Show filters
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
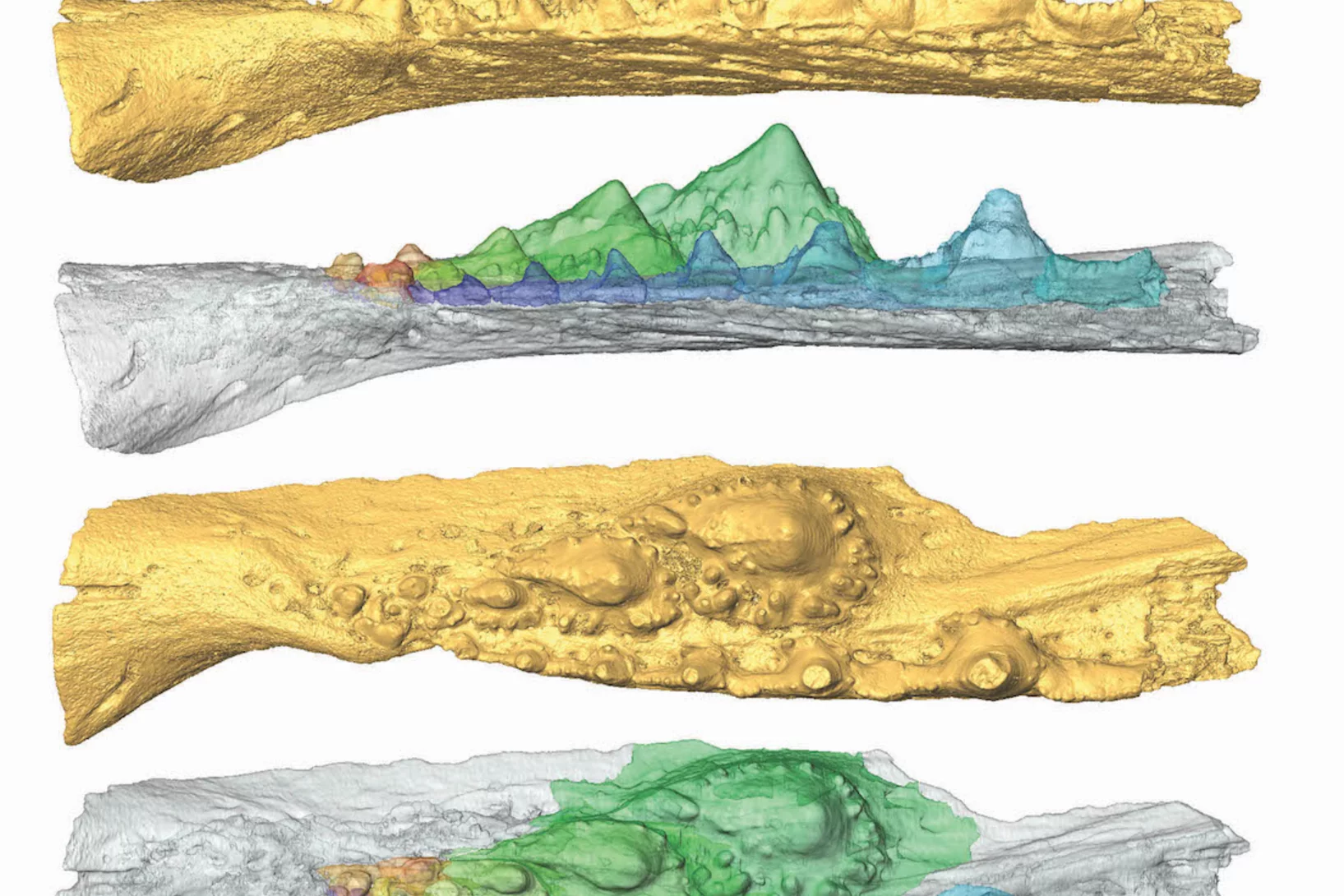
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
Women in Engineering Materials highlights Dr. Lucia Romano's work
The paper "High aspect ratio grating microfabrication by Pt assisted chemical etching and Au electroplating” by Dr. Lucia Romano & coauthors has been highlighted in the "Women in Engineering Materials" Virtual Issue published on Advanced Engineering Materials. This Virtual Issue draws attention to outstanding works within Materials Science created under the lead of women as principal investigators.
Congratulations to Lucia and the x-ray optics design and fabrication team!
SLS 2.0 approved - TOMCAT 2.0 cleared for takeoff!
