Show filters
Un cœur volumineux et des sens aiguisés: les clés du foisonnement explosif des premiers poissons
La reconstruction par rayons X d’un fossile vieux de 400 millions d’années illumine un moment clé de notre passé évolutif le plus reculé.
Un fossile maître du camouflage aux rayons X
Le procédé d’imagerie du PSI aide à décoder la stratégie de chasse d’un prédateur préhistorique.
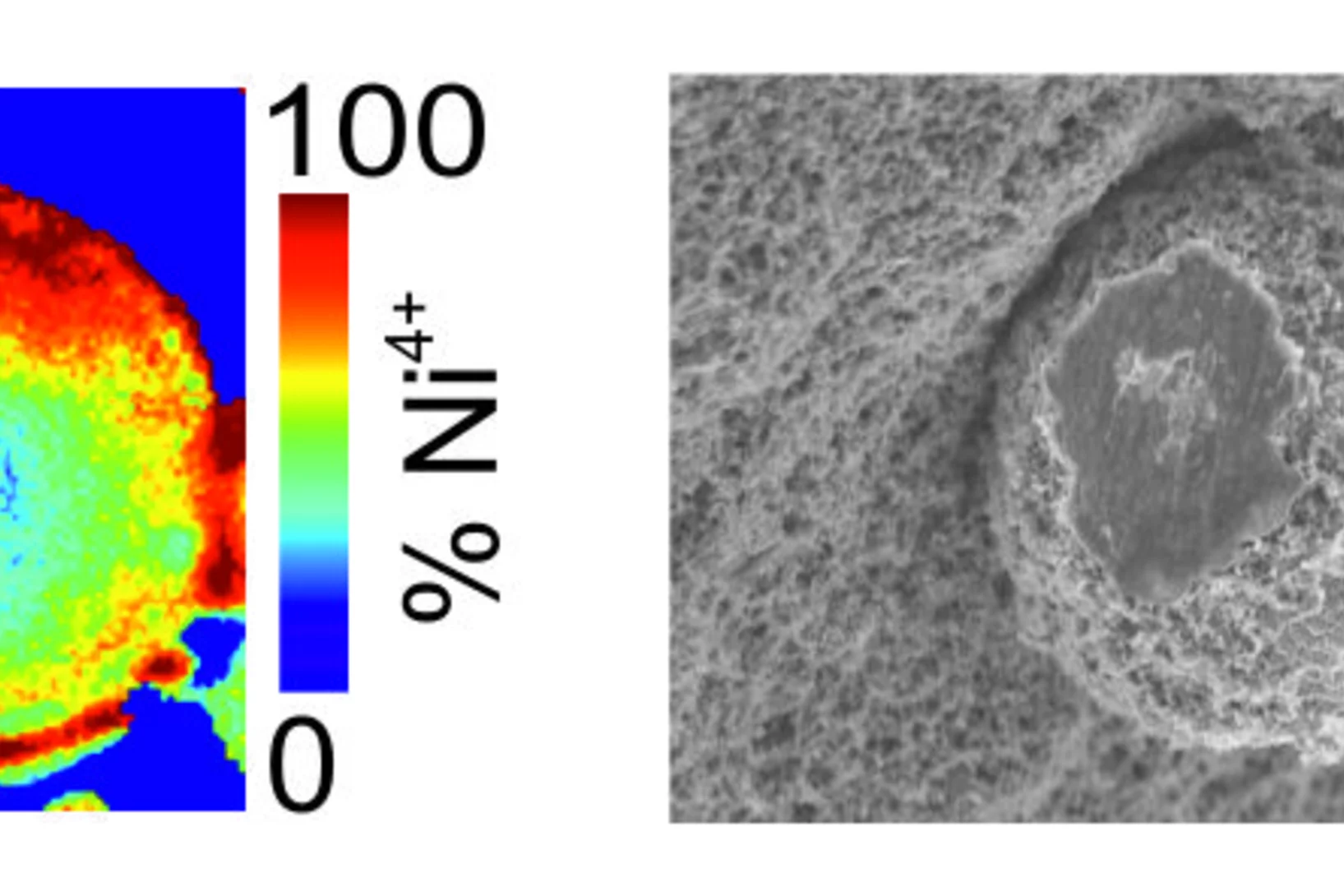
Du zinc détecté dans des seringues obstruées
Pour l'entreprise pharmaceutique MSD, ANAXAM a étudié, avec l'aide de scientifiques du PSI, si le zinc pouvait contribuer à l'obstruction des seringues préremplies.
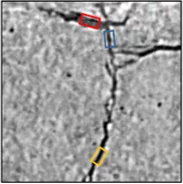
La cause du blocage des aiguilles de seringue a été identifiée
Des scientifiques du PSI et de l’entreprise de transfert de technologie ANAXAM ont découvert ce qui cause l’obstruction de seringues préremplies.
