Show filters
Welcome to LXN Kenté Kouda
Herzlich Willkommen Kenté Kouda im LXN!
Henry Bell wins ETH Medal for his MSc thesis
Henry Bell's MSc thesis work, conducted in the QPS group, has been awarded with an ETH medal.
Gilded with Science
Congratulations to Nicolai Taufertshöfer for receiving a distinction at the SNSF Scientific Image Competition.
Welcome to LXN Karina Kazarian
Herzlich Willkommen Karina Kazarian im LXN!
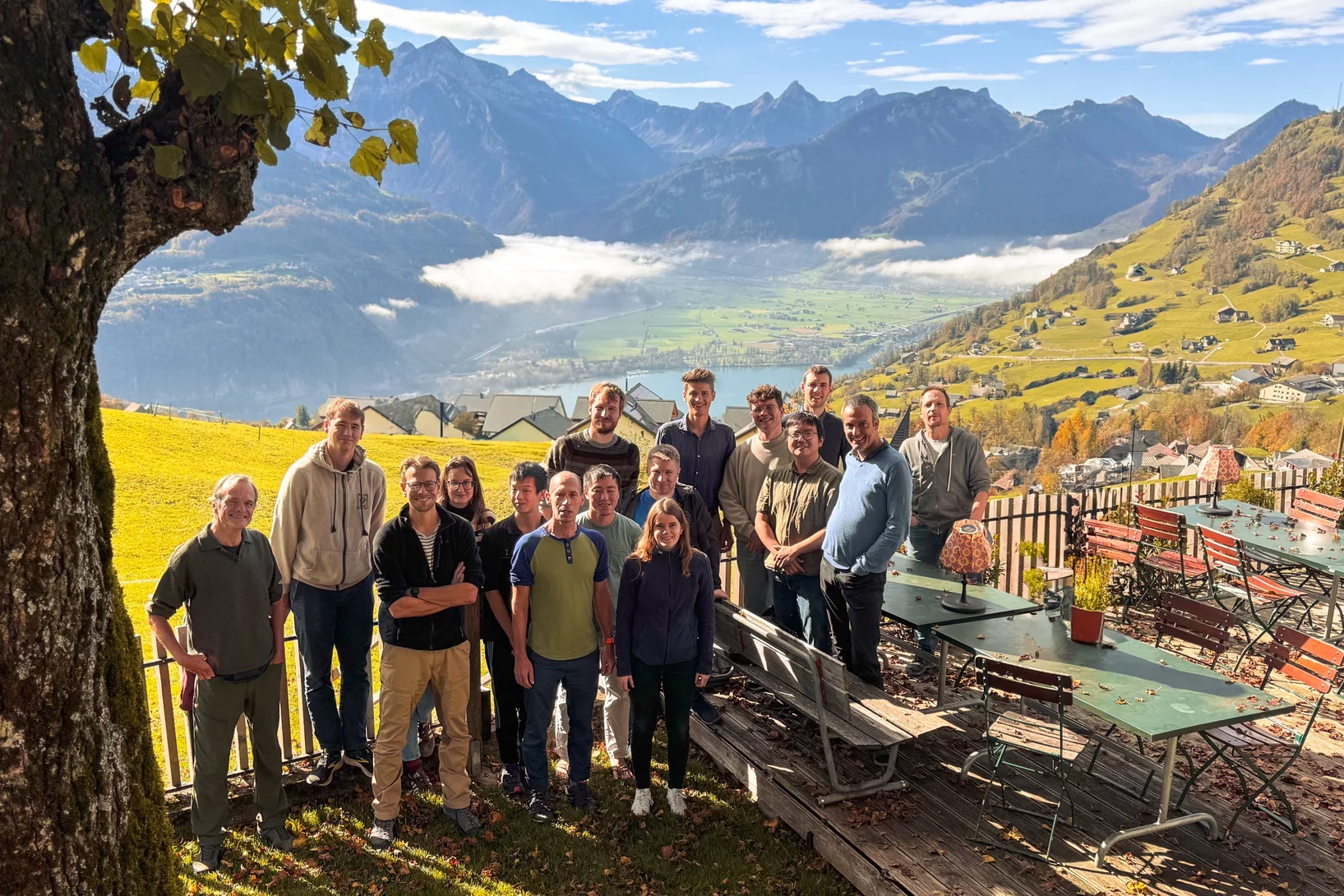
"Quantum Magnet Lunch" retreat in Amden
Our "Quantum Magnet Lunch" team - consisting of the QPS group, as well as Markus Müller's team and Gabriel Aeppli - met in Amden to review the ongoing research themes and set the agenda for the coming year.
