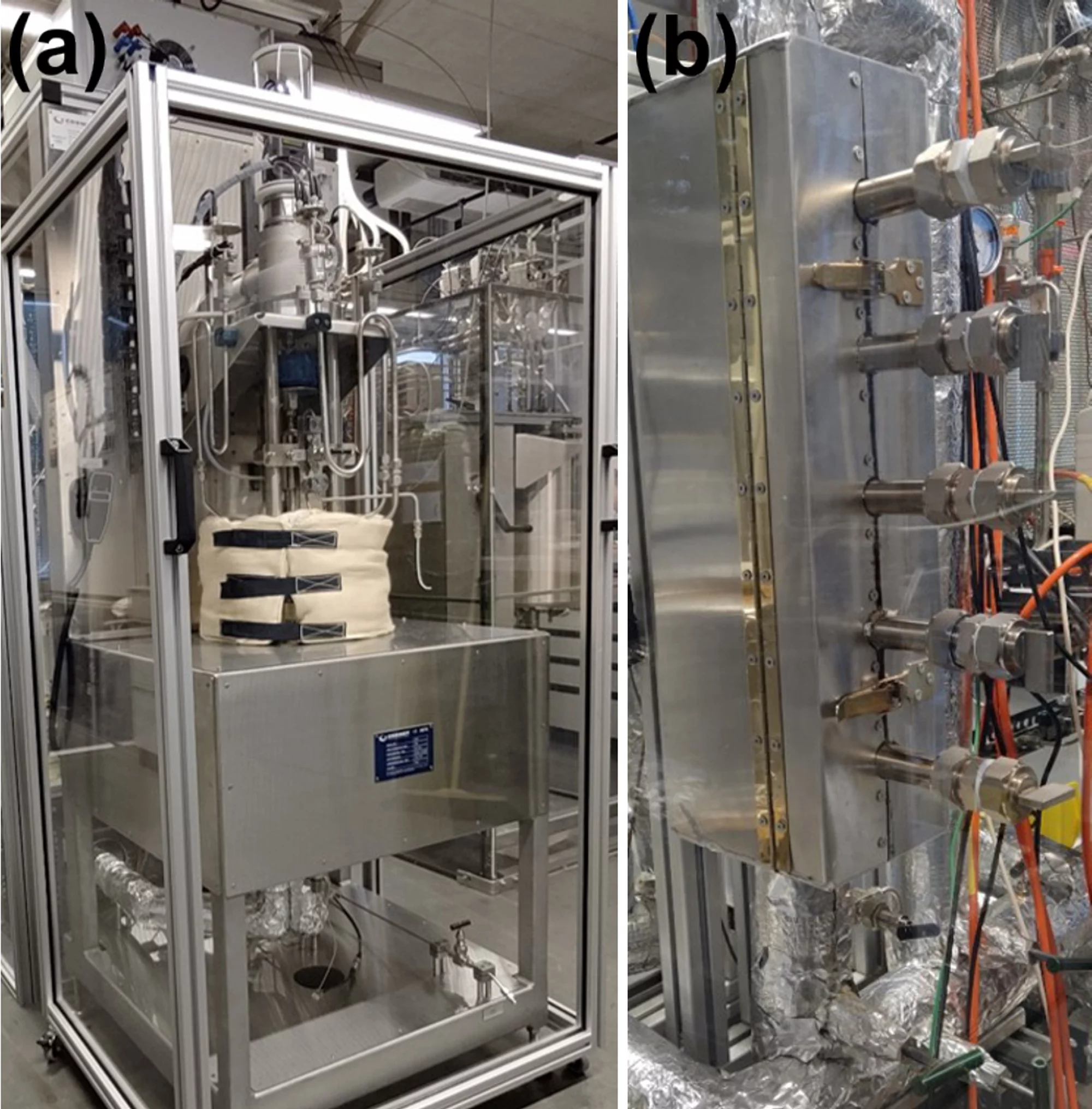
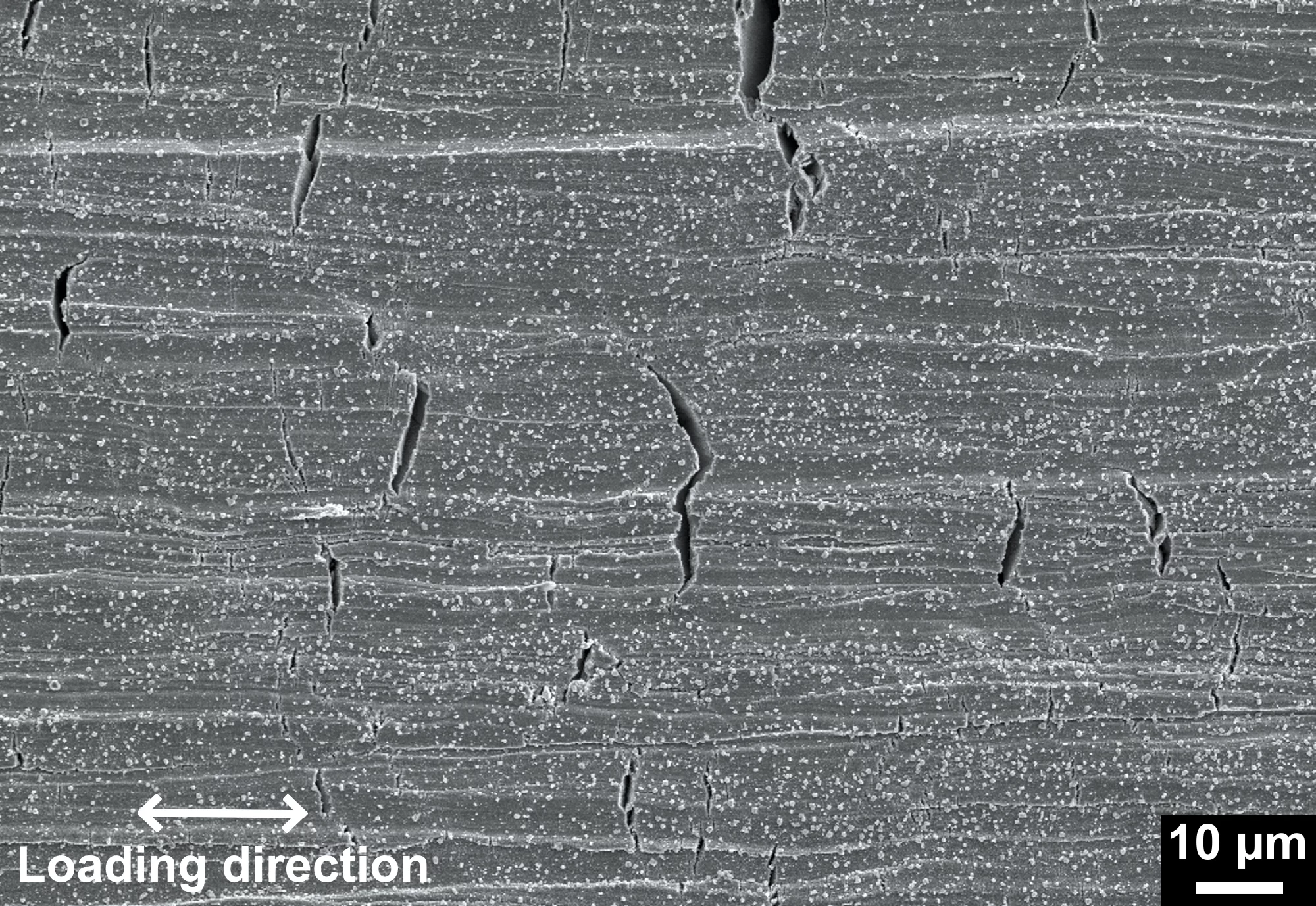
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of structural materials is one of the biggest concern in the context of long-term operation of the Swiss boiling (BWR) and pressurised water reactor (PWR) fleet. Zinc (Zn), even added in very small amounts to the reactor coolant system, has proven to be an effective method for lowering shut-down dose rates in light water reactors. Accessorily, some very few investigations have indicated that Zn-injection might also have a positive effect on minimising the degradation of structural materials. The effectiveness of Zn-injection on mitigation of SCC initiation of steam generator tubes (Alloy 600, PWR) has been shown in plants and labs. However, very little is known about the influence of Zn-injection on the SCC behaviour (especially crack propagation) of other structural materials in a reactor system. In addition, the working mechanism of Zn-injection on the SCC initiation and propagation is poorly studied.
Therefore a research project, financially supported by the Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (ENSI), has been started in 2019 to further validate the Zn-injection technique and reveal its working mechanism. The special emphasis of this project is placed on examining the SCC initiation threshold stress/time and SCC propagation rate of a Ni-based alloy (Alloy 182) and stainless steel (AISI 316L) in simulated BWR and PWR environments with different contents of Zn. Furthermore, the composition, structure, mechanical properties and repassivation kinetics of surface/crack-flank oxide films with and without Zn-injection will be characterised.