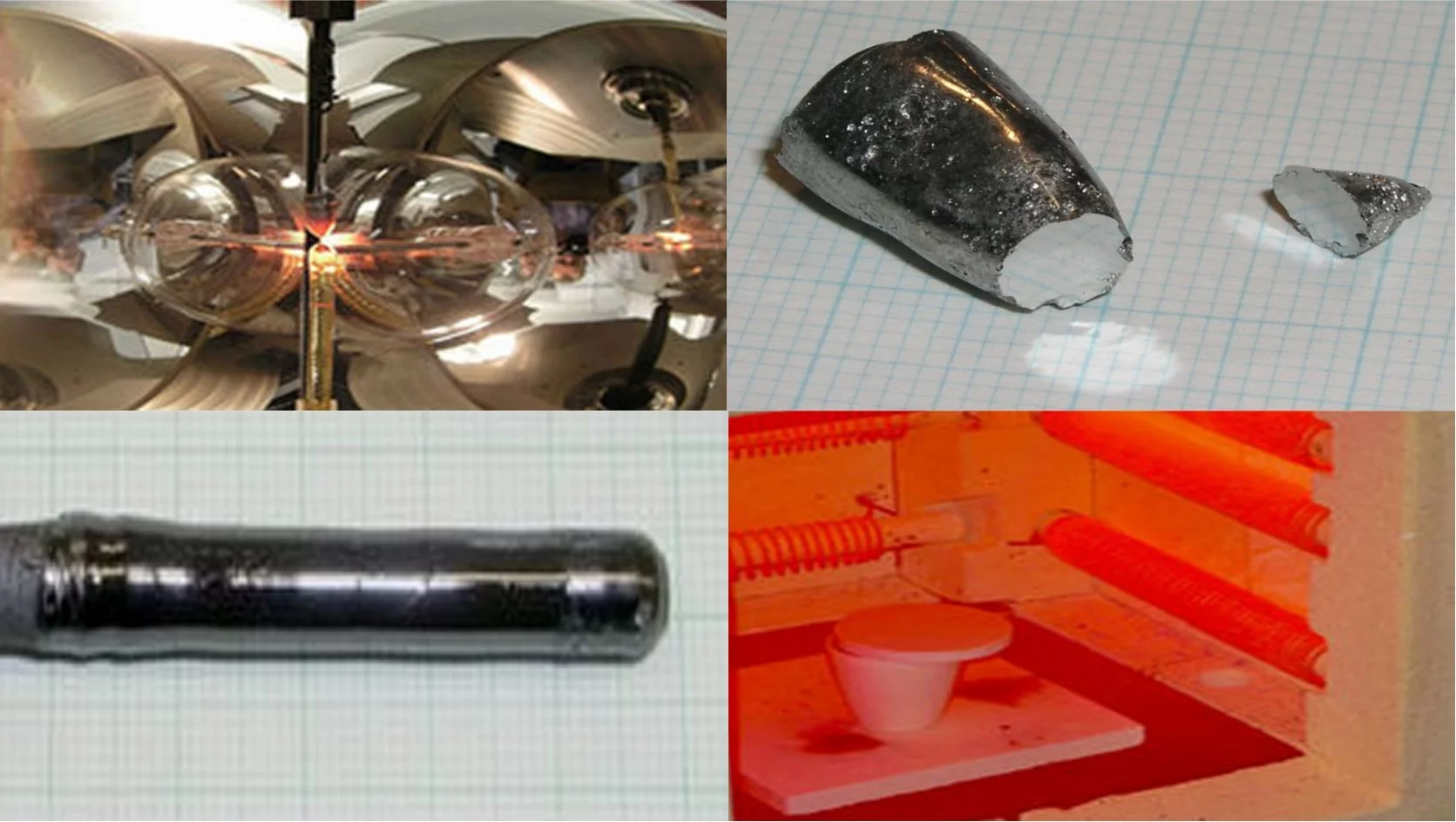
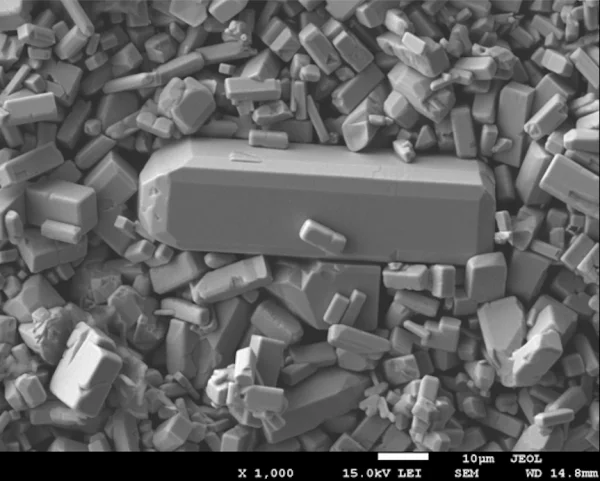
We are working on the synthesis and characterization of ceramic and single crystal materials with novel electronic and magnetic properties. Numerous complex oxide materials have been successfully crystallized by the Traveling Solvent Floating Zone (TSFZ) method using an optical furnace. This includes cuprates, manganates, orthoferrites, cobaltites, borates and phosphates. Novel chalcogenide iron superconductors have been synthesized as powders and single crystals (Bridgman method).
News
Tips and Tricks for the Crystal Growth of Inorganic Materials
We are happy to announce that the call for abstracts for the Workshop on Tips and tricks for the crystal growth of inorganic materials is now open. The workshop brings together experts from the Solid State Chemistry and Condensed Matter Physics communities in order to discuss the accomplished progress and perspectives for future developments in the synthesis and crystal growth of materials with novel and interesting physical properties. The event will take place at the Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI), Switzerland, 26th-27th of August 2024.