Welcome to LXN Rok Venturini
Herzlich Willkommen Rok Venturini im LXN!
Welcome to LXN Jamie Bragg
Herzlich Willkommen Jamie Bragg im LXN!
Welcome to LXN Tijl Degroote
Herzlich Willkommen Tijl Degroote im LXN!
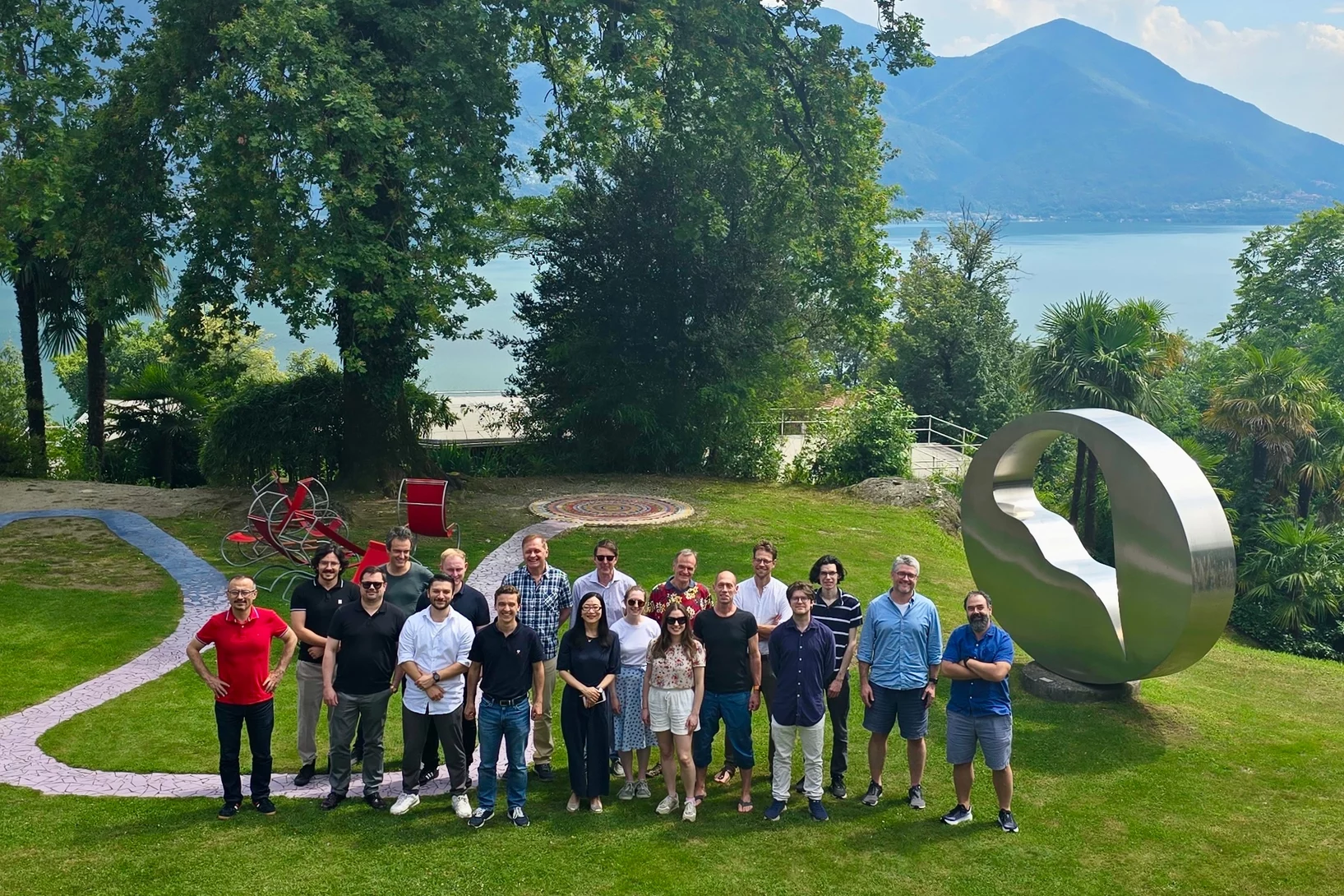
PSI-UCL-Surrey workshop on silicon and germanium based quantum devices
A team of PSI scientists as well as collaborators from UCL and the University of Surrey met at the Fondazione Monte Verità to discuss results and trace the roadmap for future research into quantum devices based on silicon and germanium.