In December 2020 the Swiss parliament approved the Swiss Dispatch on Promotion of Education, Research and Innovation (ERI) for 2021 to 2024 which includes funding for the planned SLS 2.0 upgrade. The new machine will lead to significantly increased brightness, thus providing a firm basis for keeping the SLS and its beamlines state-of-the-art for the decades to come. The TOMCAT crew is very excited that the TOMCAT 2.0 plans (deployment of the S- and I-TOMCAT branches, see SLS 2.0 CDR, p. 353ff) have been included in the Phase-I beamline upgrade portfolio. These beamlines will receive first light right after the commissioning of the SLS 2.0 machine around mid 2025. A first milestone towards this goal has just been achieved, with the successful installation of the S-TOMCAT optics hutch during W1 of 2021. The TOMCAT scientific and technical staff would like to thank Mr. Nolte and his Innospec crew for delivering perfectly on schedule.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
3 Post Docs and 1 PhD student join TOMCAT
The X-ray Tomography group welcomes Stefan Gstöhl (Post-Doc), Maxim Polikarpov (Post-Doc), Margaux Schmeltz (Post-Doc) and Aleksandra Ivanovic (PhD Student) as new members. The group also thank everybody who helped making it possible for our Post-Docs and PhD student to join PSI amidst the challenges brought by the COVID-19 pandemic.
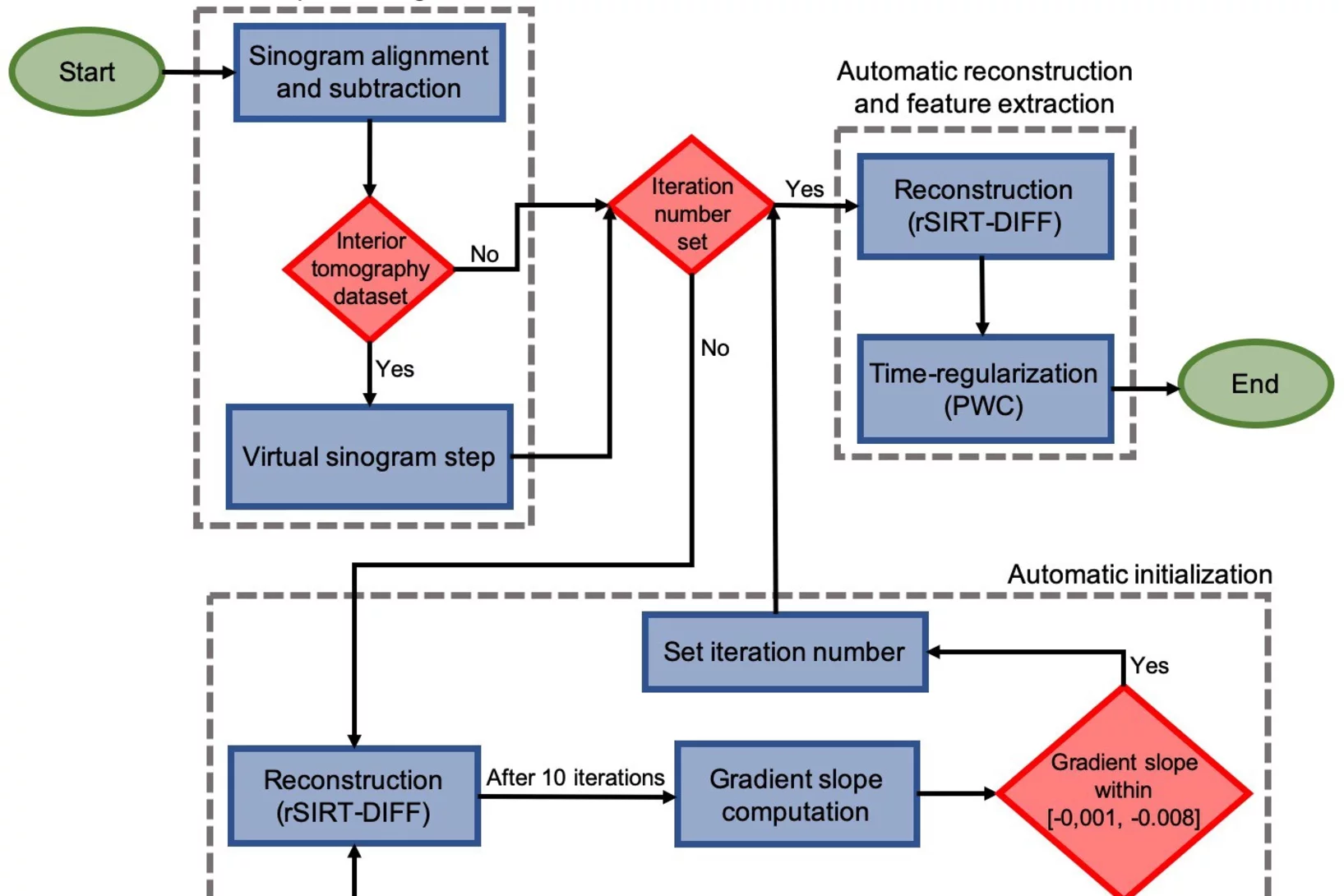
Automatic extraction of dynamic features from sub-second tomographic microscopy data
A fully automatized iterative reconstruction pipeline designed to reconstruct and segment dynamic processes within a static matrix has been developed at TOMCAT. The algorithm performance is demonstrated on dynamic fuel cell data where it enabled automatic extraction of liquid water dynamics from sub-second tomographic microscopy data. The work is published in Scientific Reports on 2 October 2020.