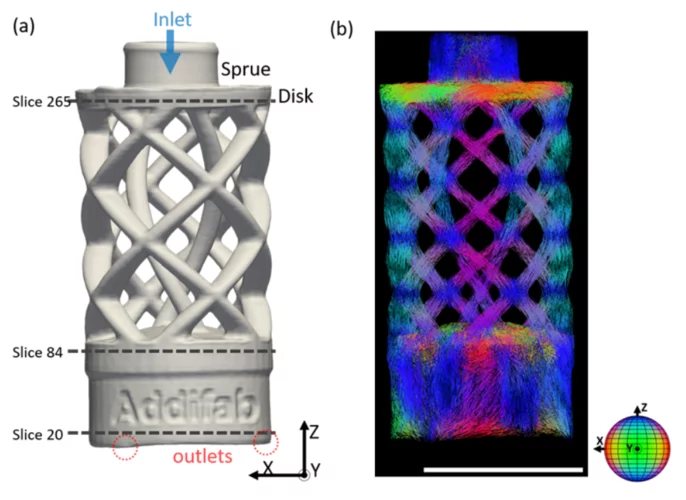
Aperçus 3D d’un procédé de fabrication novateur
Fabriquer des formes complexe avec l’impression 3D
Dépister plus précocement le cancer du sein
La radiographie en 3D précise peut améliorer le dépistage du cancer du sein.
Imagerie par rayons X après transplantations cardiaques
Après une transplantation cardiaque, la lumière synchrotron aide à évaluer si le corps rejette le nouvel organe et avec quelle sévérité.
X-ray tomography helps understand how the heart beats
Researchers at the Swiss Light Source SLS use X-ray phase contrast imaging to study a heart in action as it beats.
Un curieux fossile qui n’est pas notre ancêtre
La lumière de type rayons X résout un des mystères de l’ascendance humaine
Nominée: la radiographie précise des tissus mammaires
Traquer le cancer du sein à l’aide de rayons X à haute résolution: des chercheurs du PSI ont été nominés pour le Prix de l’inventeur européen.
Macroscopic mapping of microscale fibers in freeform injection molded fiber-reinforced composites using X-ray scattering tensor tomography
Prediction of the mechanical properties dictated by the local microfiber orientation is essential for the performance characterization of fiber-reinforced composites. Typically, tomographic imaging methods that provide fine spatial resolution are employed to investigate various materials' local micro- and nano-architecture in a non-destructive manner. However, conventional imaging techniques are limited by a substantial trade-off between the structure size of interest and the accessible field of view (FOV). Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline at Paul Scherrer Institut, Xnovo Technology ApS, and the Technical University of Denmark have demonstrated the potential of X-ray scattering tensor tomography for industrial applications by characterizing the microstructure of a centimeter-sized industrially relevant freeform injection molding fiber-reinforced composite sample. This emerging technique provides unprecedented access to microstructural information over centimeter-sized sample volumes paving the way towards its potential integration as an invaluable tool, for instance, in the fiber-reinforced-composite (FRC) industry. The obtained fiber orientation and anisotropy information over statistically relevant large volumes can be used to predict the mechanical properties of final products, optimize production parameters, and improve fiber injection molding simulation frameworks. The work is published in Composites Part B: Engineering on 15 March 2022.
Microscopie à rayons X avec 1000 images tomographiques par seconde
A la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS, des chercheurs ont établi un nouveau record dans le cadre d’une méthode d’imagerie appelée tomoscopie.
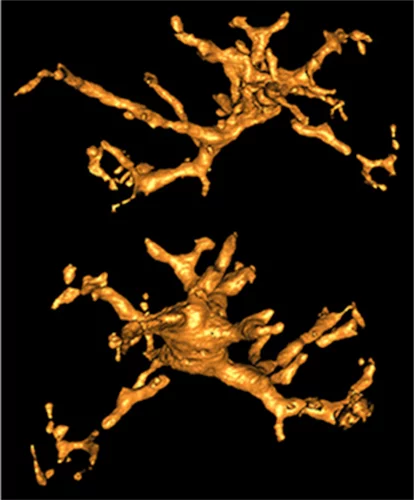
Hierarchical imaging and computational analysis of three-dimensional vascular network architecture in mouse brain
An international team involving researchers from the University and University Hospital Zürich, the Krembil Research Institute and the University and University Hospital in Toronto (Canada), the Department of Physics of Jyväskylä (Finland), the University of Leuven (Belgium), the Johannes Kepler University in Linz (Austria), the Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research in Emeryville (USA), the ETH Zürich and the Paul Scherrer Institute has developed a protocol that enables hierarchical imaging and computational analysis of vascular networks in entire postnatal- and adult mouse brains, enabling direct and quantitative comparisons of the morphological brain vascular network architecture between different postnatal and / or adult developmental stages. The results have been published on Nature Protocols on September 3rd, 2021.
