Show filters
Driving forces of mineral recrystallization in aqueous solutions derived from...
Curti et al., 2026
Recrystallization in aqueous solutions is a ubiquitous process susceptible to control the entrapment and release of toxic contaminants in the subsurface. However, unraveling the underlying mechanisms and driving forces has proven to be elusive, as recrystallization frequently follows different kinetic pathways even for the same mineral, depending on its initial state and pre-treatment. To obtain a better insight, a large body of experimental data from isotope tracer experiments carried out....
Swelling of Na-montmorillonite in the presence....
Owusu et al., 2026
Various dissolved gases, such as CO, H, and CH, may be present in the near-field geological repository due to metal corrosion or the degradation of organic waste. However, the influence of dissolved gases on the swelling behavior of bentonites, commonly used as backfill material, is still poorly understood. In this study, classical molecular dynamics simulations are conducted to....
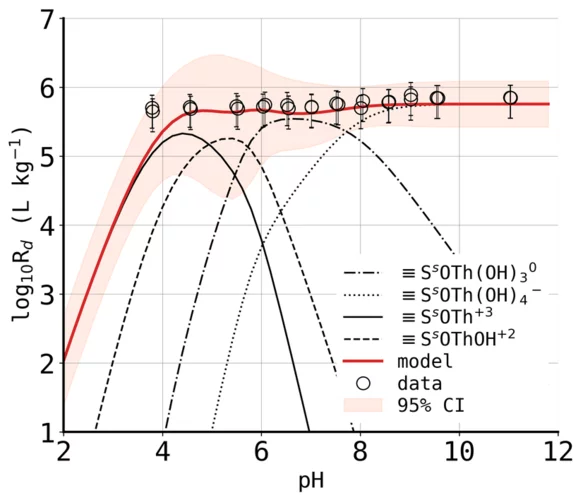
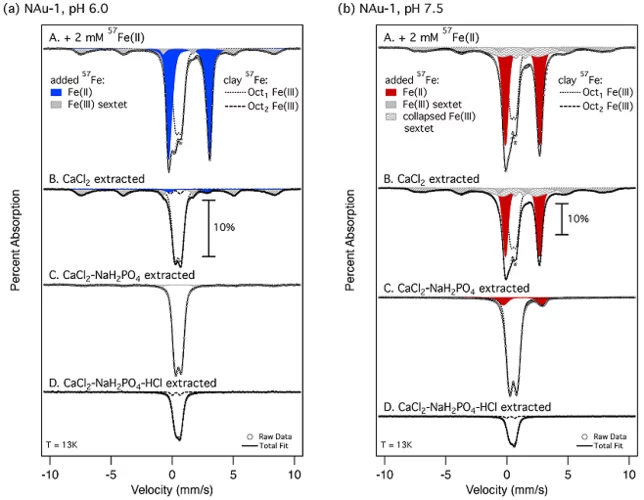
Examining the pH dependence of Fe behavior in.....
Ban et al., 2026
Hydrotalcite-group layered double hydroxide (LDH) phases are important in many technical and geological contexts, and in applications ranging from environmental processes to catalysts to cements. This study systematically investigates the roles of Fe in LDH structures across varying....
Hydrotalcite-pyroaurite solid solution in cement system...
Wang et al., 2025
Hydrotalcite-pyroaurite solid solutions, which are common minerals both in nature and in modern cementitious materials, hold significant potential for waste immobilization and cement properties yet remain insufficiently studied. In this work, we first synthesized a series of hydrotalcite...