Aidan McConnell's MSc thesis work featured by New Scientist Magazine
Aidan McConnell's work from his MSc thesis at the University of Cambridge is featured on the front cover of New Scientist Magazine.
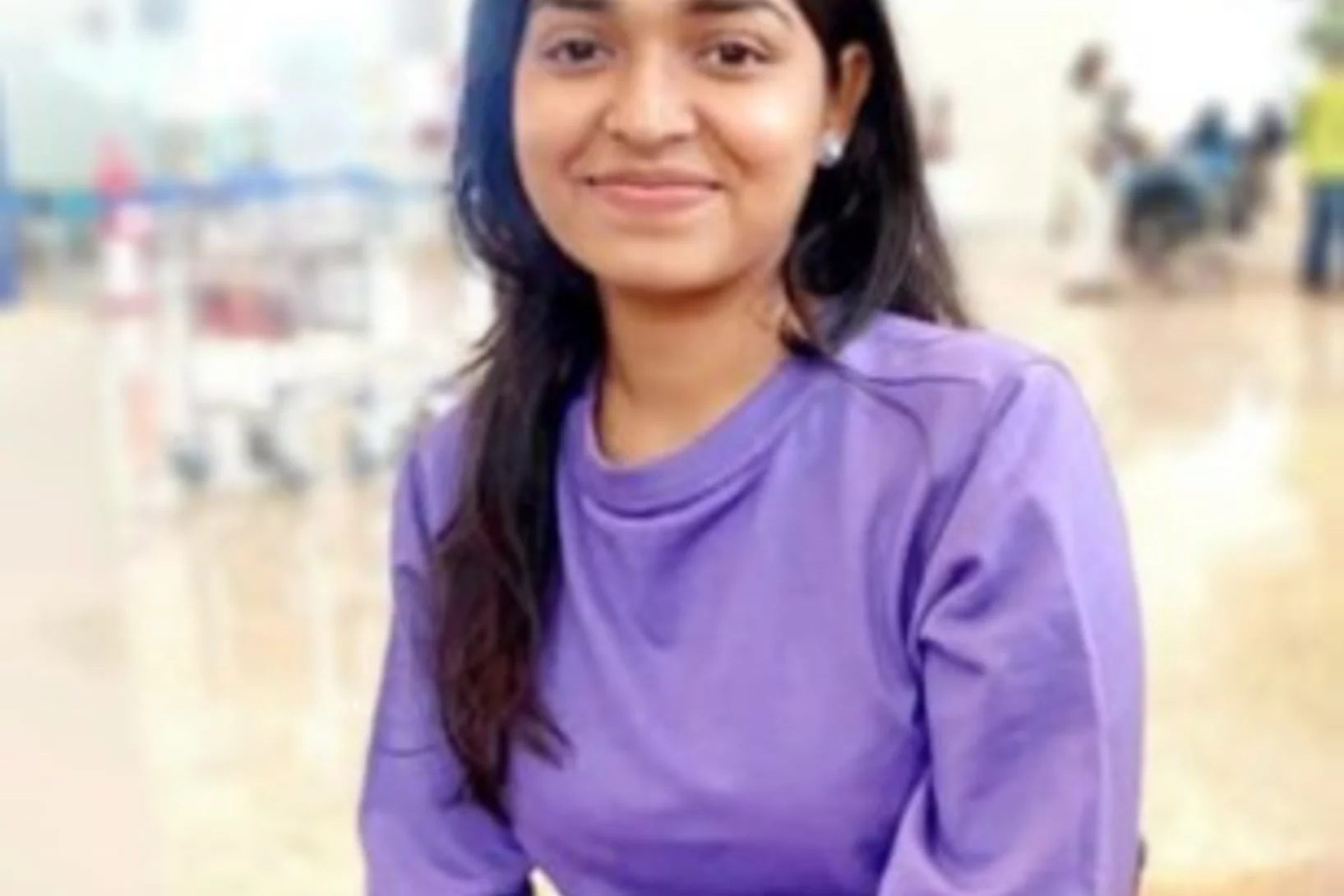
Welcome to LXN Kajal Biju
Herzlich Willkommen Kajal Biju im LXN!
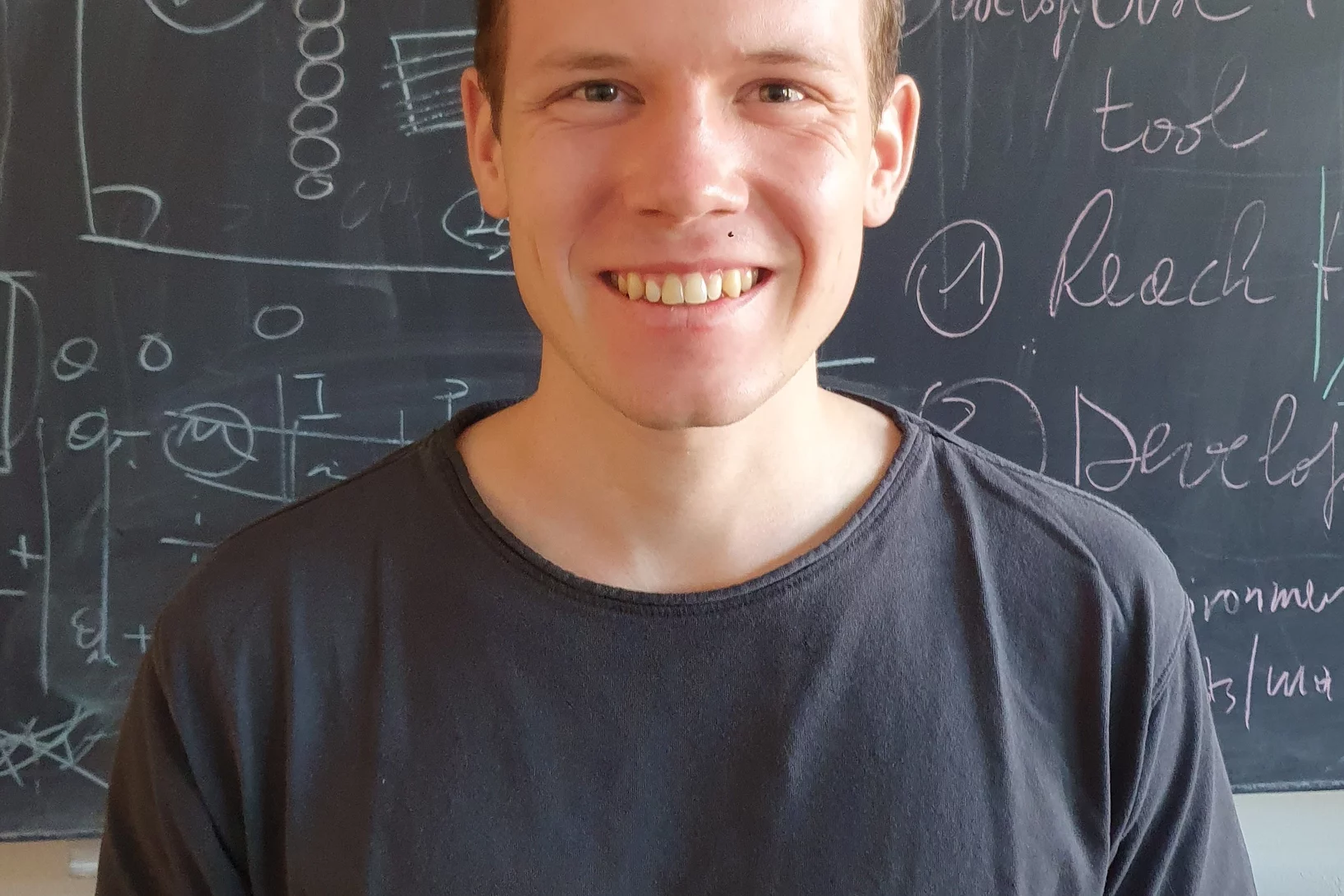
Welcome to LXN Nicolai Taufertshöfer
Herzlich Willkommen Nicolai Taufertshöfer im LXN!
Swiss Quantum Days Poster Prize for Adrian Rutschmann