Understanding Why Solid-State Batteries Fail
Researchers from the University of Oxford, the Diamond Light Source and the Paul Scherrer Institut have generated strong evidence supporting one of two competing theories regarding the mechanism by which lithium metal dendrites grow through ceramic electrolytes. A process leading to short circuit at high rates of charge. The X-ray phase-contrast imaging capabilities of the TOMCAT beamline of the Swiss light source allowed researchers to visualize and characterize the growth of cracks and dendrites deep within an operating solid-state battery. The results were published in Nature Materials on April 22, 2021.
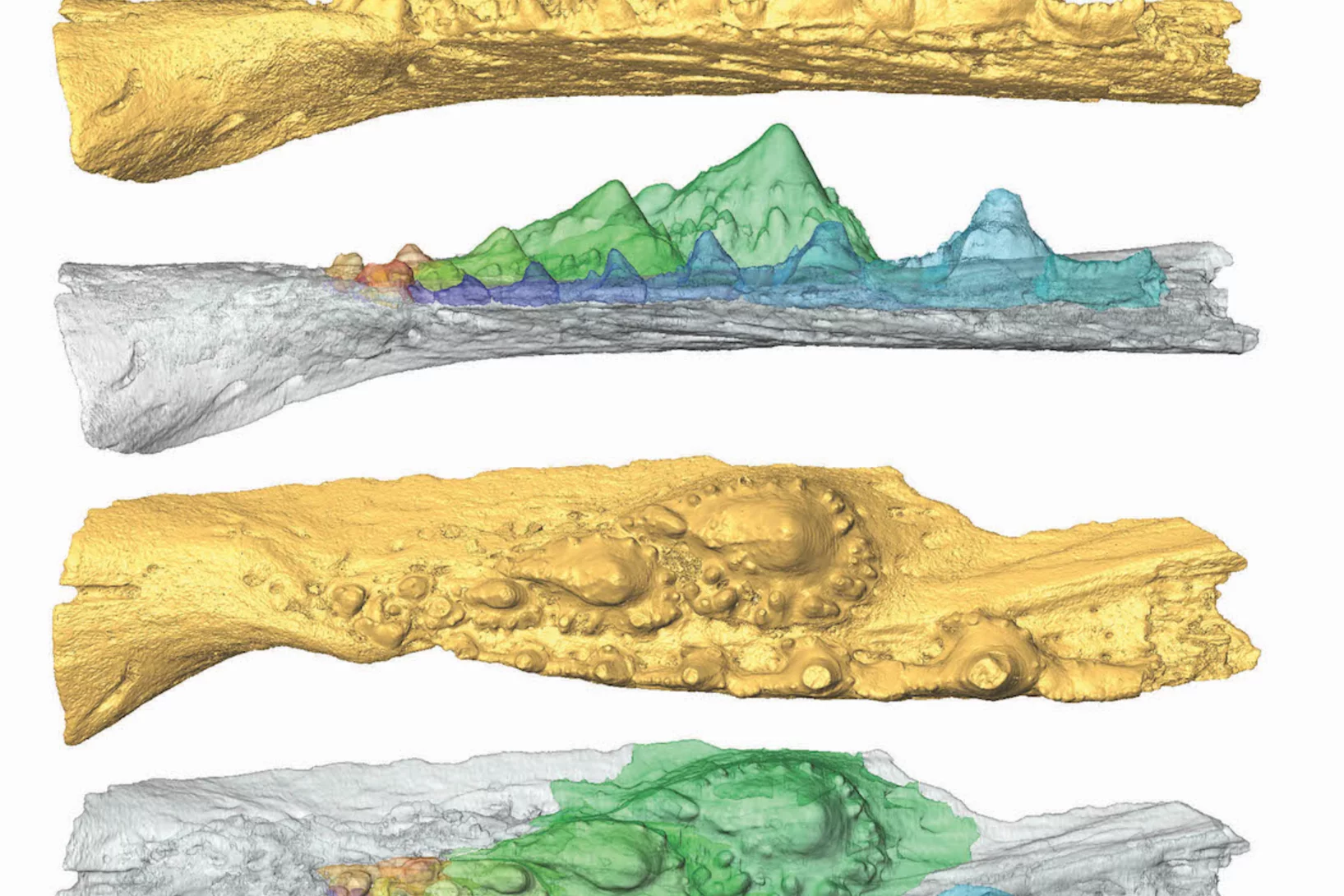
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
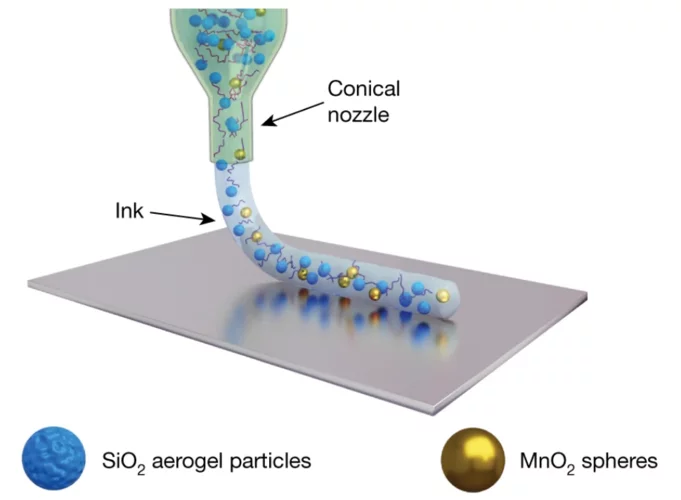
3D printing silica aerogels at the micrometer scale
A group of EMPA and ETH Zürich researchers have developed a new method to directly write ink made of silica aerogels in 3D. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline they characterized the resulting printed material with different compositions. Their results were published in Nature on August 18, 2020.