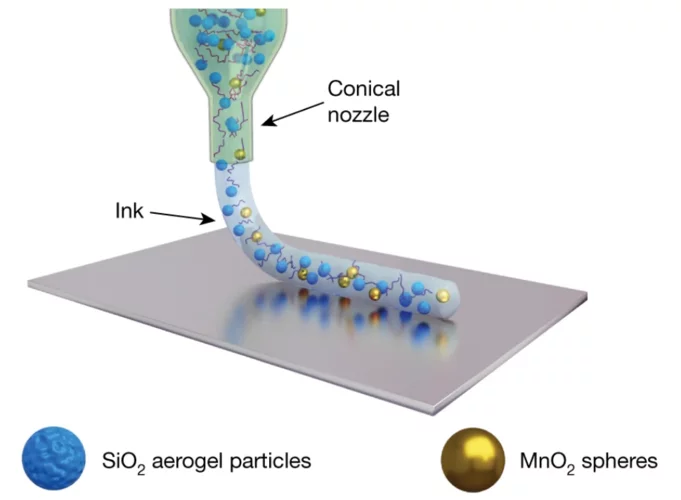
3D printing silica aerogels at the micrometer scale
A group of EMPA and ETH Zürich researchers have developed a new method to directly write ink made of silica aerogels in 3D. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline they characterized the resulting printed material with different compositions. Their results were published in Nature on August 18, 2020.
Phase contrast microtomography reveals nanoparticle accumulation in zebrafish
Metal-based nanoparticles are a promising tool in medicine – as a contrast agent, transporter of active substances, or to thermally kill tumor cells. Up to now, it has been hardly possible to study their distribution inside an organism. Researchers at the University of Basel in collaboration with the TOMCAT team have used phase contrast X-ray tomographic microscopy to take high-resolution captures of the nanoparticle aggregation inside zebrafish embryos.
The study was published in the journal Small and featured on the cover of its current issue.
4 times compression factor for tomographic data feasible
In a recent study, TOMCAT has shown that lossy compression by a factor of at least 3 to 4 of raw acquisitions generally does not affect the reconstruction quality and that higher factors (six to eight times) can be achieved for tomographic volumes with a high signal-to-noise ratio as it is the case for phase-retrieved datasets. This finding is relevant to current challenges on large tomography data management and storage especially at synchrotron facilities. The results of this study was published in Journal of Synchrotron Radiation.
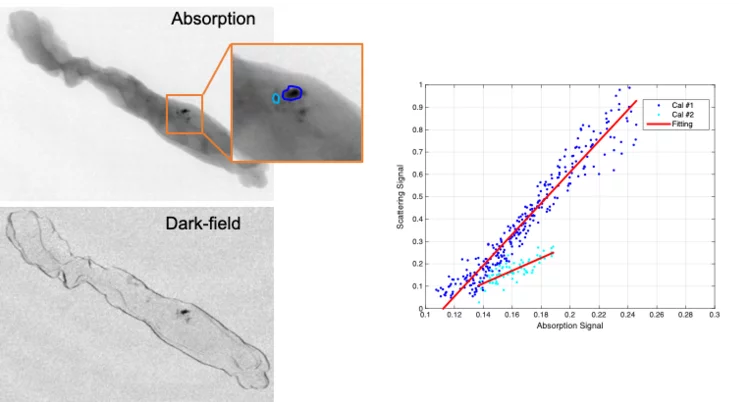
Looking into the hints of early breast cancer detection
Microcalcifications are the most important indicator in the diagnosis of early breast cancer. The team of X-ray tomography group, in collaboration with Kantonsspital Baden, has carried out a reader study to characterize microcalcifications non-invasively using grating interferometry. This study reveals a potential way to discriminate benign and malignant lesions at early stage.
A new etcher is just unpacked!
TOMCAT has a new etcher tool for the fabrication of very high aspect ratio gratings in silicon. The new SPTS Rapier system for silicon deep reactive ion etching just arrived and unpacked from the crate in front of the Laboratory of Micro and Nanotechnology at PSI! We thank the LMN technical staff for the support and the great job of moving in!