Congratulations Adrian Rutschmann for winning a prize at the Swiss Quantum Days 2024 for a poster on our recent X-ray-detected ferromagnetic resonance experiment at SwissFEL.
Welcome to LXN Maria Szola
Herzlich Willkommen Maria Szola im LXN!
Welcome to LXN Henry Bell
Herzlich Willkommen Henry Bell im LXN!
Welcome to LXN Javier Rodriguez Alvarez
Herzlich Willkommen Javier Rodriguez Alvarez LXN!
Welcome to LXN Adrian Rutschmann
Herzlich Willkommen Adrian Rutschmann im LXN!
Welcome to LXN Peng Han
Herzlich Willkommen Peng Han im LXN!
"Quantum Magnet Lunch" retreat in Seelisberg
Our "Quantum Magnet Lunch" team - consisting of the QPS group, as well as, Markus Müller's team and Gabriel Aeppli - met for a two-day retreat to review our ongoing research and set the agenda for the coming year.
SwissFEL #LightSourceSelfie of Maël Clémence
Check out Maël Clémence's #LightSourceSelfie about his PhD project on quantum properties of magnetic materials at the Cristallina-Q endstation of SwissFEL.
Welcome to LXN Gabriel Weber
Herzlich Willkommen Gabriel Weberin LXN!
Welcome to LXN Céline Hensky
Herzlich Willkommen Céline Hensky in LXN!