Phase contrast microtomography reveals nanoparticle accumulation in zebrafish
Metal-based nanoparticles are a promising tool in medicine – as a contrast agent, transporter of active substances, or to thermally kill tumor cells. Up to now, it has been hardly possible to study their distribution inside an organism. Researchers at the University of Basel in collaboration with the TOMCAT team have used phase contrast X-ray tomographic microscopy to take high-resolution captures of the nanoparticle aggregation inside zebrafish embryos.
The study was published in the journal Small and featured on the cover of its current issue.
Miniaturized fluidic circuitry observed in 3D
The team of Prof. Thomas Hermans at the University of Strasbourg in France managed to create wall-less aqueous liquid channels called anti-tubes. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline those anti-tubes could be observed in 3D. The exciting results were published in Nature on May 6, 2020.
X-ray Imaging for Biomedicine: Imaging Large Volumes of Fresh Tissue at High Resolution
The TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source specializes in rapid high-resolution 3-dimensional tomographic microscopy measurements with a strong focus on biomedical imaging. The team has recently developed a technique to acquire micrometer-scale resolution datasets on the entire lung structure of a juvenile rat in its fresh natural state within the animal’s body and without the need for any fixation, staining or other alteration that would affect the observed structure (E. Borisova et al., 2020, Histochem Cell Biol).
MacEtch in gas phase: a new nanofabrication technology at PSI
The grating fabrication team of the X-ray tomography group has scored another record in etching technology of silicon by realizing a MacEtch process in gas phase. Ultra-high aspect ratios (up to 10 000 : 1) in the nanoscale regime (down to 10 nm) were achieved by platinum assisted chemical etching of silicon in the gas phase. The results were published in Nanoscale Horizons on February 17, 2020.
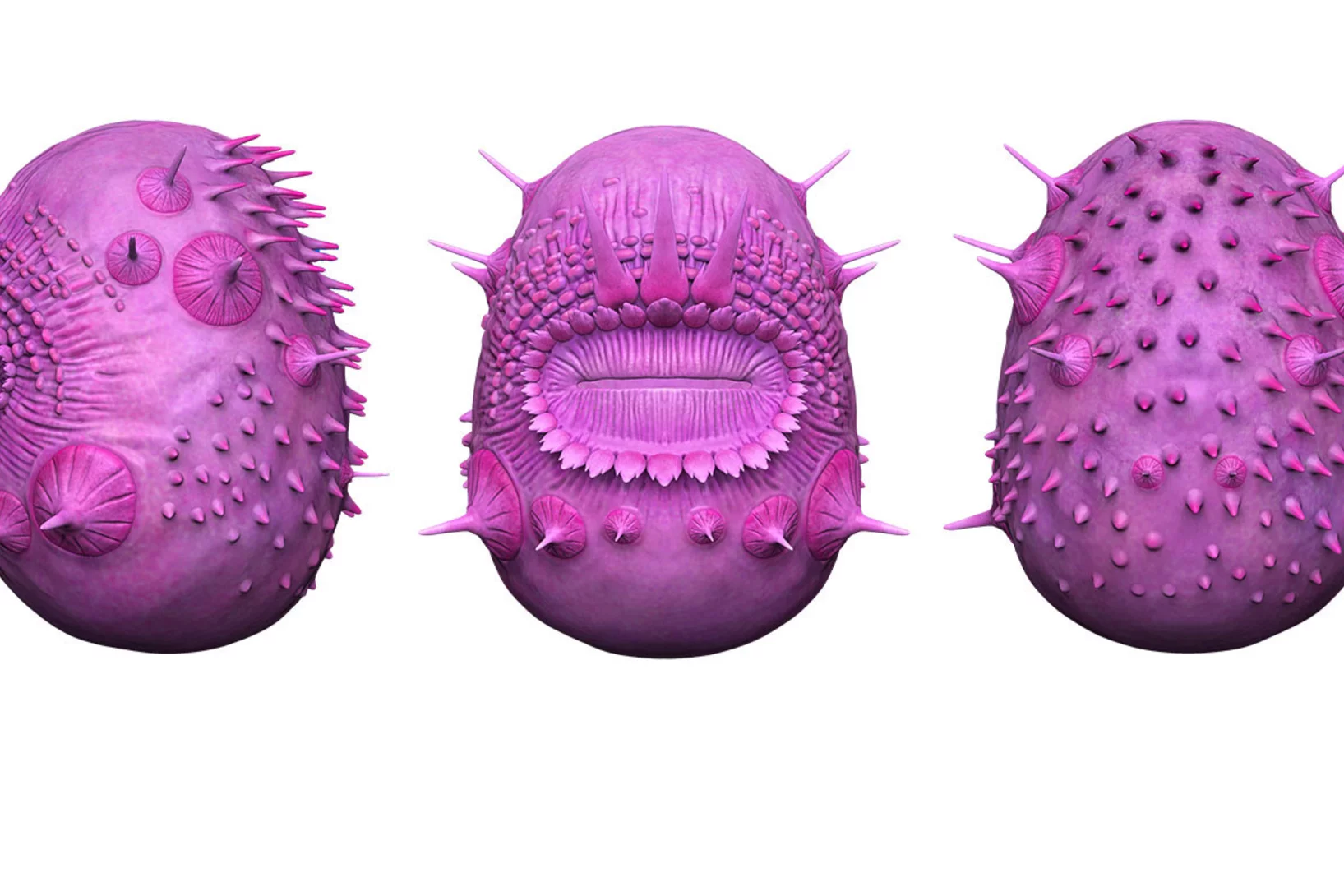
Animal embryos evolved before animals
Detailed characterization of cellular structure and development of exceptionally preserved ancient tiny fossils from South China by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the University of Bristol and Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology to the discovery that animal-like embryos evolved long before the first animals appear in the fossil record.
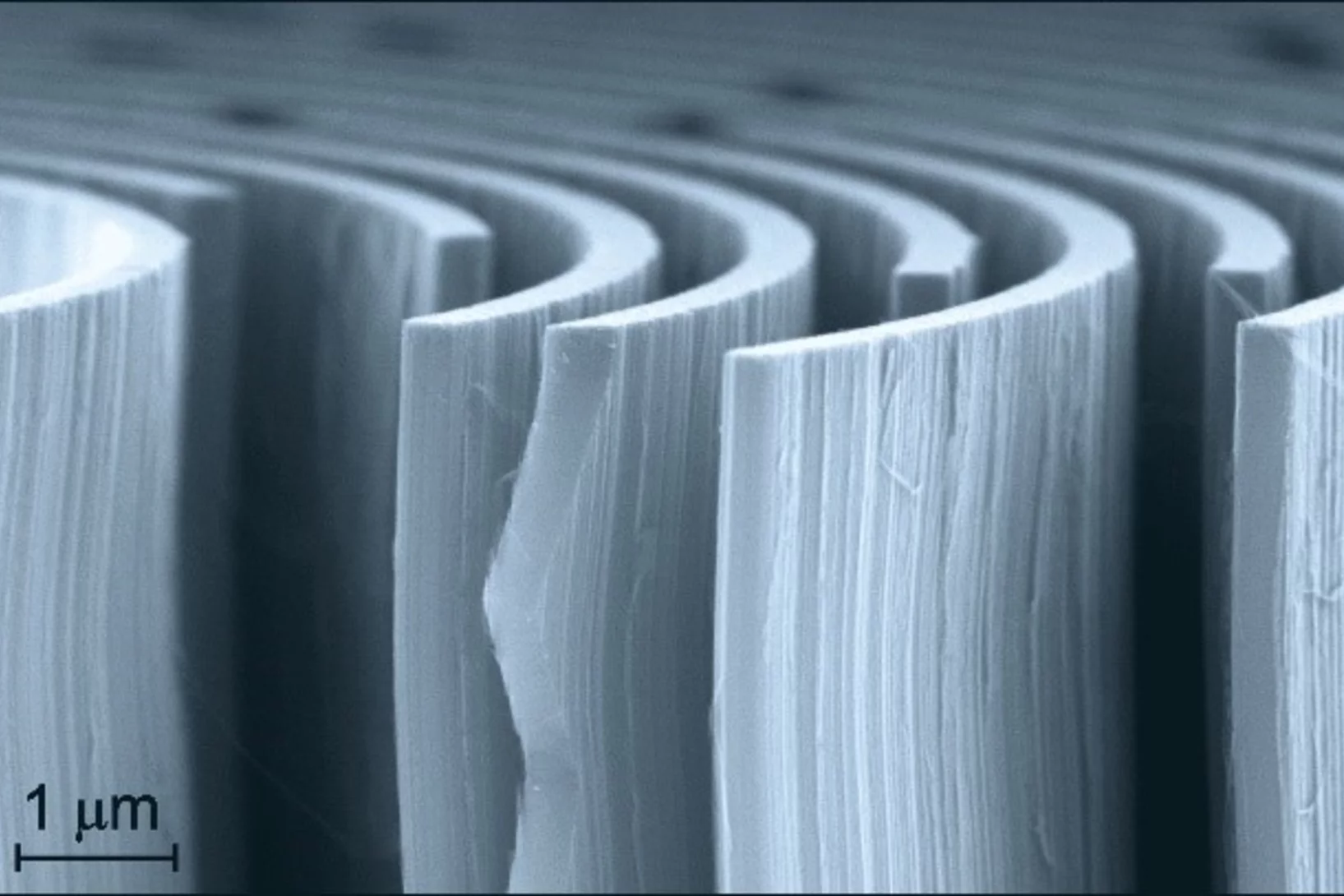
Radiographier rapidement et précisément des matériaux composites renforcés de fibres
