Show filters
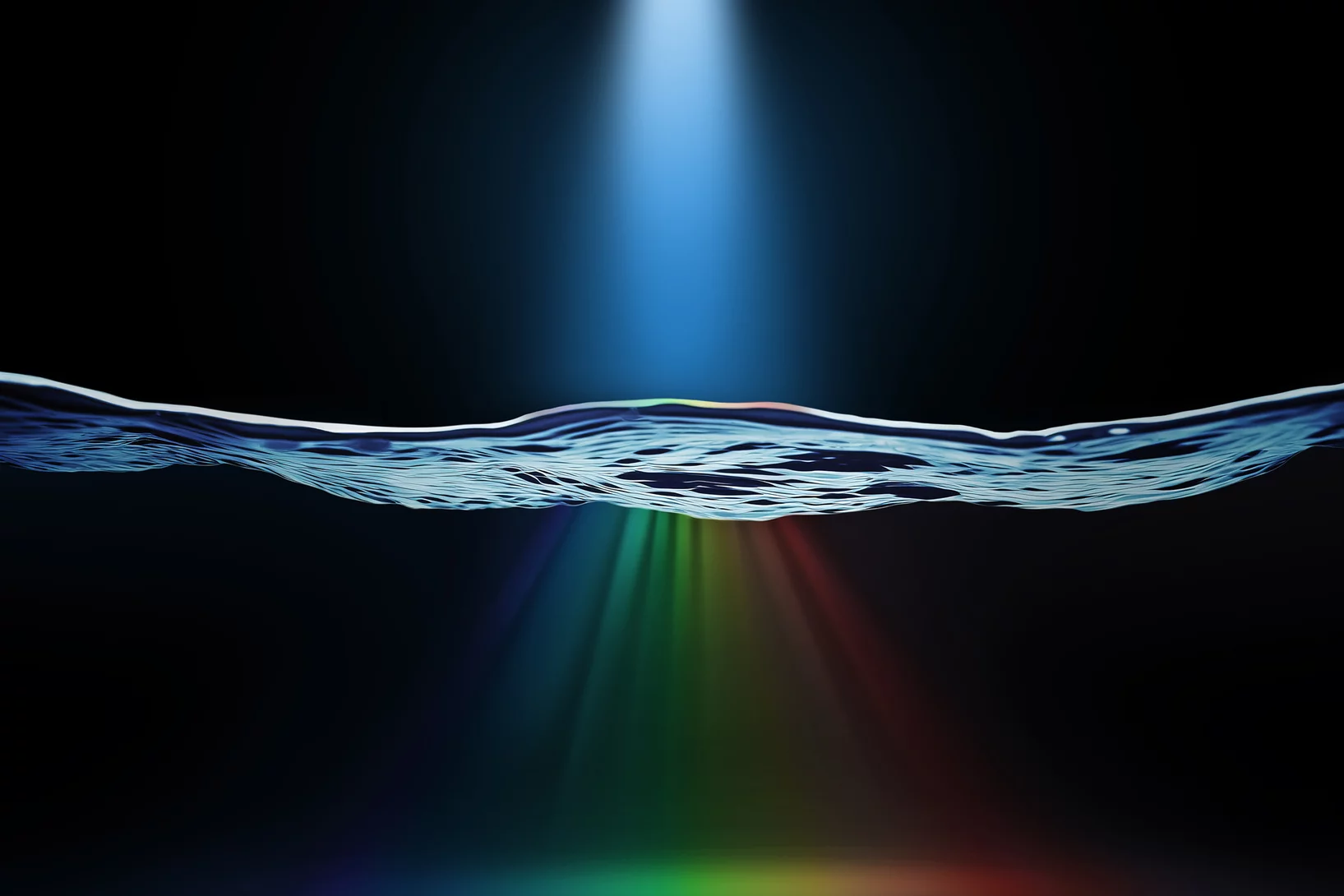
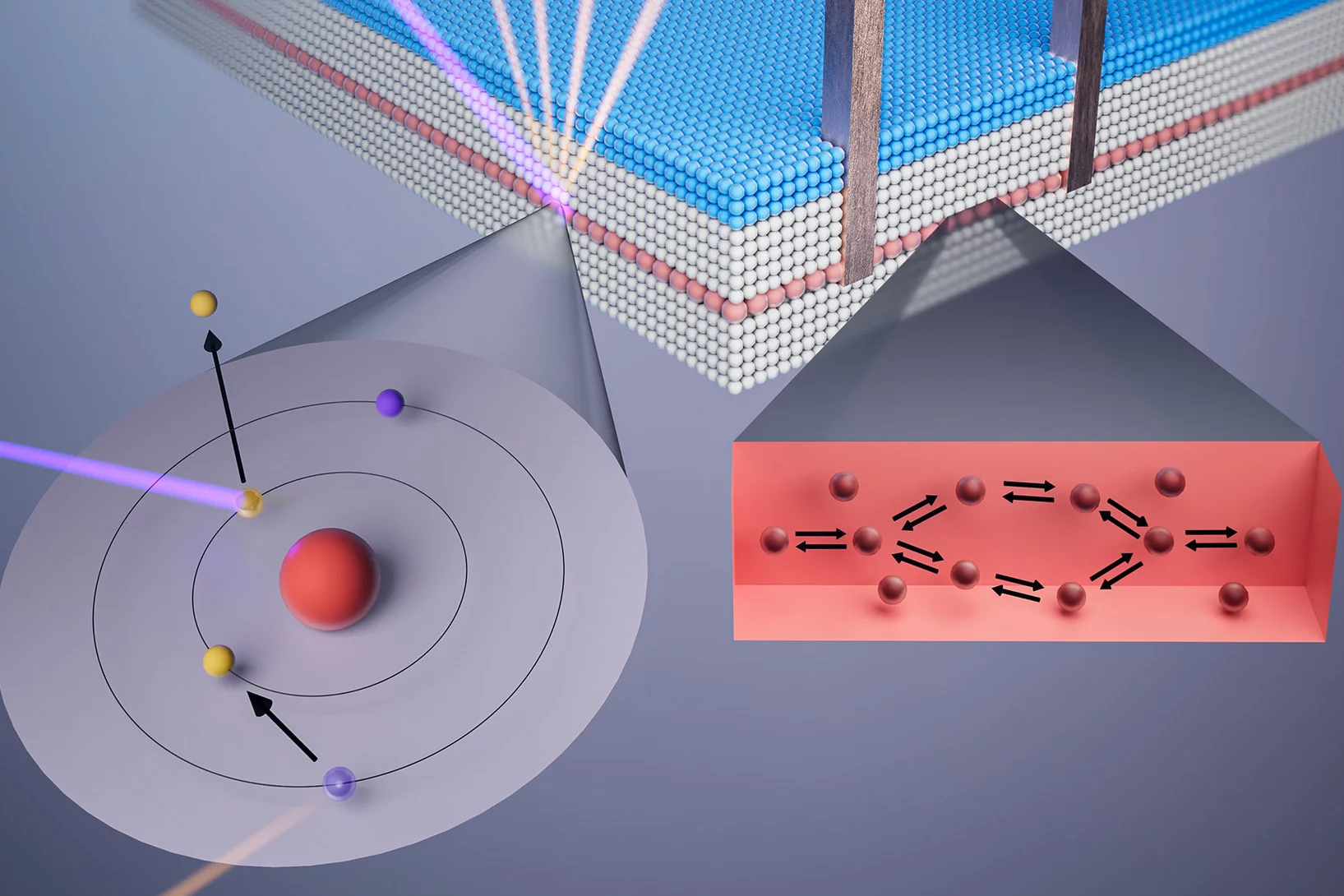
Le laser à rayons X suisse révèle comment les électrons interagissent
Une nouvelle technique de rayons X au SwissFEL permet d’observer les électrons «danser» ensemble – et pourrait