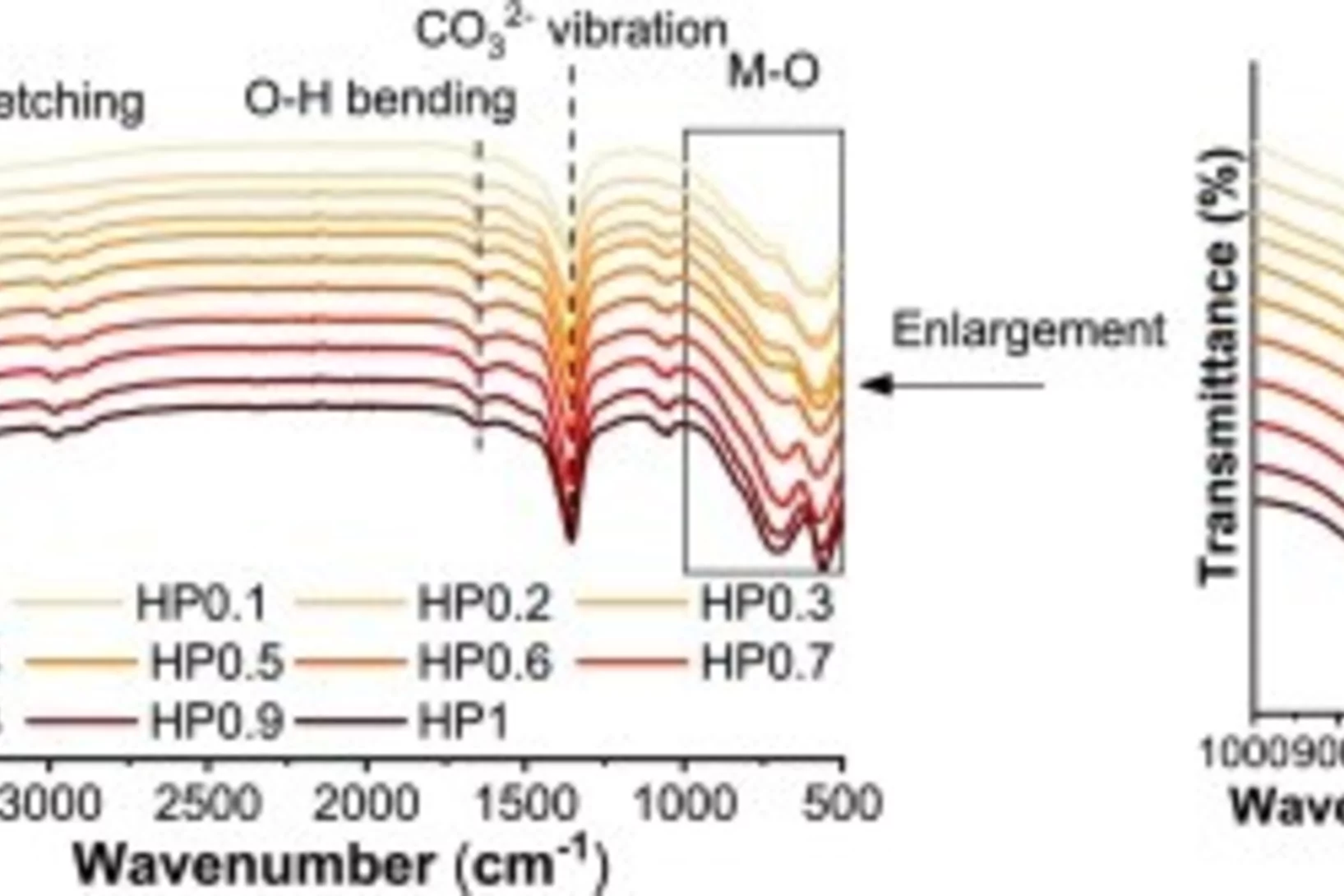
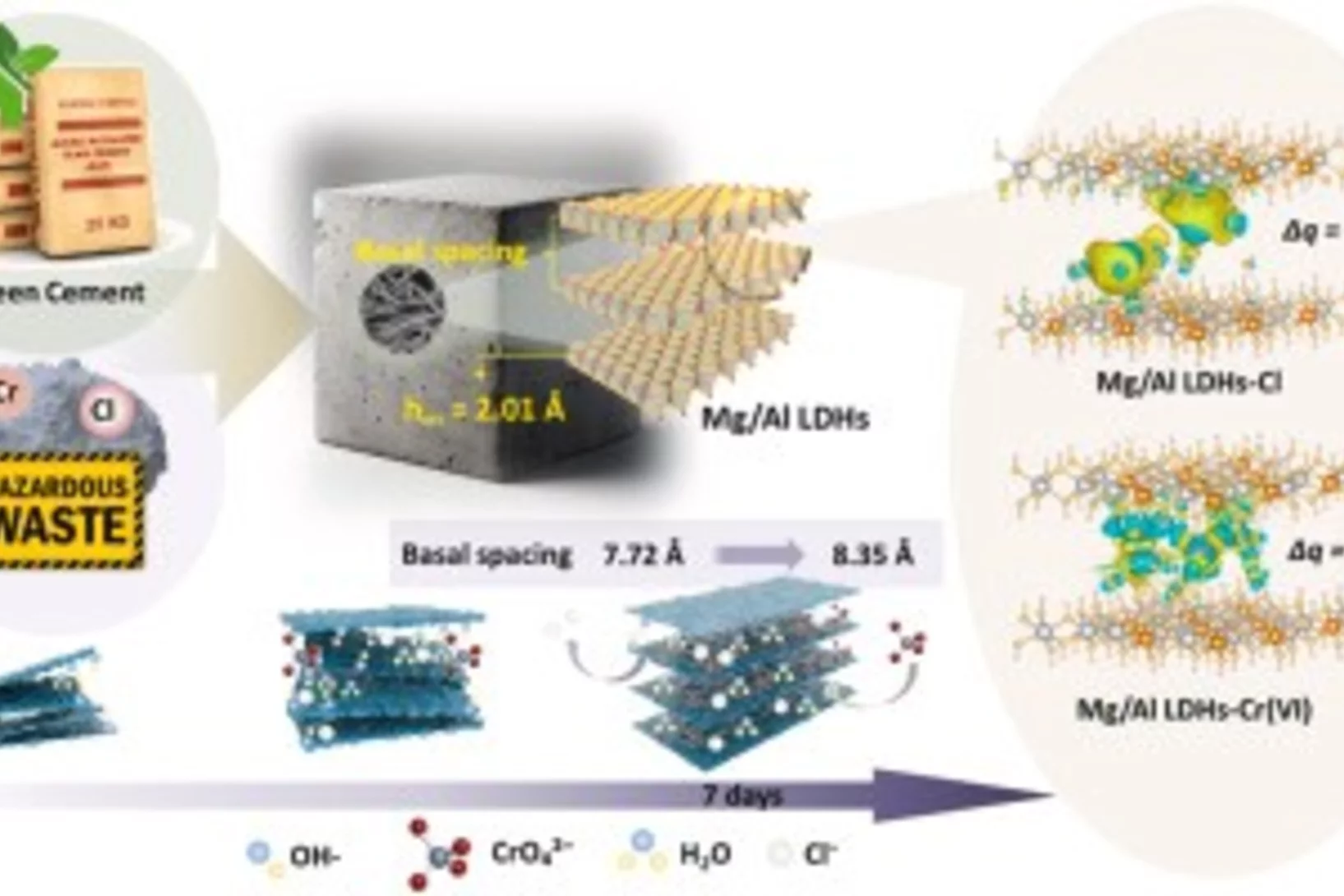
Reconstruction kinetics and structural evolutions of chromate and...
Zhang et al., 2025
Understanding the early-stage reconstruction of Mg/Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) is critical for enhancing anion immobilization in low-carbon cementitious systems. Here, we combined in-situ and ex-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analyses to reveal the time-dependent and reversible layered structure transformation of Mg/Al-LDH from calcined Mg/Al-LDH (CLDH) in cementitious environments enriched with...
ClaySor 2023: Implementation of the 2SPNE SC/CE sorption model and...
Marinich et al., 2025
The ClaySor 2023 model package within the GEM-Selektor software includes an updated version of the two-site protolysis non-electrostatic surface complexation and cation exchange model for illite and montmorillonite, as well as the first implementation of the generalised caesium sorption model for illite. These models have been harmonised with the most recent PSI Chemical Thermodynamic Database 2020, resulting in the updated.....
“Watching concrete set is a lot more exciting than you might think”
Grey, hard, boring – for most people, these three words adequately describe concrete as a material. John Provis has a different view. This scientist at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has devoted his research career to this ubiquitous and economically important building material. He hopes to unlock the secrets of concrete.