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont mis au point une méthode de diffusion des rayons X aux petits angles qui peut être utilisée pour le développement ou le contrôle qualité de matériaux composites novateurs renforcés de fibres. Grâce à elle, les analyses de ces matériaux pourraient se faire à l’avenir non seulement par recours aux rayons X issus de sources puissantes comme la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS, mais aussi avec le rayonnement issu de tubes à rayons X conventionnels.
World record in time-resolved tomography
Researchers from the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the TOMCAT beamline have achieved a new world record in time-resolved tomography by measuring over 200 tomographies per second during heating of an evolving aluminium metal foam.
Une lentille virtuelle améliore la microscopie à rayons X
Une nouvelle méthode développée par des chercheurs du PSI permet d’améliorer encore les radiographies de matériaux. Pour ce faire, les chercheurs ont déplacé une lentille optique et réalisé chaque fois une image individuelle. A partir de là, ils ont calculé une image globale à l’aide d’algorithmes informatiques.
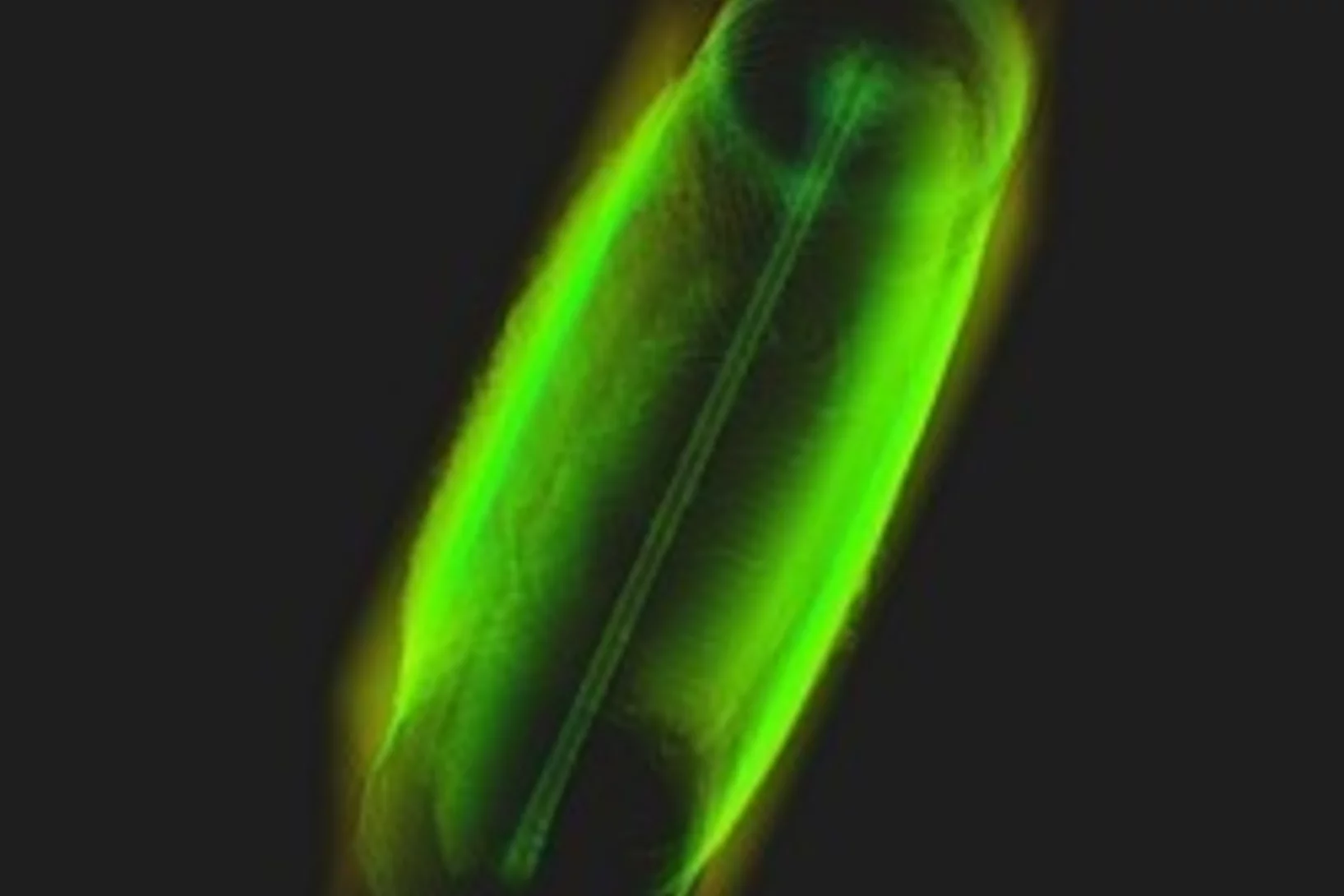
Soft-tissue evidence for homeothermy and crypsis in a Jurassic ichthyosaur