un jour montrer pourquoi l’information quantique se perd si facilement.
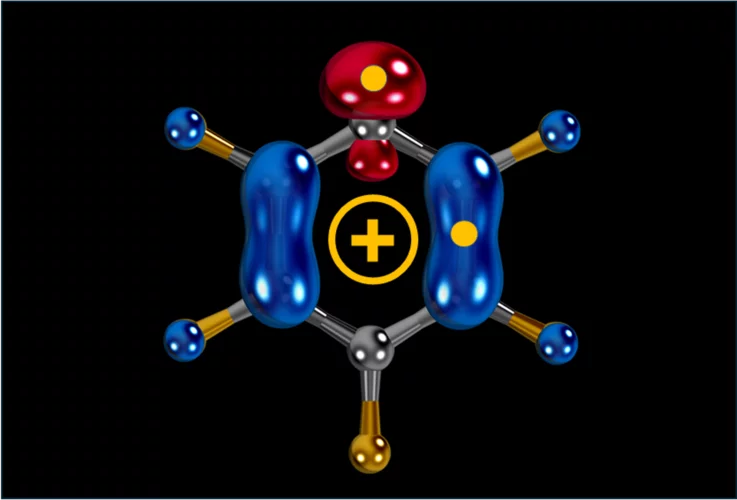
Carbocation, diradical, and superelectrophile in one molecule?
The pentafluorophenyl cation (C₆F₅⁺) breaks these rules with a borderline “crazy” reactivity.