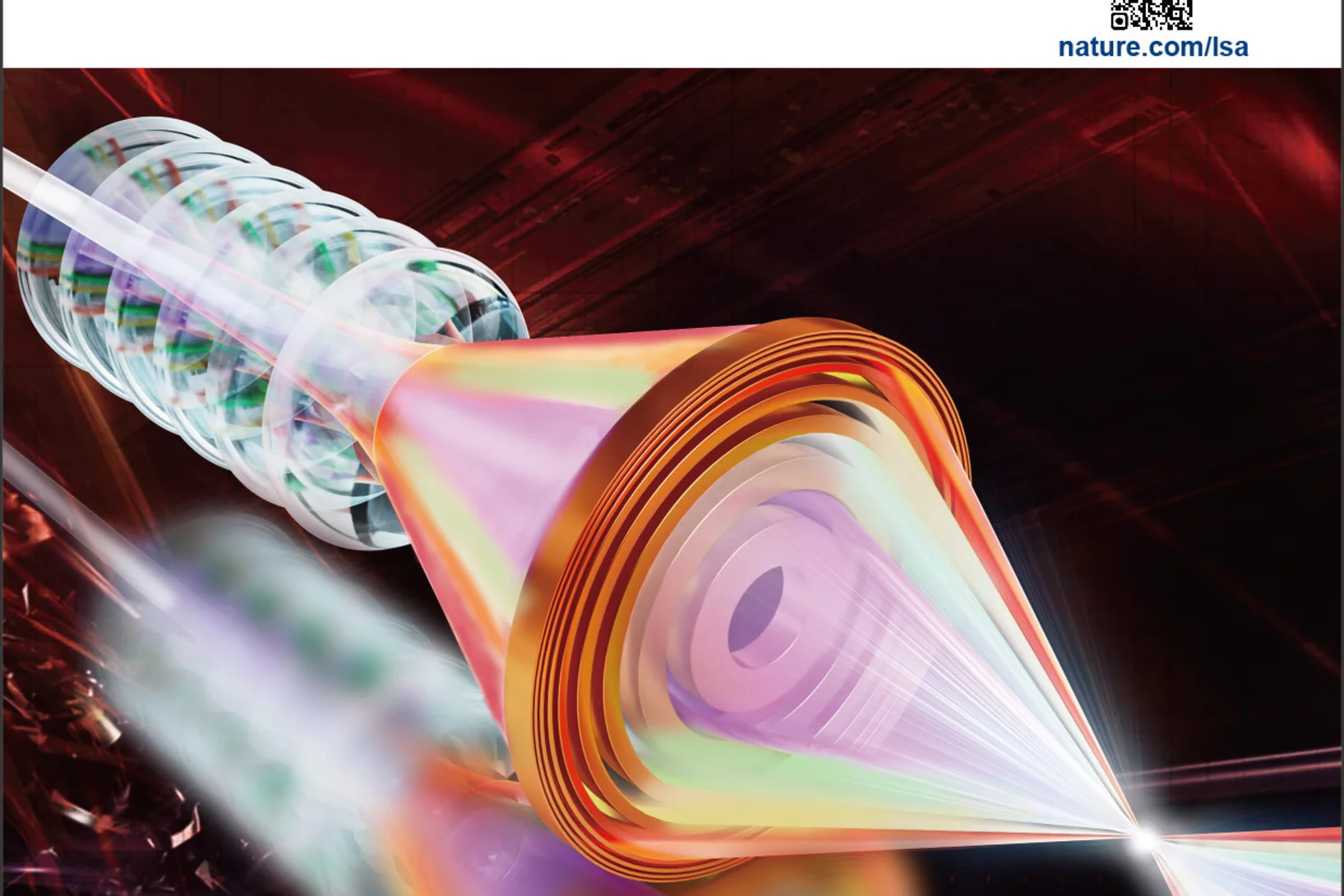
Apochromatic X-ray focusing as Editor's Highlight in Light: Science & Applications
Our recent work on the 1st demonstration of apochromatic X-ray lenses has been selected as an Editor's Highlight in Light: Science & Applications.