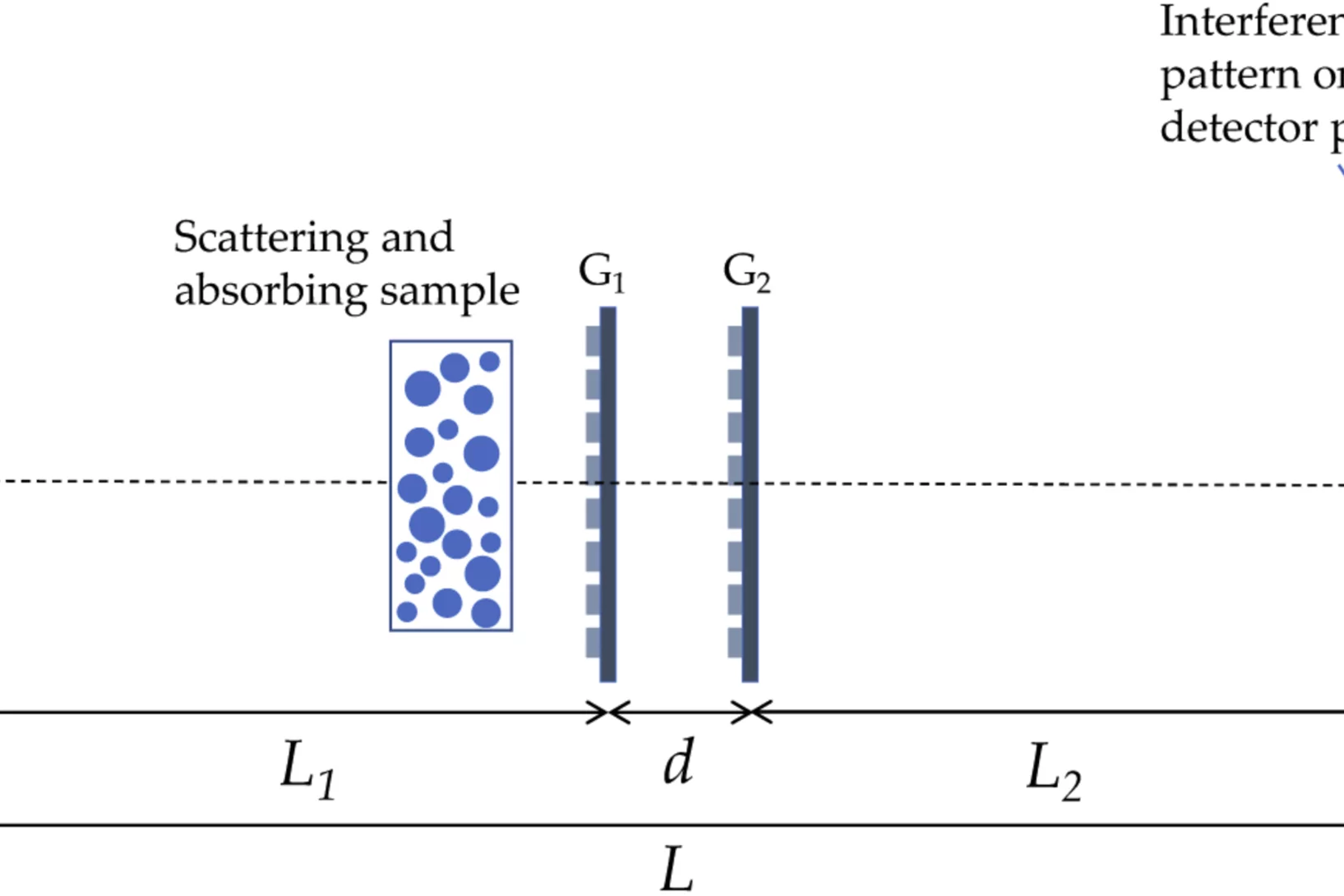
How to correct beam hardening effects in dual phase grating interferometry?
Researchers at the X-ray tomography group have expanded the theoretical understanding of dual phase grating interferometry with polychromatic sources. As a result, beam hardening effects can be corrected and a real space correlation function of a sample can be retrieved in dark-field imaging. These are significant steps towards application of the method for the quantitative investigation of microstructures of materials and devices using dual phase grating interferometry. The results of the work were published in Optics Express on June 12, 2020.
Miniaturized fluidic circuitry observed in 3D
The team of Prof. Thomas Hermans at the University of Strasbourg in France managed to create wall-less aqueous liquid channels called anti-tubes. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline those anti-tubes could be observed in 3D. The exciting results were published in Nature on May 6, 2020.
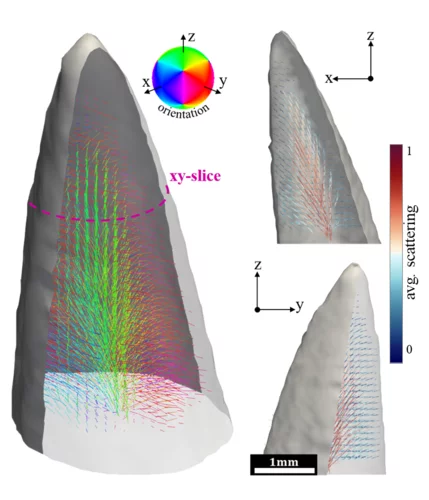
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
SNF funds dynamic X-ray imaging of the human auditory system in motion
In collaboration with clinicians from the Inselspital and engineers of the University Hospital of Bern, the X-Ray Tomography Group will be part of a new SNF project entitled “The Human Auditory System in Motion: Direct Observation of the Microfunction of Sound Transmission using Dynamic Phase-contrast X-ray Imaging”.