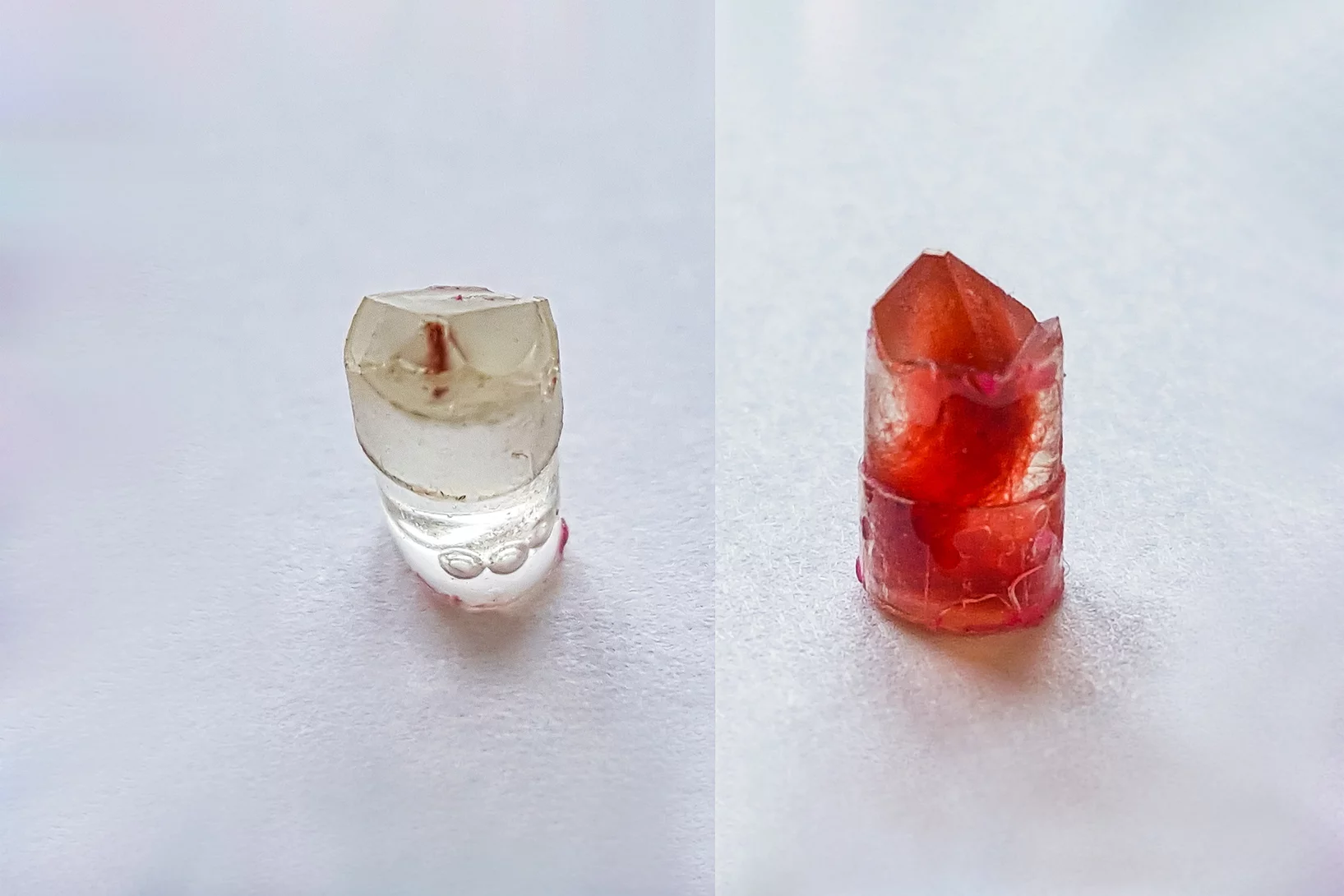
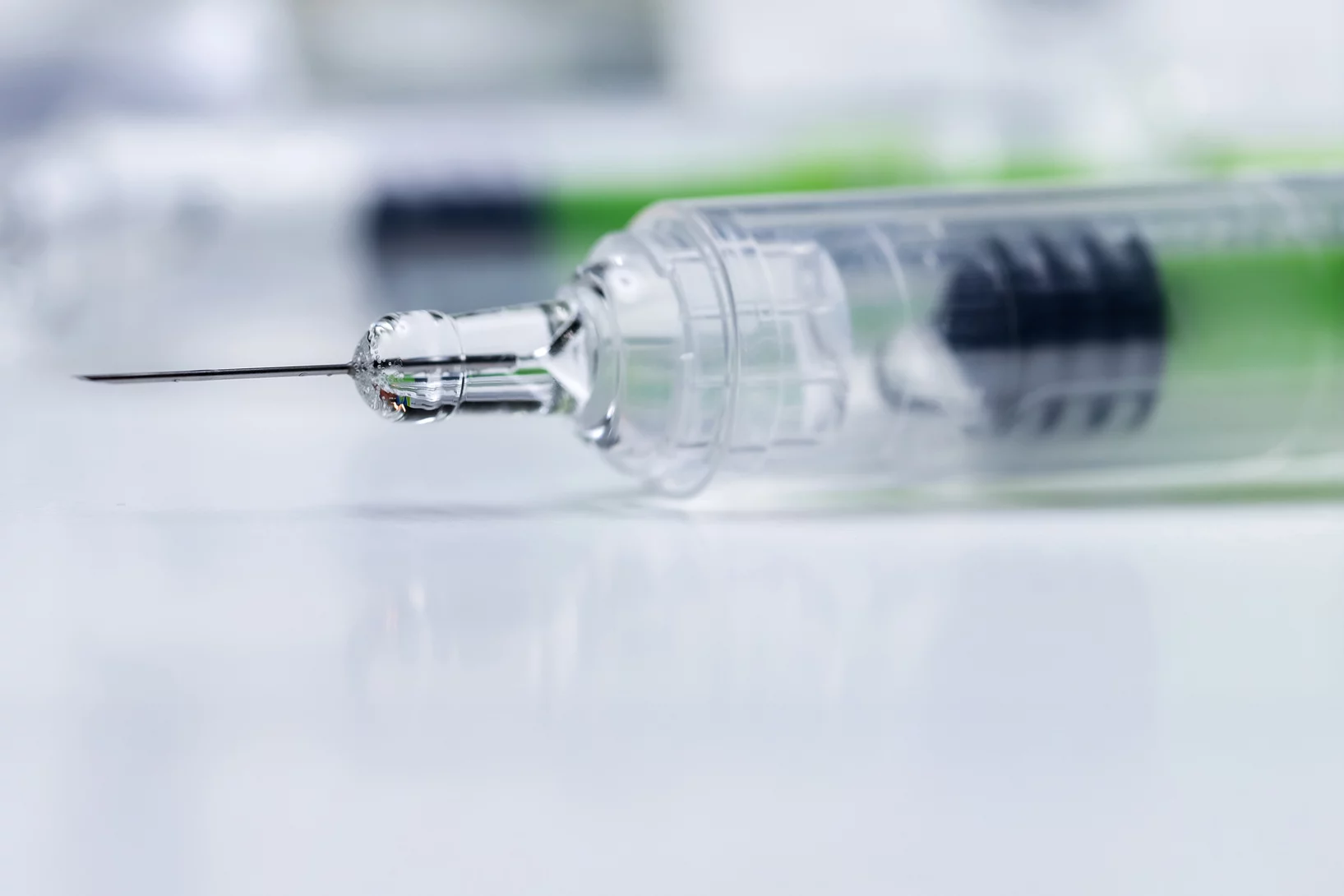
Du zinc détecté dans des seringues obstruées
Pour l'entreprise pharmaceutique MSD, ANAXAM a étudié, avec l'aide de scientifiques du PSI, si le zinc pouvait contribuer à l'obstruction des seringues préremplies.
