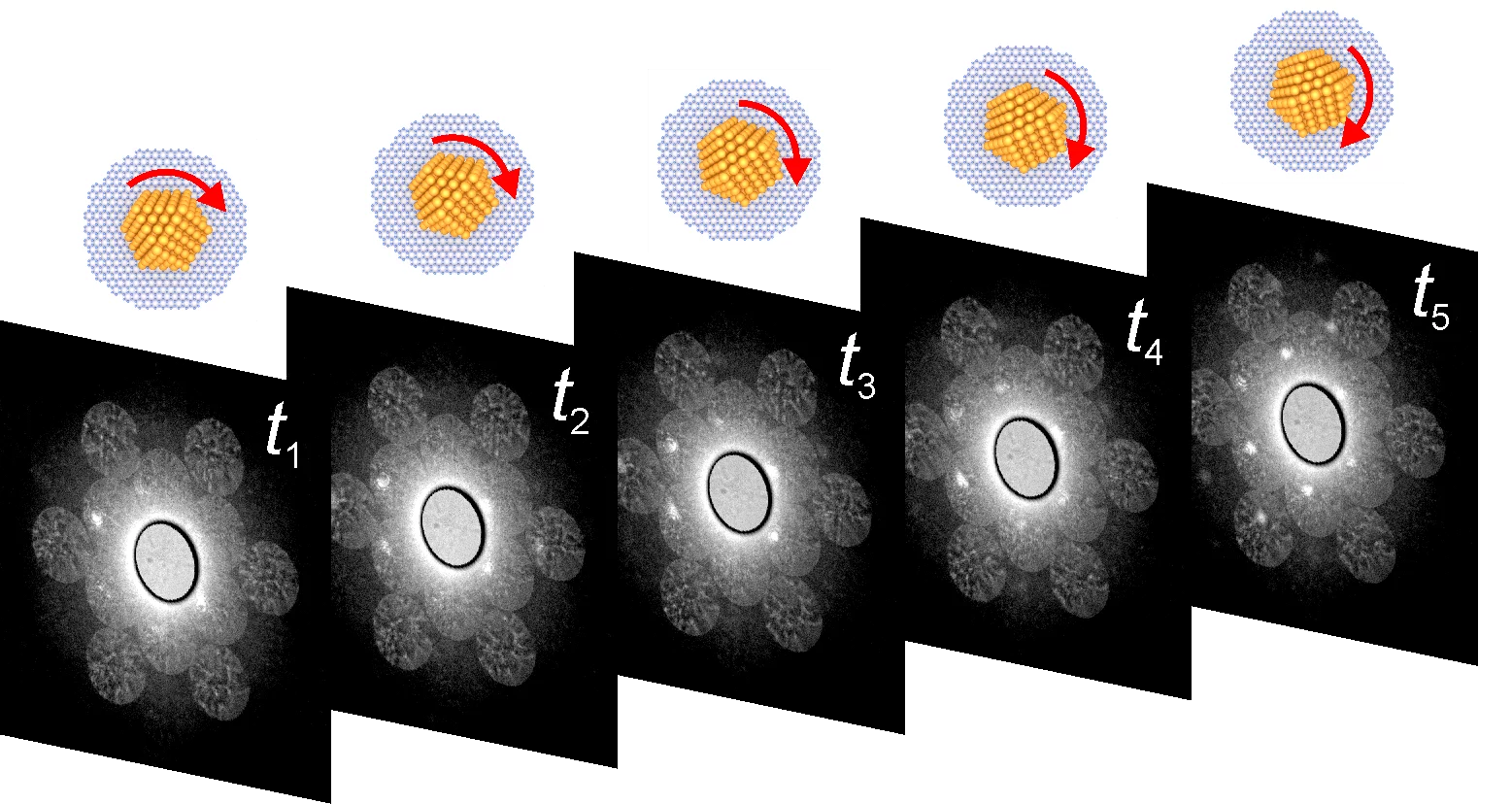
Dynamics of single Au nanoparticles on graphene were probed simultaneously in real- and diffraction space by time-series convergent beam electron diffraction.
Convergent beam electron diffraction (CBED) on two-dimensional materials allows simultaneous recording of the real-space image (tens of nanometers in size) and diffraction pattern of the same sample in one single-shot intensity measurement. In this study, we employ time-series CBED to visualize single Au nanoparticles deposited on graphene. The real-space image of the probed region, with the amount, size, and positions of single Au nanoparticles, is directly observed in the zero-order CBED disk, while the atomic arrangement of the Au nanoparticles is available from the intensity distributions in the higher-order CBED disks. From the time-series CBED patterns, the movement of a single Au nanoparticle with rotation up to 4° was recorded. We also observed facet diffraction lines ̶ intense bright lines formed between the CBED disks of the Au nanoparticle, which we explain by diffraction at the Au nanoparticle's facets. This work showcases CBED as a useful technique for studying adsorbates on graphene using Au nanoparticles as a model platform, and paves the way for future studies of different objects and biological macromolecules, deposited on graphene.
Contact
Original Publication
-
Mustafi S, Cai R, Sullivan-Allsop S, Smith M, Clark NJ, Lindley M, et al.
Dynamics of single Au nanoparticles on graphene simultaneously in real- and diffraction space by time-series convergent beam electron diffraction
Micron. 2025; 194: 103814 (12 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2025.103814
DORA PSI