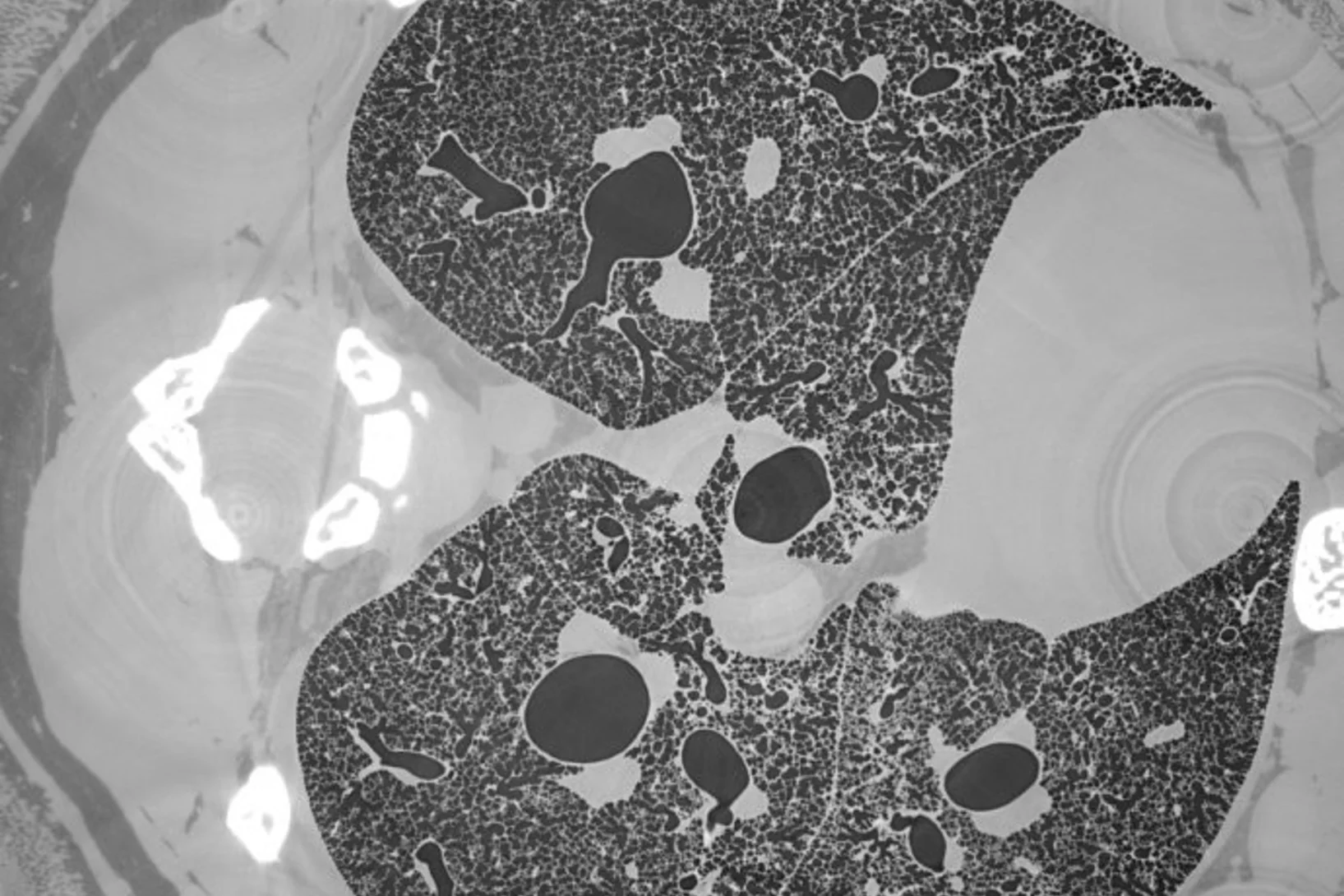
X-ray Imaging for Biomedicine: Imaging Large Volumes of Fresh Tissue at High Resolution
The TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source specializes in rapid high-resolution 3-dimensional tomographic microscopy measurements with a strong focus on biomedical imaging. The team has recently developed a technique to acquire micrometer-scale resolution datasets on the entire lung structure of a juvenile rat in its fresh natural state within the animal’s body and without the need for any fixation, staining or other alteration that would affect the observed structure (E. Borisova et al., 2020, Histochem Cell Biol).