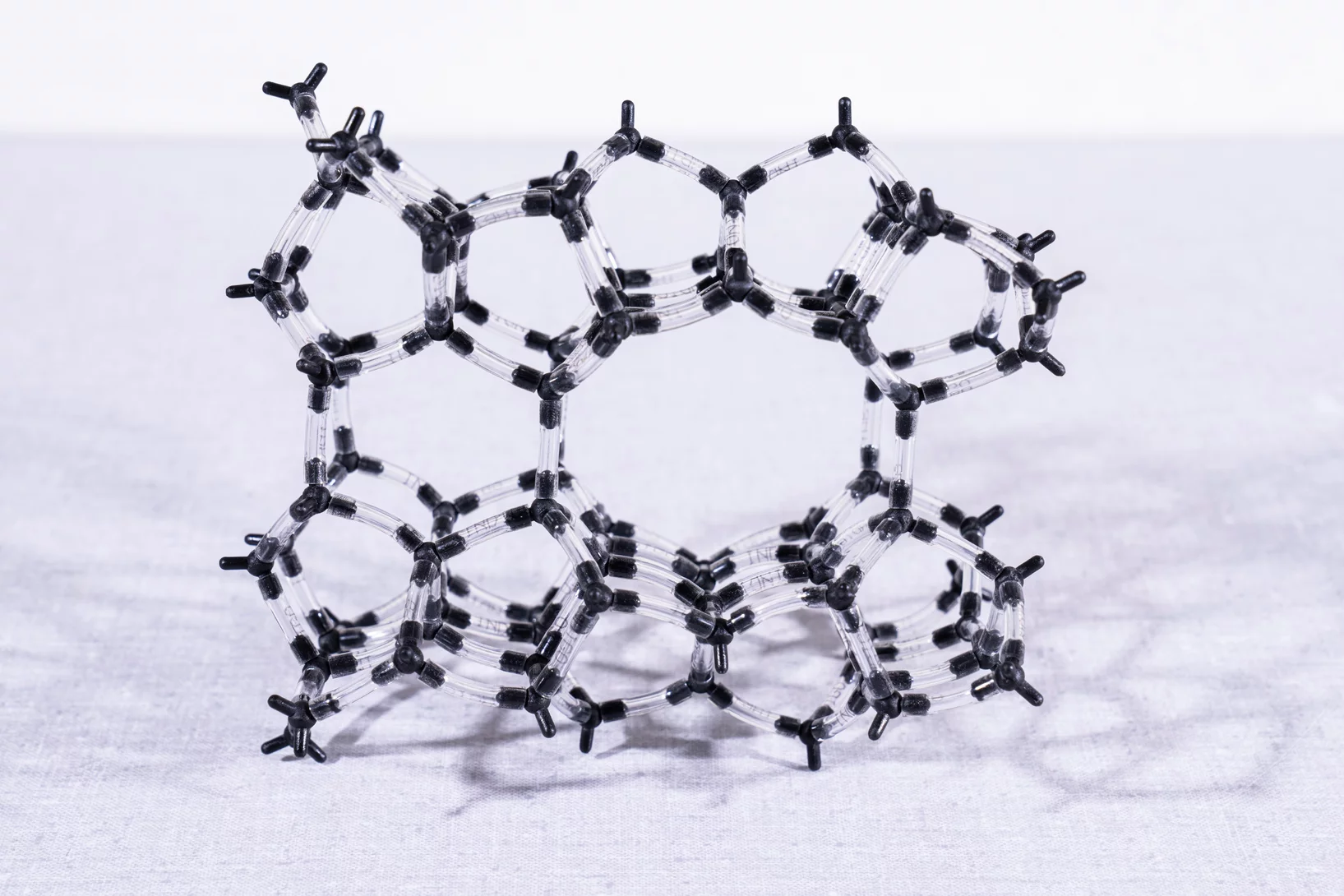
L’aluminium devient visible
Des scientifiques du PSI ont réussi une première: déterminer précisément la position des atomes d’aluminium dans des zéolithes, qui font de ces matériaux des catalyseurs si performants.
