Show filters
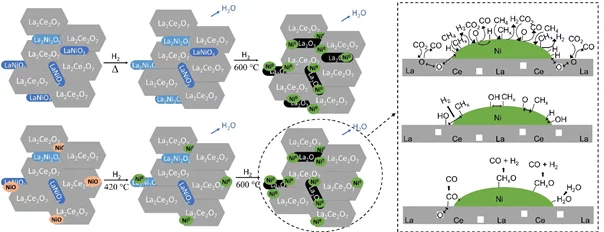
In situ Study of Low-temperature Dry Reforming of Methane Over La2Ce2O7 and LaNiO3 Mixed Oxides
The combination of in situ spectroscopy methods allowed to detect the evolution of a catalyst precursor to the catalytic material, and investigate a relevant reaction. The reduction of a mixture of perovskite, pyrochlore and nickel leads to the formation of active and selective catalytst, converting carbon dioxide and methane to syngas.
PUBLISHED IN SCIENCE: A surface-promoted redox reaction occurs spontaneously on solvating inorganic aerosol surfaces
Ammonium sulfate has been used as a probe for aerosol particles and investigated in situ by means of ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Unexpectedly, when the particles start to absorb water, a spontaneous redox reaction leading to nitrogen and elemental sulfur takes place.
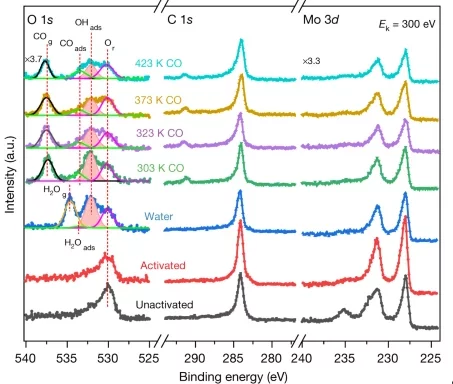
Direct evidence of cobalt oxyhydroxide formation on a LSCO perovskite water splitting catalyst
In situ and ex situ ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy have been used to investigate the solid-liquid interface of a LSCO water splitting catalyst. Experimental results, supported by theoretical simulations of the core-electron binding energy, detect the formation of cobalt oxyhydroxide under working conditions.
Temperature and Reaction Environment Influence the Nature of Platinum Species Supported on Ceria
The evolution of atomically dispersed platinum species on ceria has been investigated by means of ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy. Experimental results, supported by the theoretical simulation of the phase diagram, show that atomically dispersed species evolve towards nanoparticles during the activation of the catalysts. Such an evolution is influenced by the temperature and the reaction environment.
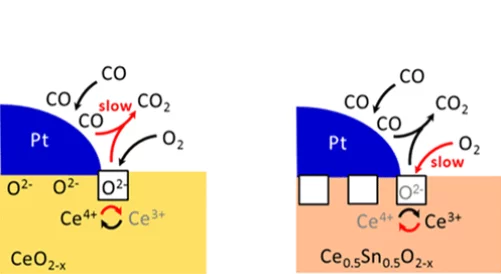
Enhanced Reducibility of the Ceria-Tin Oxide Solid Solution Modifies the CO Oxidation Mechanism at the Platinum-Oxide Interface
The introduction of tin into ceria strongly influences its reducibility. In turn, the reaction mechanism towards the oxidation of carbon monoxide changes: the oxidation rate increases, the apparent activation energy decreases and the reaction order in oxygen increases.
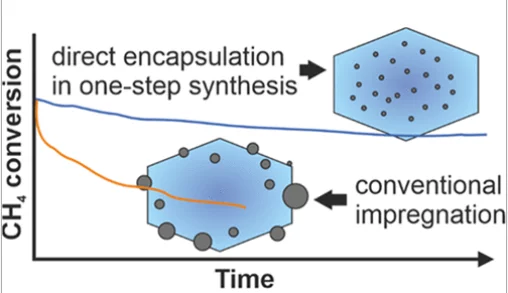
Stable Palladium Oxide Clusters Encapsulated in Silicalite-1 for Complete Methane Oxidation
Encapsulation of highly dispersed palladium oxide clusters in the microporous channels and voids of the nanosized silicalite-1 crystals has been achieved by using an amine-based ligand.
PUBLISHED IN NATURE: A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
Platinum isolated atoms and clusters supported on molybdenum carbide have been extensively characterized. The presence of both species is essential to boost the stability, so that the catalysts displays high metal-normalized turnover number of 4,300,000 moles of hydrogen per mole of platinum
The dynamics of overlayer formation on catalyst nanoparticles and strong metal-support interaction
The strong metal support interaction has been investigated in situ by means of electron microscopy, XPS and XRD, to provide a complete overview about the interplay between the metal and the support.
Surface Segregation Acts as Surface Engineering for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction on Perovskite Oxides in Alkaline Media
The temperature-dependent segregation of strontium-containing species on LSCO electrodes has been studied by means of XPS, SEM and XRD. Such surface species dissolve almost quantitatively upon immersion in water, leaving cobalt oxide, the active site of the reaction, free.
Role of water on the structure of palladium for methane complete oxidation
The mechanism of methane oxidation in the presence of water has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.
Kinetics of the Thermal Oxidation of Ir(100) Studied by APXPS
The thermal oxidation of single-crystalline Ir(100) films toward rutile IrO2(110) has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.