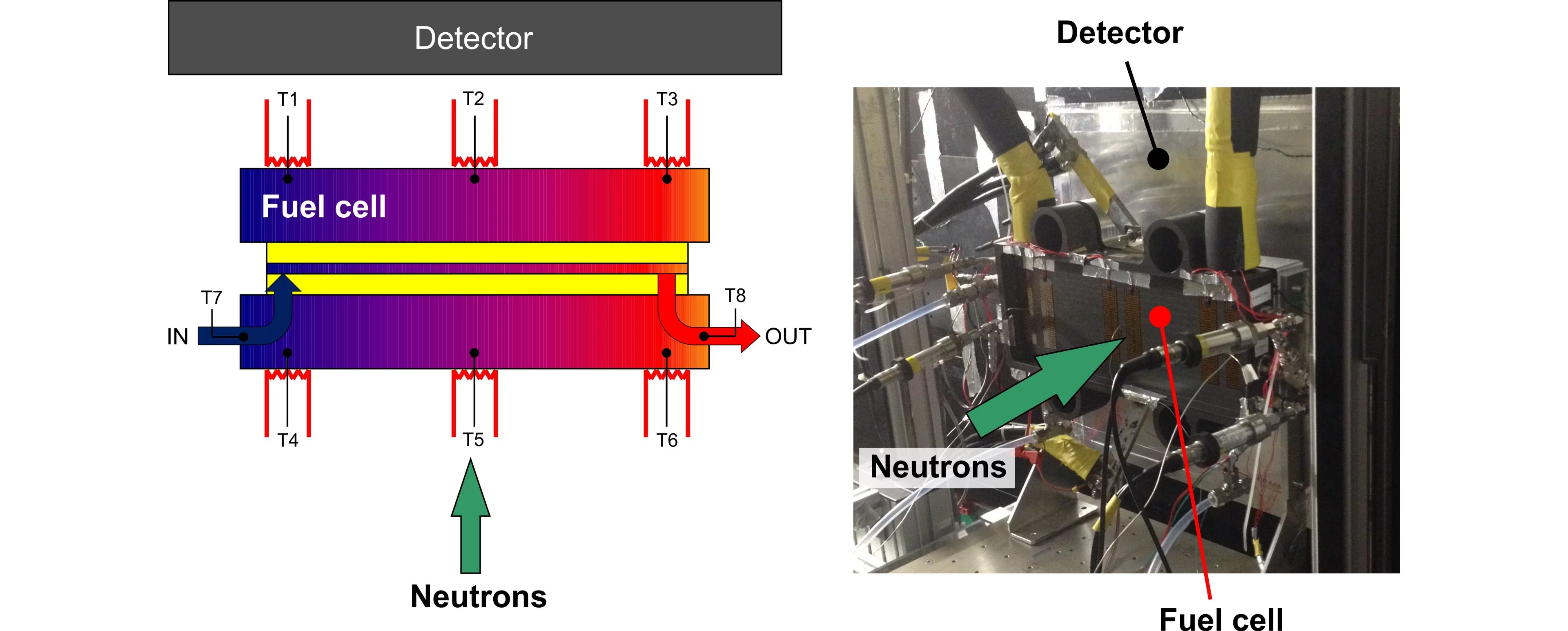
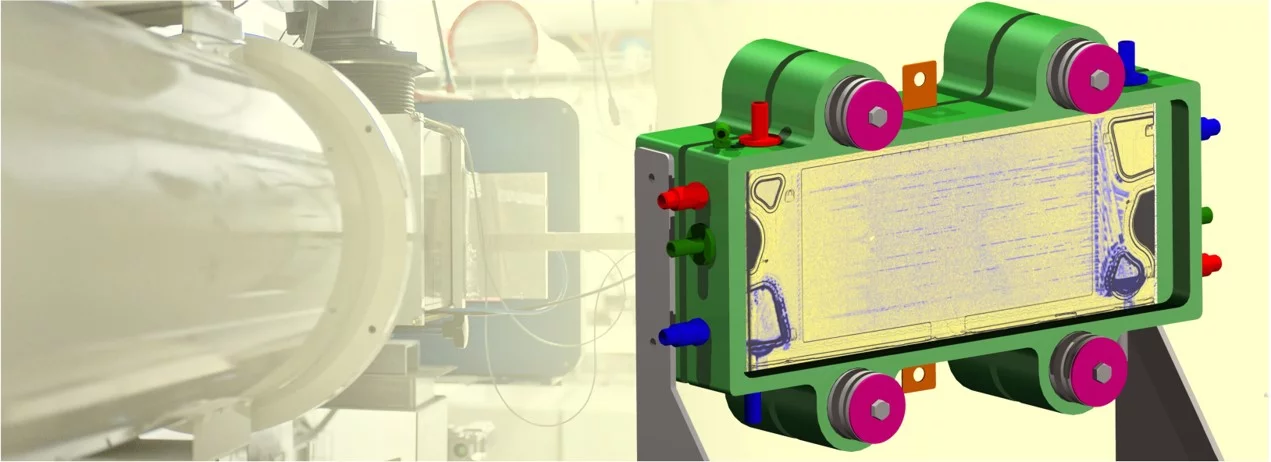
The high penetration of neutrons through large thicknesses of metals (e.g. > 10 cm of aluminum) allows imaging the water distribution in single fuel cells of full size design, even between the thick compression bodies requested to ensure enough flatness over a large area. For the single cell to have thermal boundary conditions similar to those of a cell integrated in a stack, the compression bodies are heated and a specific temperature gradient is applied to mimic the temperature gradient in the cell itself.
Typical setup for neutron imaging of full size cells
- The beam diameter and detector size at the NEUTRA beam line of PSI allows imaging objects up to a size of 400 mm x 400 mm in a single shot.
- Typical exposure times of 5 to 10 seconds allow observing the temporal evolution of water in the flow channels.
- With accumulated exposure time of 2-3 minutes, a low noise image is obtained, which allows identifying the presence of water in the GDLs in regions free of channel water.
- The NRES group has extensive infrastructure and expertise to setup and perform operando neutron imaging experiments with full size cells.
Example: Imaging of the AutoStack-Core fuel cell (300 cm2 active area) at the NEUTRA beam line
Contact
Dr. Pierre Boillat
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC) and
Neutron Imaging and Activation Group (NIAG)
5232 Villigen PSI
Switzerland
Telephone: +41 56 310 2743
Fax +41 56 310 4415
Email: pierre.boillat@psi.ch