Doctoral thesis award 2022 for Igor Plokhikh
Doctoral thesis award of the Dr. Alfons Paulus Foundation at the University of Regensburg, Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy for Igor Plokhikh
On 14th of July 2022 Dr Igor Plokhikh (currently postdoc at SSCG, LMX PSI) has been awarded with the Doctoral thesis award of the Dr. Alfons Paulus Foundation at the University of Regensburg, Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy. He completed his doctoral studies at the group of Prof. Arno Pfitzner working on synthesis, crystal growth and characterization of crystal and magnetic structures of new magnetic Eu2+-containing compounds. This work resulted in discovery of over 10 new compounds, some of which exhibit complex magnetic phase diagrams.
NCCR-MARVEL Highlight 2021
First-ever rare earth nickelate single crystals lead to first experimental evidence supporting predicted multiferroicity
Scientific Highlight
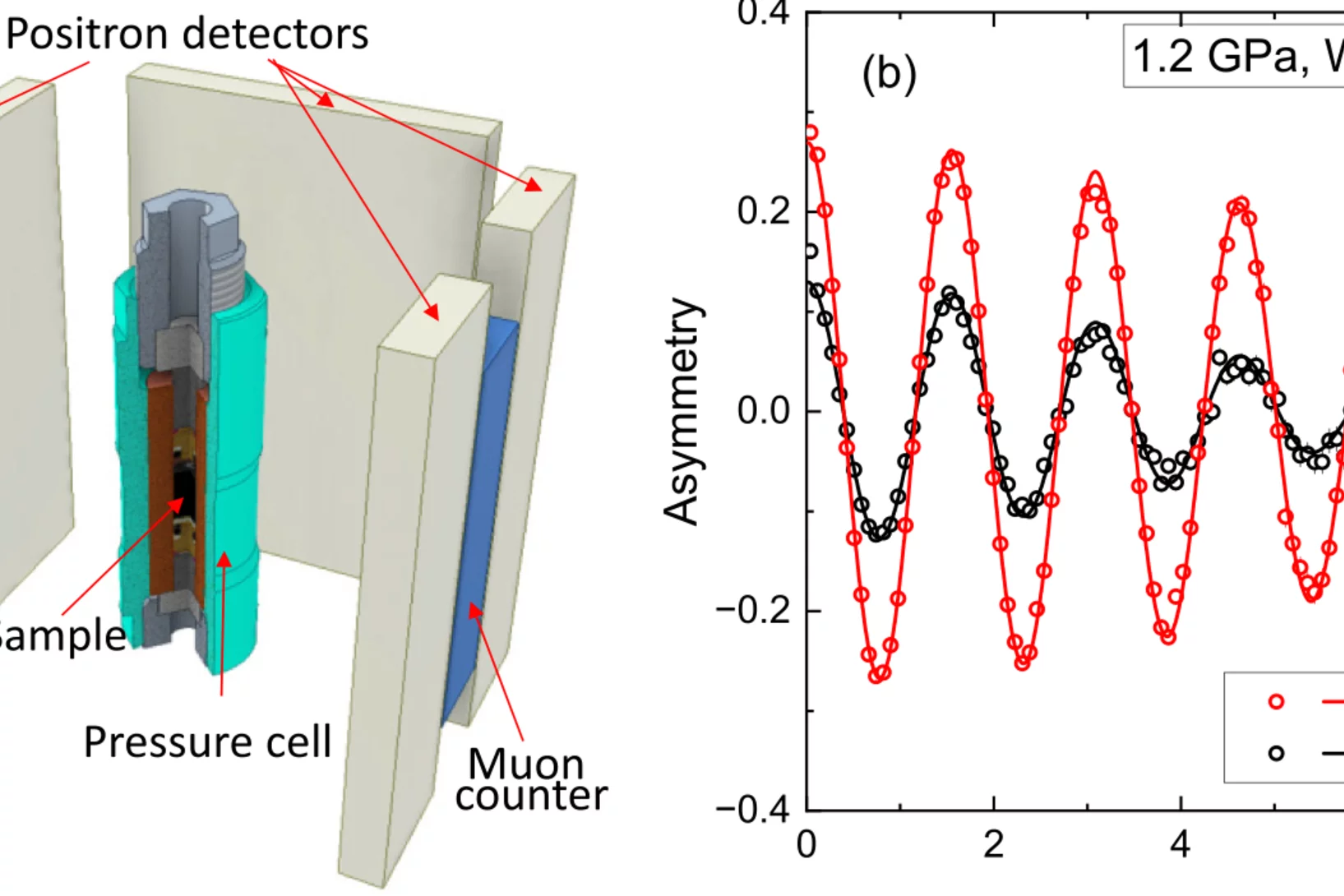
Pressure effect on the spin density wave transition in La2PrNi2O6.96
High-pressure studies reveal a stark contrast between the superconducting properties of double-layer Ruddlesden-Popper (RP) nickelates La2PrNi2O7 and La3Ni2O7. While La2PrNi2O7 exhibits bulk superconductivity, La3Ni2O7 displays filamentary behavior, suggesting that superconductivity is confined to phase interfaces rather than the bulk. Since magnetism emerges ...
Anomalous Hall Effect due to Magnetic Fluctuations in a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal
The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) has emerged as a key indicator of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) and topological features in electronic band structures. Absent of a magnetic field, the AHE requires spontaneous TRSB but has proven hard to probe due to averaging over domains. The anomalous component of the Hall effect is thus frequently derived from extrapolating the magnetic field dependence of the Hall response. We show ....