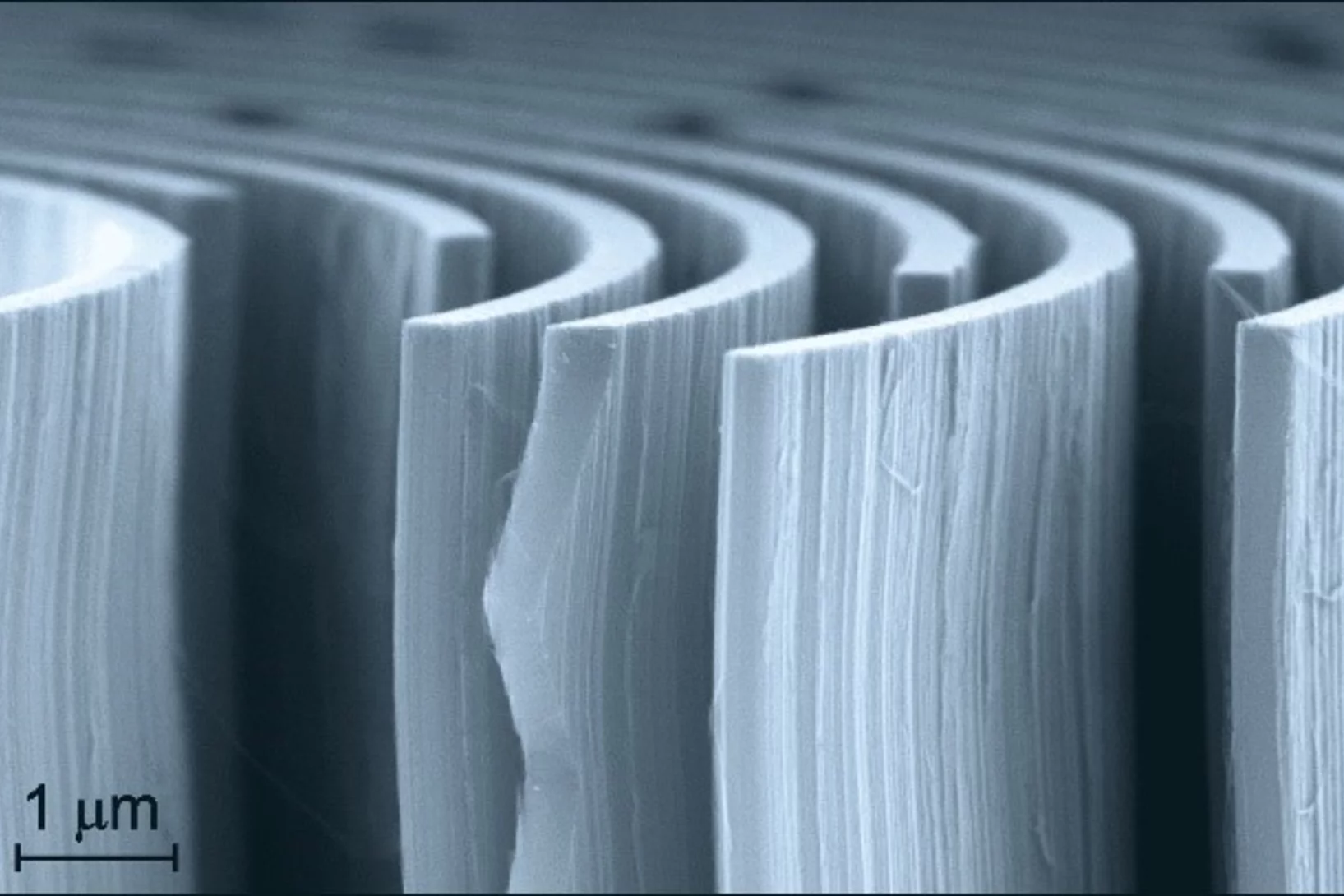
MacEtch in gas phase: a new nanofabrication technology at PSI
The grating fabrication team of the X-ray tomography group has scored another record in etching technology of silicon by realizing a MacEtch process in gas phase. Ultra-high aspect ratios (up to 10 000 : 1) in the nanoscale regime (down to 10 nm) were achieved by platinum assisted chemical etching of silicon in the gas phase. The results were published in Nanoscale Horizons on February 17, 2020.
Towards dynamic feedback control during time-resolved CT at TOMCAT
Researchers from the CWI in Amsterdam and the TOMCAT beamline have developed and implemented a real-time CT reconstruction, visualisation, and on-the-fly analysis approach to monitor dynamic processes as they occur. With the processing of multiple sets of CT slices per second, this represents the next crucial step towards adaptive feedback control of time-resolved in situ tomographic experiments. The results of this study were published in Scientific Reports on December 5, 2019.