Water gets in shape for VUV absorption
Nanometre‑thin, free‑flowing liquid sheets now let Swiss Light Source users record pristine VUV absorption spectra of water, and soon any solvent.
Subvention prestigieuse pour trois projets de recherche au PSI
Béton, catalyse chimique et quête d’une nouvelle physique: trois chercheurs du PSI ont reçu chacun un grant du Fonds national pour ces thèmes de recherche
Nobel Prize winner Anne L’Huillier visits SwissFEL
X-ray free-electron lasers could unlock the next frontier in attosecond research
Permettre l’utilisation quotidienne de batteries lithium-air performantes
Les faisceaux de neutrons et la lumière synchrotron révèlent les processus chimiques qui se jouent dans les batteries lithium-air.
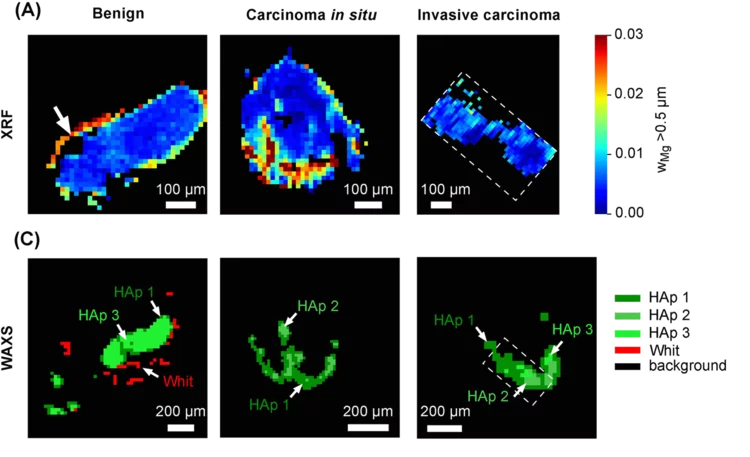
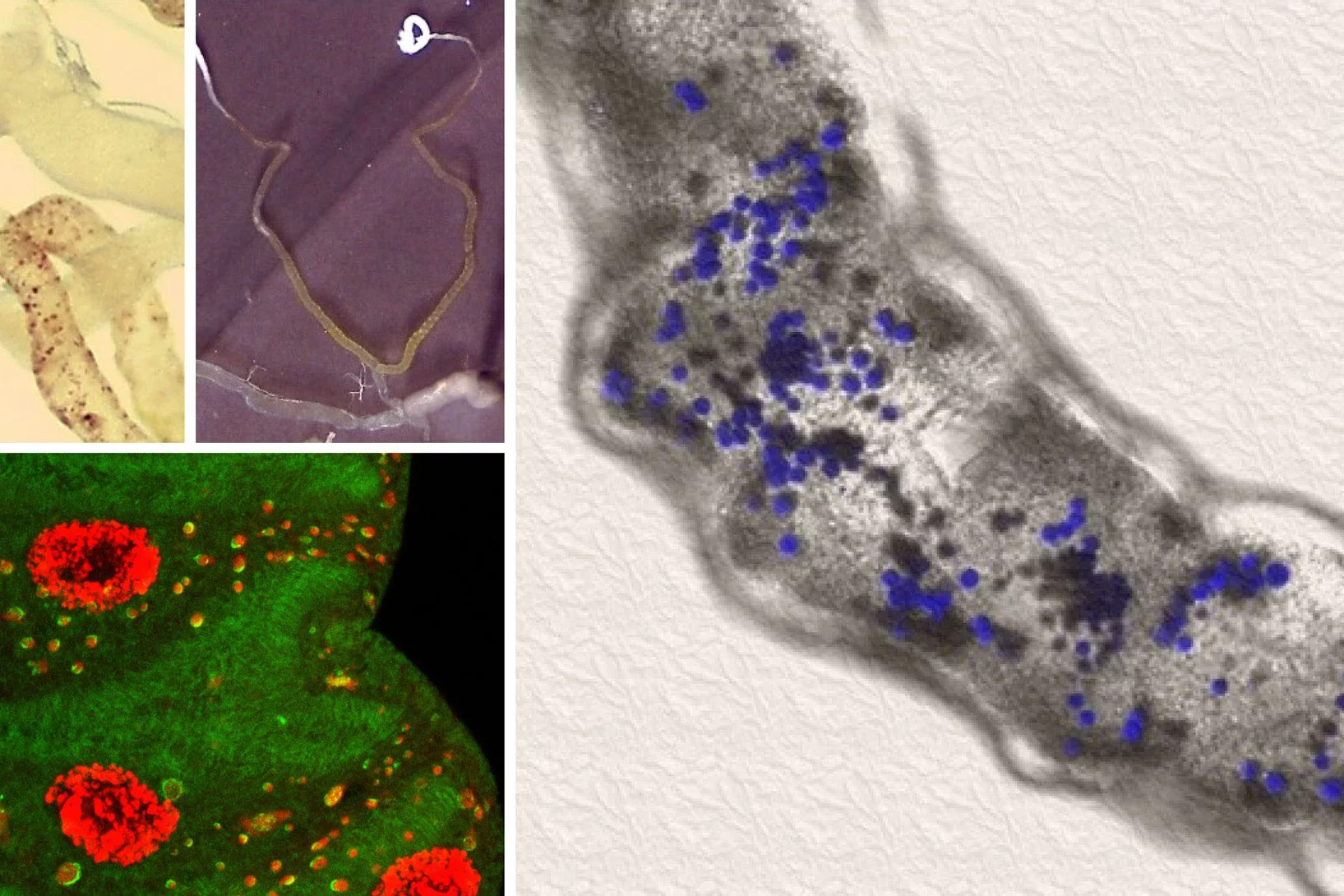
Whitlockite in mammary microcalcifications is not associated with breast cancer
Microcalcifications, small deposits of calcium-containing minerals that form in breast tissue, are often, but not always, a warning sign of breast cancer. The relationship between