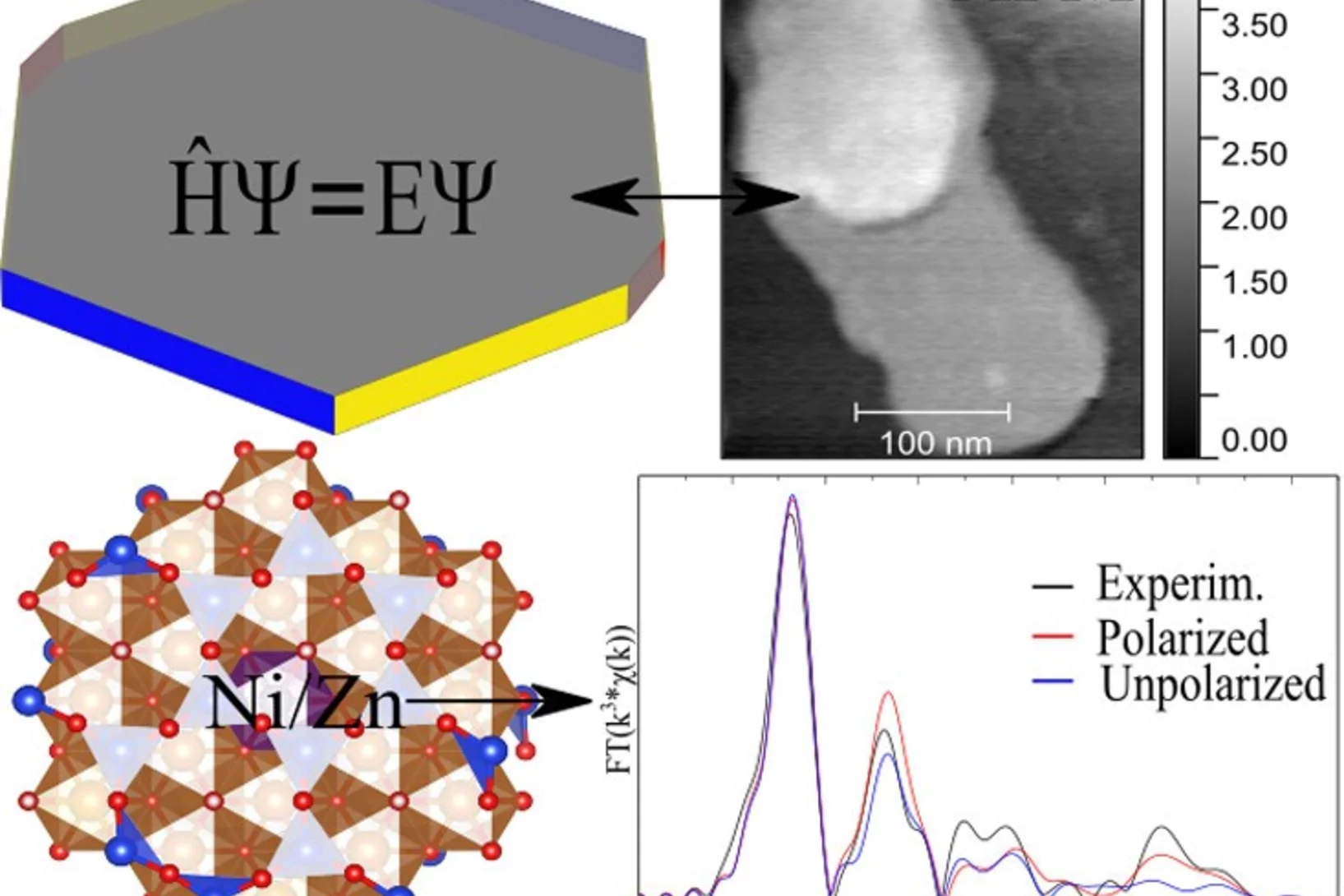
Local Crystal Structure of Ni2+ and Zn2+ Doped Saponite Determined by...
Stotskyi et al., 2025
Due to their small particle size and high surface reactivity, clay minerals control geochemical conditions in soils. Particularly important are the sorption phenomena. In this work, the structure and speciation of the most stable edge surfaces of synthetic trioctahedral smectite saponite are measured by atomic force microscopy and modeled using molecular simulations based on density functional theory...
Reduction-Driven Mobilization of Structural Fe in Clay Minerals with High Fe Content
Neumann et al., 2025
Clay minerals contain significant amounts of Fe in their alumosilicate framework, and this structural Fe can be reduced and re-oxidized, constituting a potentially renewable source of reduction equivalents in sedimentary environments. However, dissolution and/or clay mineral transformations during microbial Fe reduction contradict this concept....