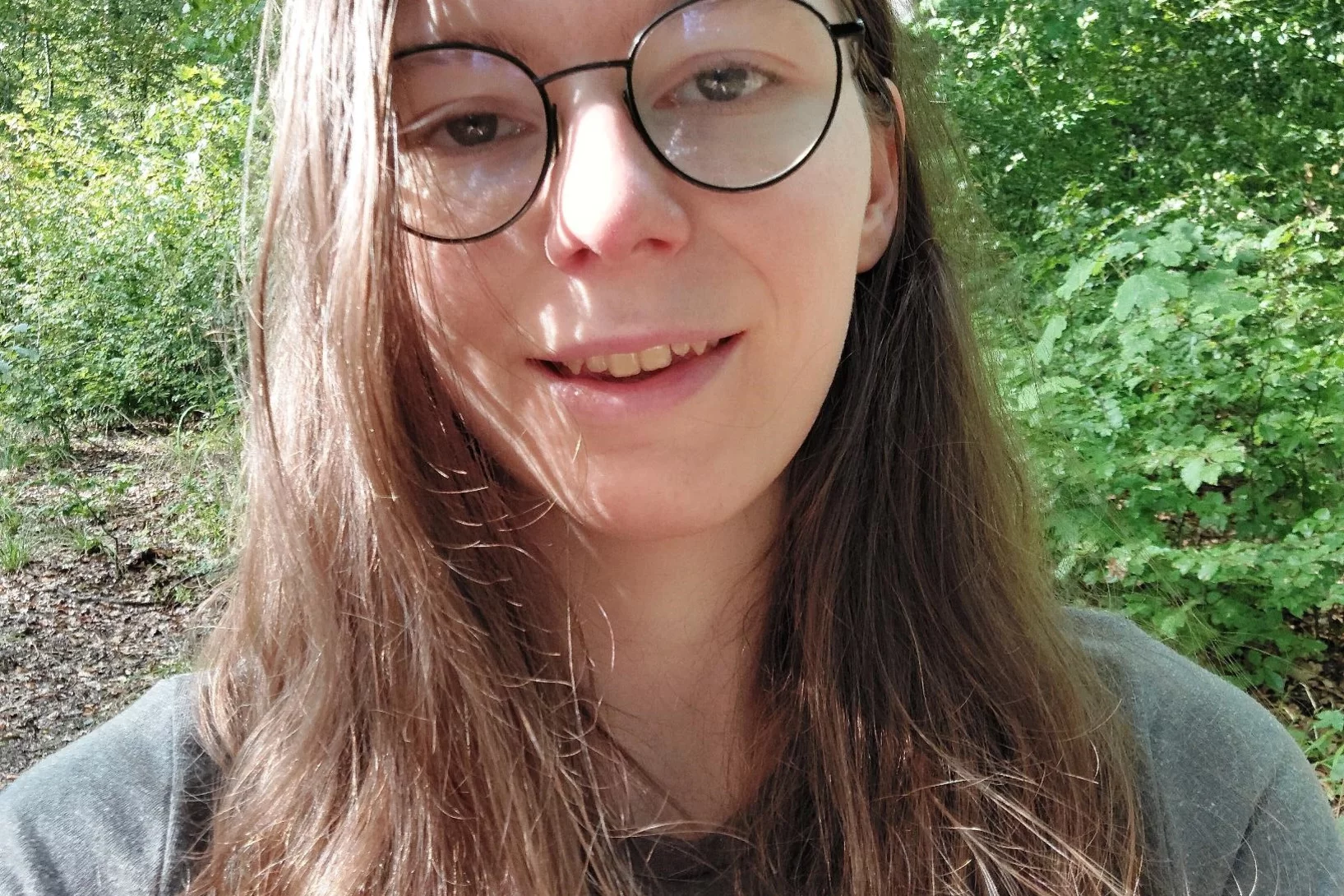
Welcome to LXN Narmadha Devi
Herzlich Willkommen Narmadha Devi in LXN!