Synchrotron-based X-ray tomographic microscopy of melanophores (skin pigment cells) of an amazingly well preserved 180 million years old ichtyosaur (extinct marine reptile similar to whales) contributed in a multidisciplinary investigation to the new findings published today in Nature.
La spin-off du PSI GratXray remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017
Une spin-off du PSI remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017: la jeune entreprise GratXray développe une nouvelle méthode de diagnostic précoce du cancer du sein.
Single shot grating interferometry demonstrated using direct conversion detection
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute's Swiss Light Source in Villigen, Switzerland, have developed an X-ray grating interferometry setup which does not require an analyzer grating, by directly detecting the fringes generated by the phase grating with a high resolution detector. The 25um pitch GOTTHARD microstrip detector utilizes a direct conversion sensor in which the charge generated from a single absorbed photon is collected by more than one channel. Therefore it is possible to interpolate to achieve a position resolution finer than the strip pitch.
Watching lithium move in battery materials
In order to understand limitations in current battery materials and systematically engineer better ones, it is helpful to be able to directly visualize the lithium dynamics in materials during battery charge and discharge. Researchers at ETH Zurich and Paul Scherrer Institute have demonstrated a way to do this.
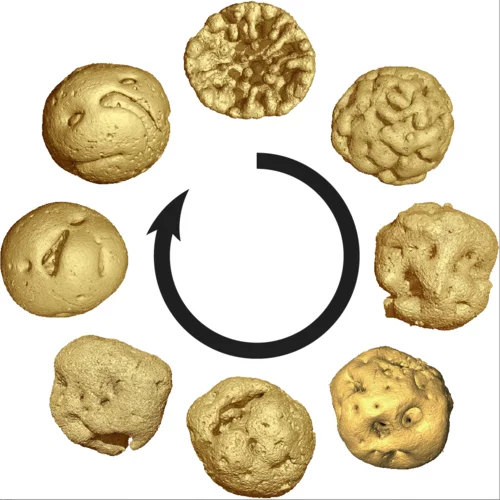
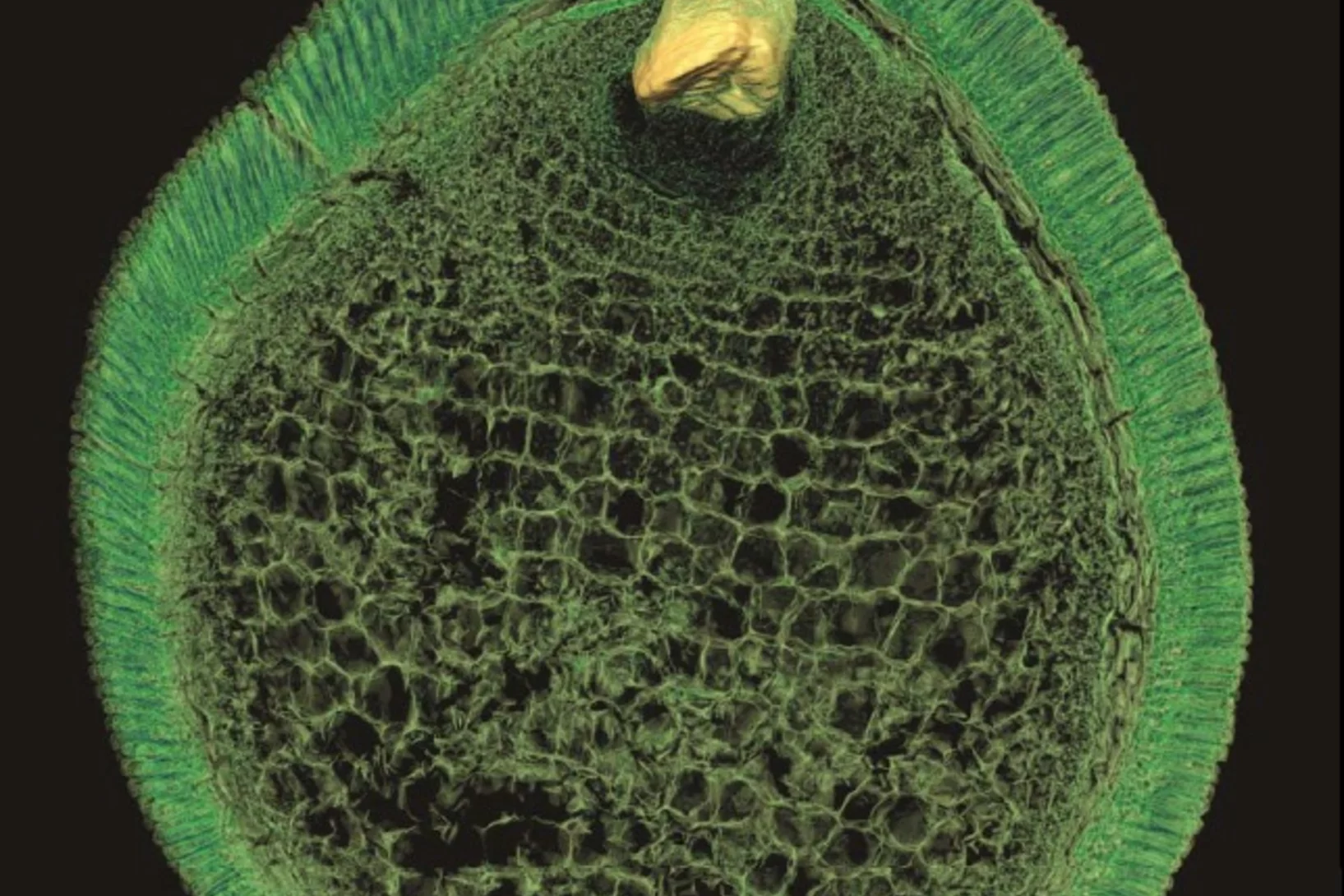
Preserved Embryos Illustrate Seed Dormancy in Early Angiosperms
The discovery of exceptionally well-preserved, tiny fossil seeds dating back to the Early Cretaceous corroborates that flowering plants were small opportunistic colonizers at that time, according to a new Yale-led study.
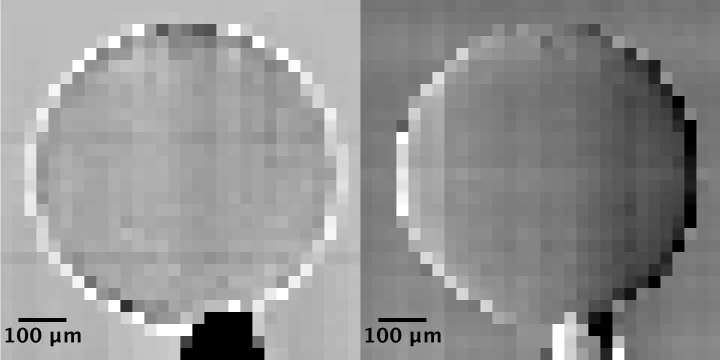
Multiresolution X-ray tomography, getting a clear view of the interior
Researchers at PSI have developed a technique that combines tomography measurements at different resolution levels to allow quantitative interpretation for nanoscale tomography on an interior region of interest of the sample. In collaboration with researchers of the institute AMOLF in the Netherlands and ETH Zurich in Switzerland they showcase their technique by studying the porous structure within a section of an avian eggshell. The detailed measurements of the interior of the sample allowed the researchers to quantify the ordering and distribution of an intricate network of pores within the shell.