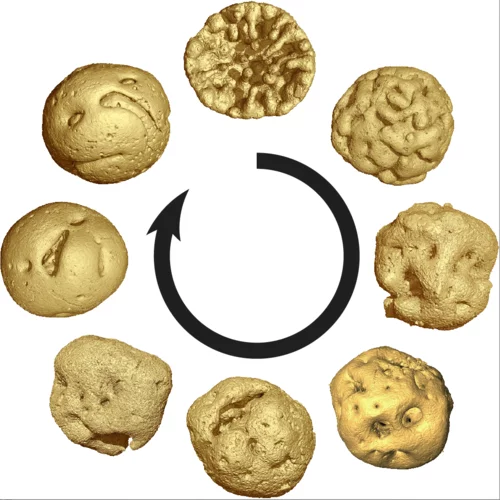
Animal embryos evolved before animals
Detailed characterization of cellular structure and development of exceptionally preserved ancient tiny fossils from South China by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the University of Bristol and Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology to the discovery that animal-like embryos evolved long before the first animals appear in the fossil record.
The X-ray Tomography Group welcomes Dr. Nazanin Samadi as Post Doc
Dr. Nazanin Samadi will help develop tools for comprehensive simulation of tomography beamline design and will contribute in the technical design report of the future TOMCAT 2.0 beamline upgrade. Before joining the group, she was a PhD student at the University of Saskatchewan in Canada.
Faserverstärkte Verbundstoffe schnell und präzise durchleuchten
Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI haben eine neues Verfahren entwickelt, mit dem sich faserverstärkte Verbundwerkstoffe präzise durchleuchten lassen. Das könnte helfen, bessere Materialien mit neuartigen Eigenschaften zu entwickeln.
Dr. Anne Bonnin got tenured
Congratulations to Dr. Anne Bonnin for having been tenured. Anne spent 2 years of post-doc and 4 years as beamline scientist at TOMCAT.
Dr. Jinqiu Xu joins the X-ray Tomography Group as Post Doc
Dr. Jinqiu Xu will work with the team developing X-ray phase contrast CT for breast cancer diagnosis. Before coming to PSI, she worked on CT reconstruction from incomplete data at Capital Normal University (Beijing, China).
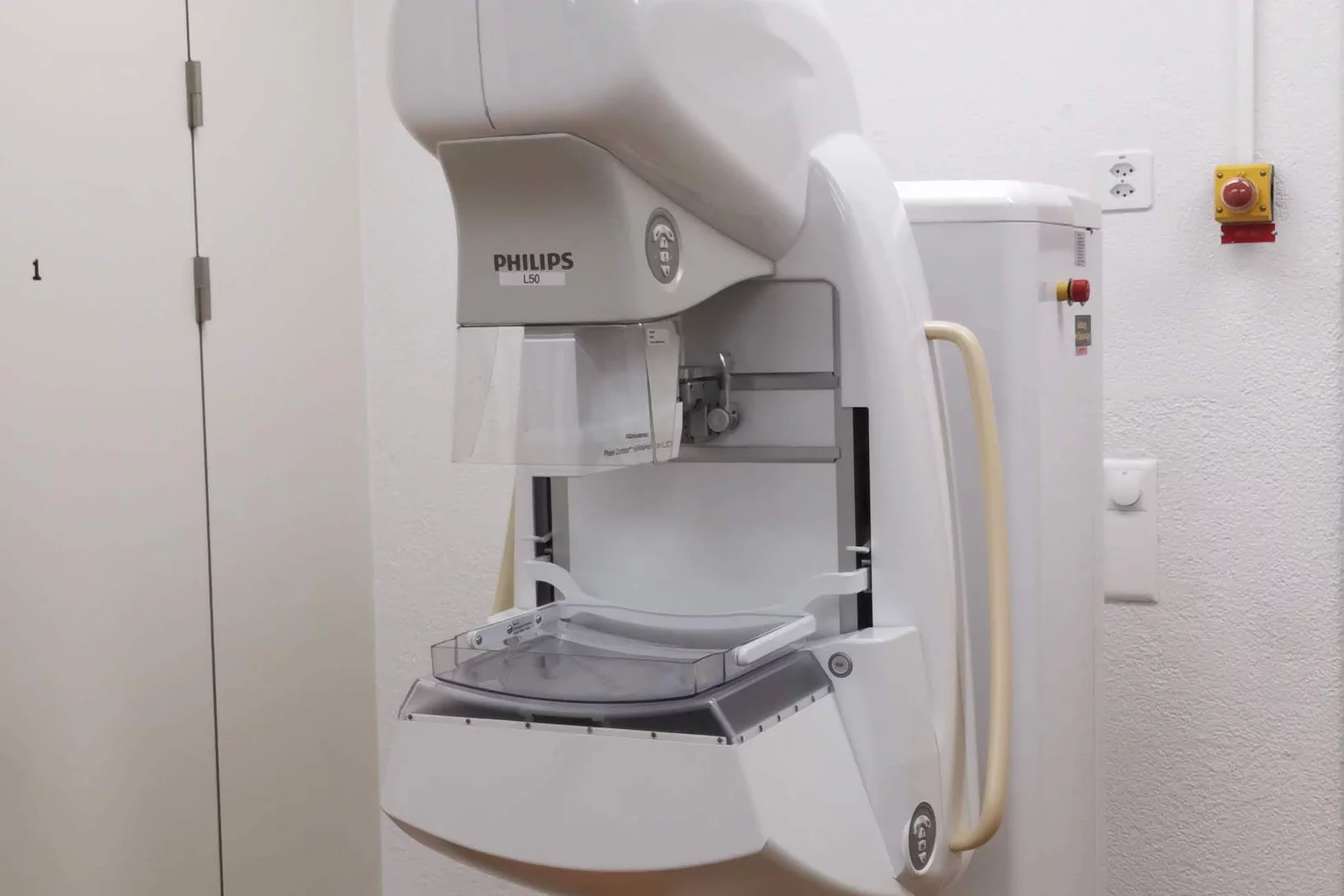
Towards clinical grating-interferometry mammography
The team of X-ray tomography group has developed the word-first clinical grating-interferometry mammography system in collaboration with Philips Research Hamburg, Kantonsspital Baden and Universitätspital Zurich. The novel imaging method shines a light on more accurate breast cancer detection. The prototype is installed at Universitätspital Zurich for clinical trial.
World record in time-resolved tomography
Researchers from the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the TOMCAT beamline have achieved a new world record in time-resolved tomography by measuring over 200 tomographies per second during heating of an evolving aluminium metal foam.