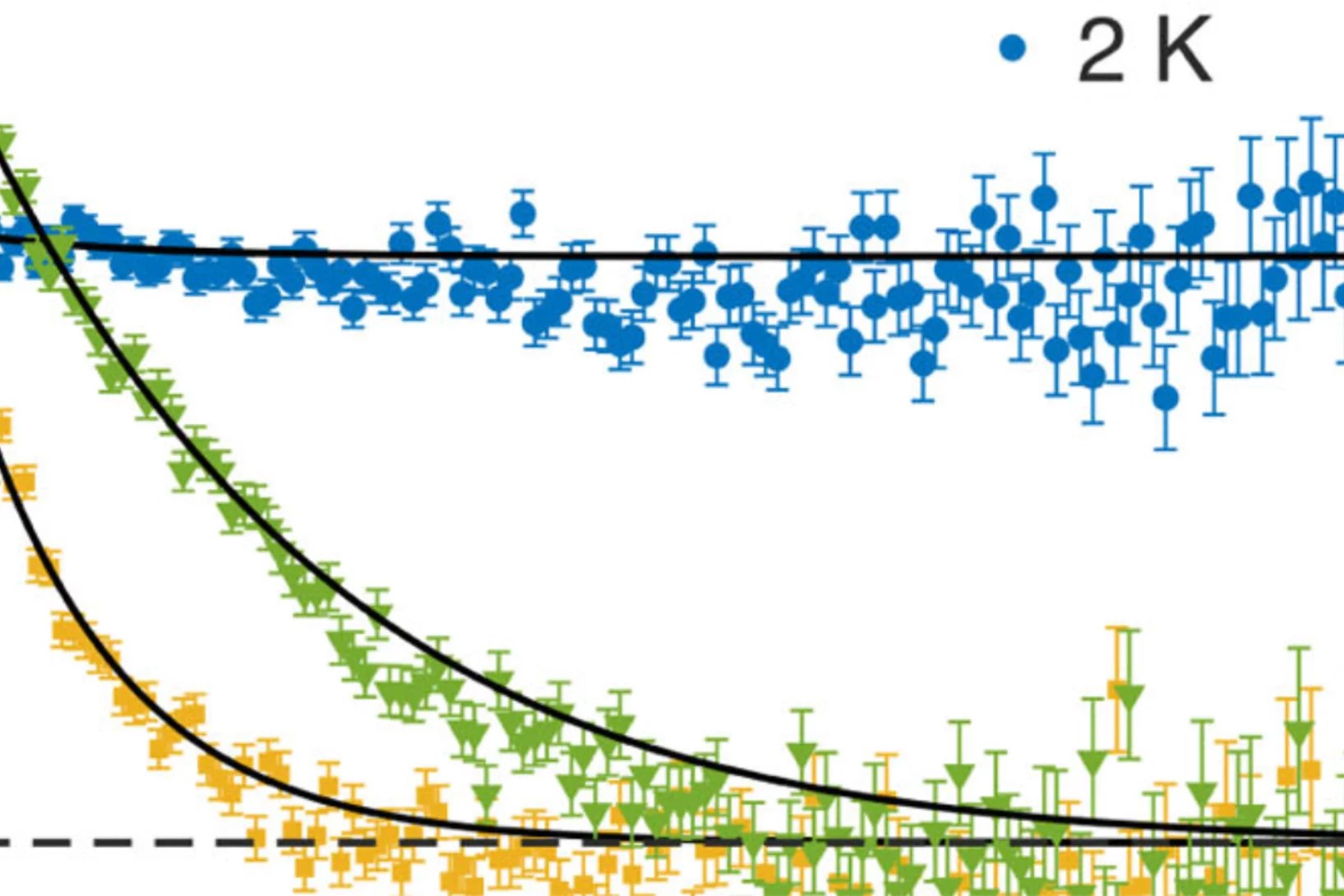
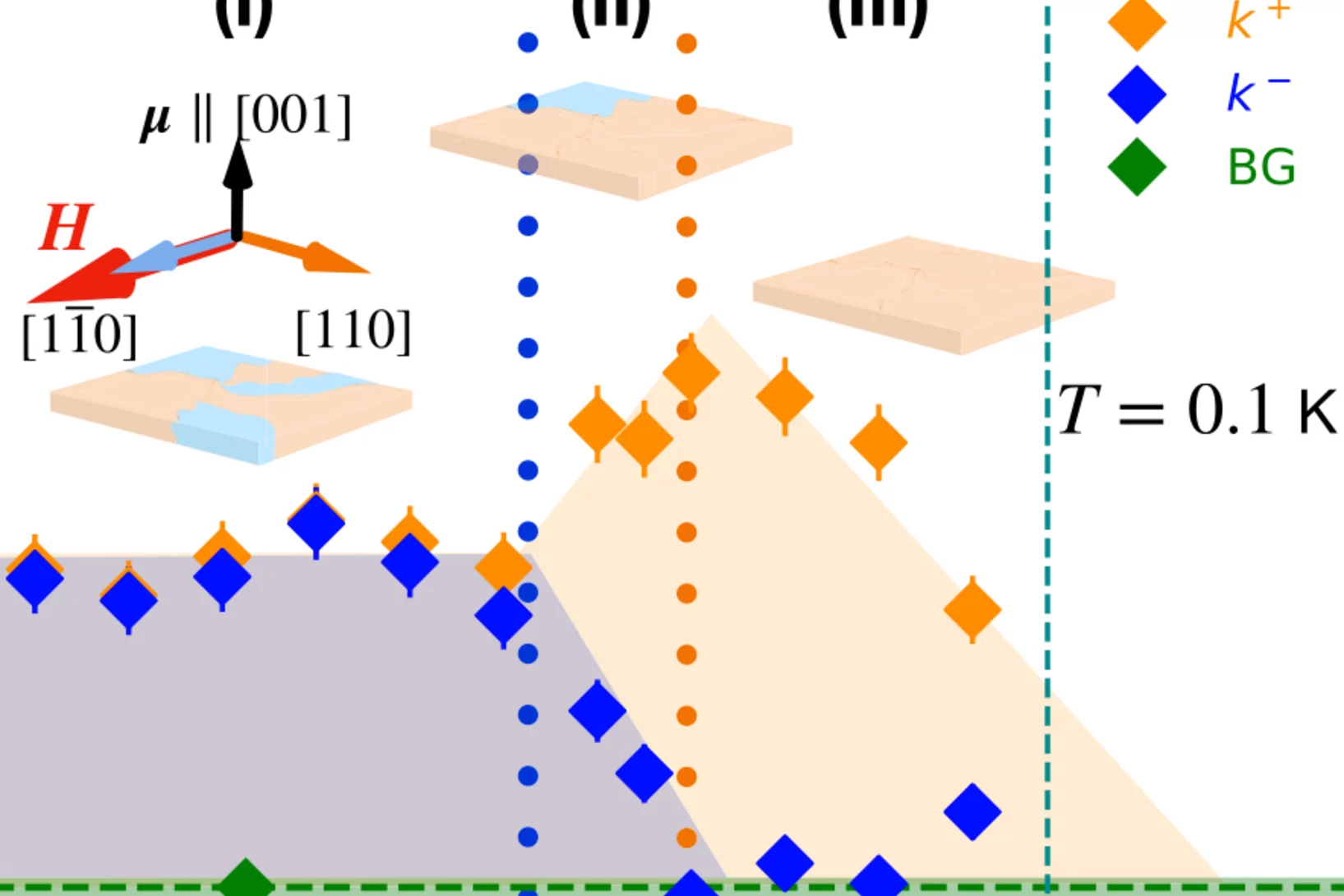
Spin-orbit control of antiferromagnetic domains without a Zeeman coupling
Encoding information in antiferromagnetic (AFM) domains is a promising solution for the ever growing demand in magnetic storage capacity. The absence of a macroscopic magnetization avoids crosstalk between different domain states, enabling ultrahigh density spintronics while being detrimental to the domain detection and manipulation. Disentangling these merits and disadvantages seemed so far unattainable. We report evidence ...
Fun Facts about Crystal Growth
The video is from the Visitor Centre psi forum of the Paul Scherrer Institute, where a cartoon avatar of Ekatarina Pomjakushina, group leader of the Solid State Chemistry group, explains about her research to science enthusiasts.
Contact
Solid State Chem. Group
Laboratory for Multiscale materials eXperiments
PSI
CH-5232 Villigen PSI
Switzerland
Head of Group
Dr. Ekaterina Pomjakushina
+41 56 310 32 07
ekaterina.pomjakushina@psi.ch
Homepage CNM
Research with Neutrons and Muons NUM Division at PSI
Open Positions
Job Opportunities at Research Division NUM.PSI Scientific Reports
Archive 2006-2012. The Scientific Reports – containing accounts of research topics from all the different areas – provide an impression of the variety of subjects researched at PSI.