microcalcifications and cancer has not been fully understood thus far. Researchers discovered now that the relationship between microcalcifications and tumors seems to be linked to the presence of a particular mineral called whitlockite, which is rich in magnesium and is found in microcalcifications only in the absence of tumors.
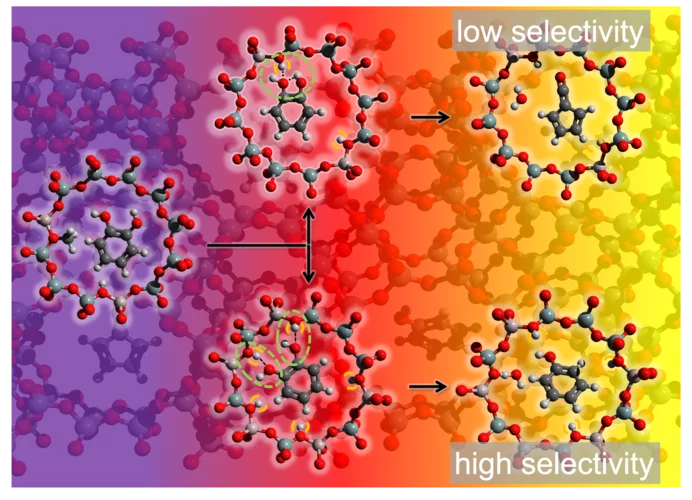
Unveiling the reaction mechanism shines light on the selectivity increase in catalytic processes
Increasing the selectivity of a chemical process through rational catalyst design is the Holy Grail of heterogeneous catalysis. Researchers at PSI and ETH Zürich showcase how revealing hidden steps in reaction pathways can steer processes towards preferred products, as demonstrated in a study focused on biomass valorization.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
Quality control of future transistors: Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Comment les «footballènes» se forment dans l’espace
Une équipe internationale de recherche montre comment les fullerènes se forment dans l’espace.
