Two-dimensional (2D) kagome lattice metals are interesting because their corner sharing triangle structure enables a wide array of electronic and magnetic phenomena. Recently, post-growth annealing is shown to both suppress charge density wave (CDW) order and establish long-range CDW with the ability to cycle between states repeatedly in the kagome antiferromagnet FeGe.
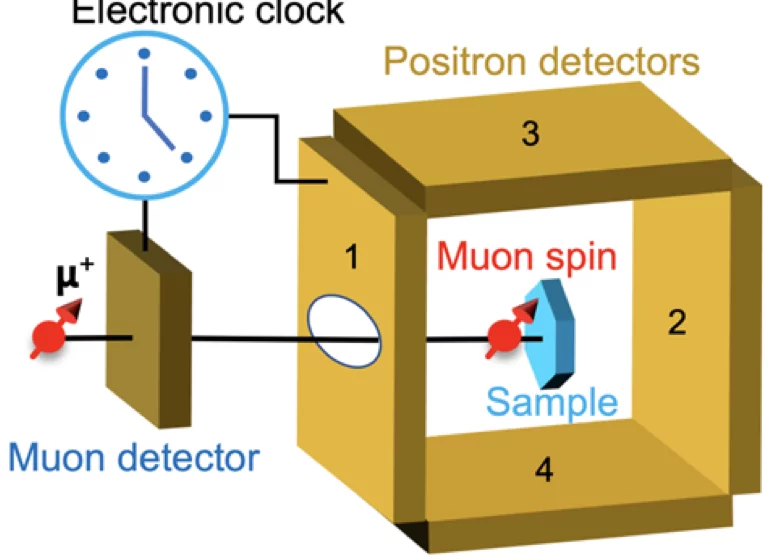
Here we perform transport, neutron scattering, scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), and muon spin rotation (μSR) experiments to unveil the microscopic mechanism of the annealing process and its impact on magneto-transport, CDW, and magnetism in FeGe. Annealing at 560 °C creates uniformly distributed Ge vacancies, preventing the formation of Ge-Ge dimers and thus CDW, while 320 °C annealing concentrates vacancies into stoichiometric FeGe regions with long-range CDW. The presence of CDW order greatly affects the anomalous Hall effect, incommensurate magnetic order, and spin-lattice coupling in FeGe, placing FeGe as the only kagome lattice material with tunable CDW and magnetic order.
Facility: SμS
Reference: M.L. Klemm et al, Nature Communications 16, 3313 (2025)
Read full article: here