TOMCAT team hikes the UNESCO World Heritage Site Tectonic Arena Sardona
As summer tradition TOMCAT hikes in the Alps to enjoy fresh mountain air and have fun in each other's company. This year the TOMCAT team hikes in the UNESCO World Heritage Site Tectonic Arena Sardona.
High-numerical-aperture optics is key to ultra-fast tomographic microscopy
A novel high-numerical-aperture macroscope optics dedicated to high-temporal and high-spatial resolution X-ray tomographic microscopy is available at TOMCAT. Coupled with the in-house developed GigaFRoST camera, this highly efficient imaging setup enables tomographic microscopy studies at 20 Hz and beyond, opening up new possibilities in tomographic investigations of dynamic processes. A detailed characterization of the macroscope performance was published in Journal of Synchrotron Radiation on May 21, 2019.
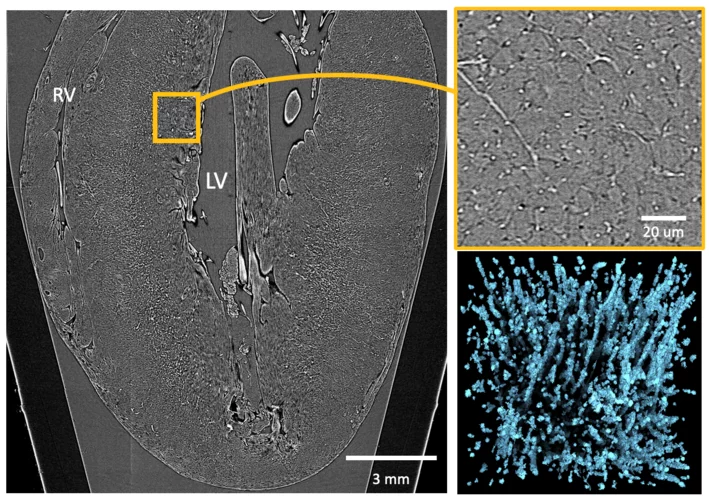
From whole organ imaging down to single cell analysis
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline, University College London (UCL), IDIBAPS and Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) have developed a methodology that allows the multiscale analysis of the structural changes resulting from remodelling cardiovascular diseases, from whole organ down to single-cell level. This methodology has been published as an article in the journal Scientific Reports on May 6th 2019.
Dr. Margie Olbinado joins as Industrial Liaison Scientist
Dr. Margie Olbinado joins the X-ray Tomography group as scientist to take care of industrial tomographic imaging and business strategies for the growing TOMCAT industrial portfolio. Before joining PSI, Margie was a scientist at The European Synchrotron - ESRF in France. As industrial liaison, she will work in collaboration with the PSI Technology Transfer, ANAXAM and SLS TT AG.
PSI Thesis Medal goes to Dr. Matias Kagias
The PSI Thesis Medal is awarded every second year to the best PhD thesis performed at the Paul Scherrer Institut. Matias received the prize for his excellent thesis entitled "Direct Self-Imaging Methods for X-ray Differential Phase and Scattering Imaging". Congratulations!