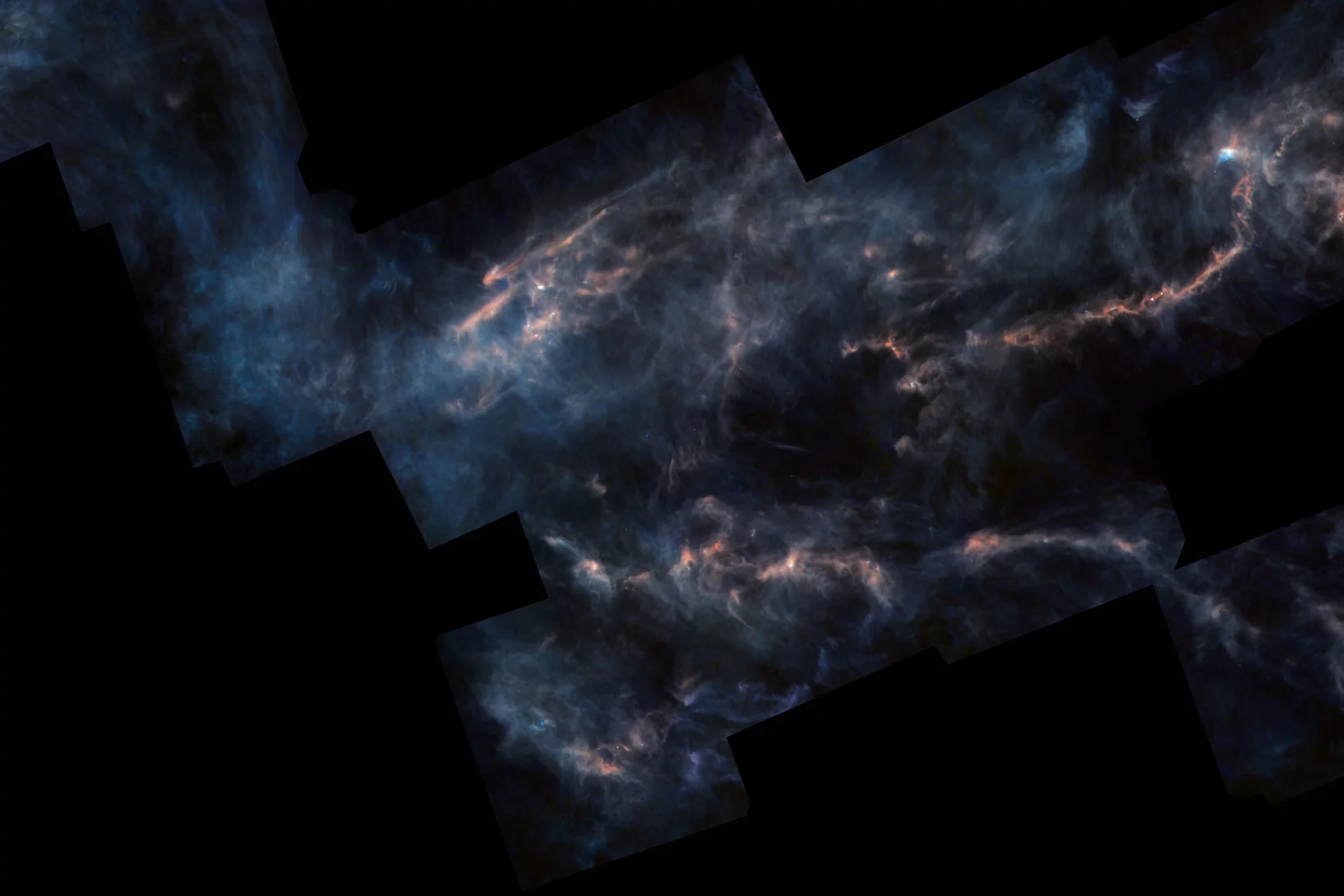
A star is born
Swiss Light Source SLS reveals complex chemistry inside ‘stellar nurseries’
3,1 millions de subventions pour de nouveaux projets de recherche au PSI
Zurab Guguchia et Kirsten Schnorr, tous deux chercheurs au PSI, reçoivent du Fonds national suisse des subsides de recherche d’un montant total de 3,1 millions de francs pour leurs projets tournés vers l’avenir.
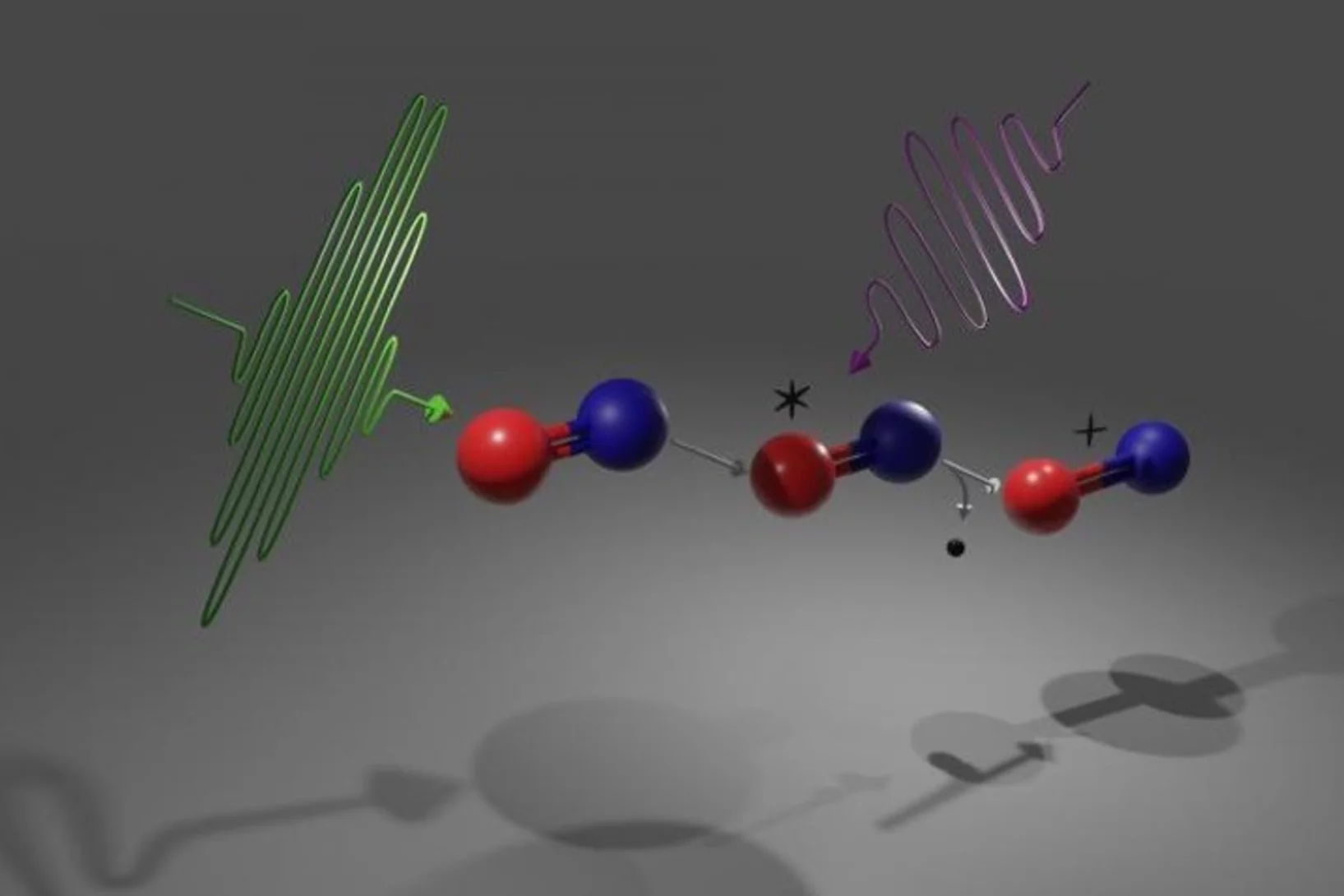
Tracking chemical bond changes with element selectivity and in real time
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy probes the chemical environment in a molecule at a specific atomic site. Now the concept is extended with a site selective trigger to follow chemical bond changes as they occur on the femtosecond time scale.
PSI researcher Patrick Hemberger honored in the Rising Stars special issue in Energy & Fuels
To celebrate contributions of highly influential early and mid-career researchers in energy research, the journal Energy & Fuels established an annual recognition of Energy and Fuels Rising Stars.
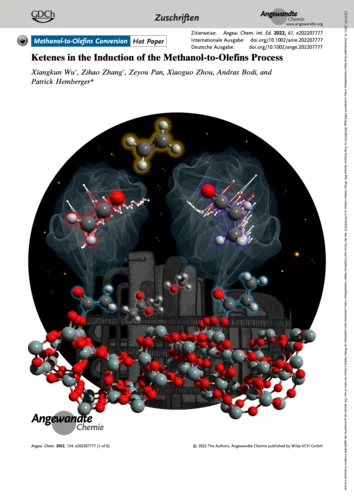
Finding Ketenes in the Methanol to Olefins Process
How are the first olefins formed in the early stages of the methanol-to-olefins process? Detection of two reactive ketene species solves this long-standing puzzle.
The chemical complex that regulates body zinc storage
Zinc deficiency compromises the immune system and is a global public health problem. Through experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS and BESSYII, researchers gained new insights into zinc storage, with implications for understanding COVID-19 severity.