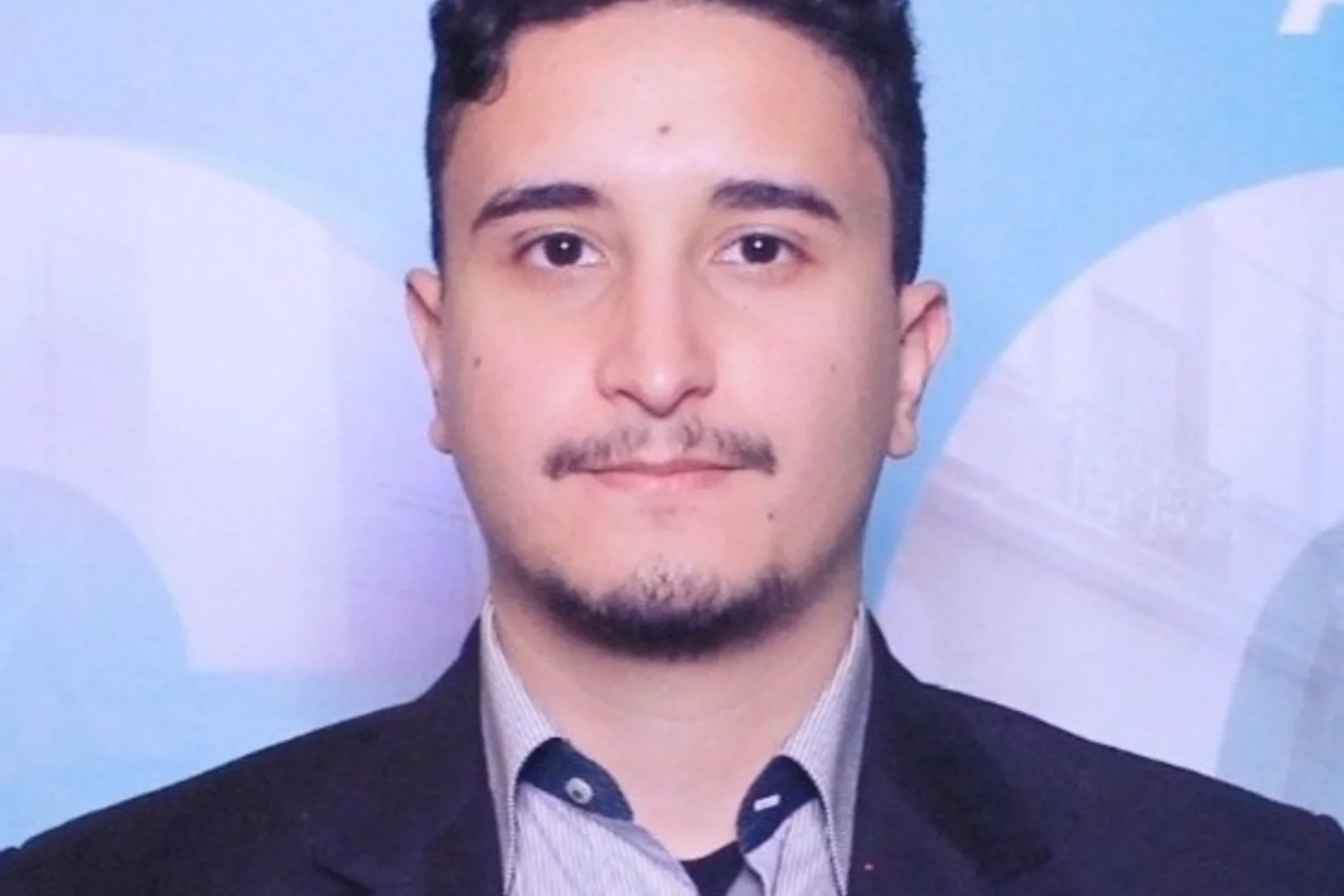
Welcome to LXN Bechir Braham
Herzlich Willkommen Bechir Braham in LXN!
Welcome to LXN Adil Dogan
Herzlich Willkommen Adil Dogan in LXN!
Welcome to LXN Denis Hnidenko
Herzlich Willkommen Denis Hnidenko in LXN!
Welcome to LXN Savanna Coffel
Herzlich Willkommen Savanna Coffel in LXN!
Welcome to LXN Daniel Melvin
Herzlich Willkommen Daniel Melvin in LXN!
Welcome to LXN Frederik Schirdewahn
Herzlich Willkommen Frederik Schirdewahn in LXN!