Reaction insights help make sustainable liquid fuels
Methanol made from CO2 in the air can be transformed into carbon neutral fuels. New mechanistic understanding aids development of this sustainable alternative.
New SwissFEL soft X-ray endstation welcomes first users
Maloja is go. First user experiments mark a double first, not only for the Maloja endstation but also for the second beamline of SwissFEL, Athos.
Hercules School 2022
PSI hosted again the Hercules School in March 2022. We had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and scientists to demonstrate our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities, the Swiss Light Source (SLS), the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source (SINQ) and our free electron laser SwissFEL.
Une simulation pour faire avancer les travaux de déblaiement à Fukushima
Une nouvelle simulation des débris radioactifs les plus dangereux de la centrale nucléaire de Fukushima devrait faire avancer les travaux de déblaiement.
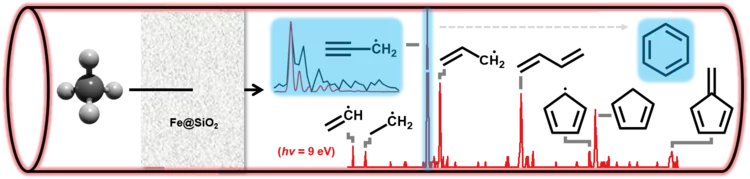
Watch them growing: New mechanistic insights into catalytic methane coupling
Methane valorization is a promising technology to utilize this platform compound to produce aromatics and hydrocarbons. Researchers from PSI and ETH Zürich unveiled this reaction mechanism and observed the molecular growth from the ground up. Besides stepwise CH3 addition, novel routes involving the dimerization of resonantly stabilized propargyl (C3H3) radicals to benzene (C6H6) were identified. These mechanistic insights will aid the development of valorisation strategies.
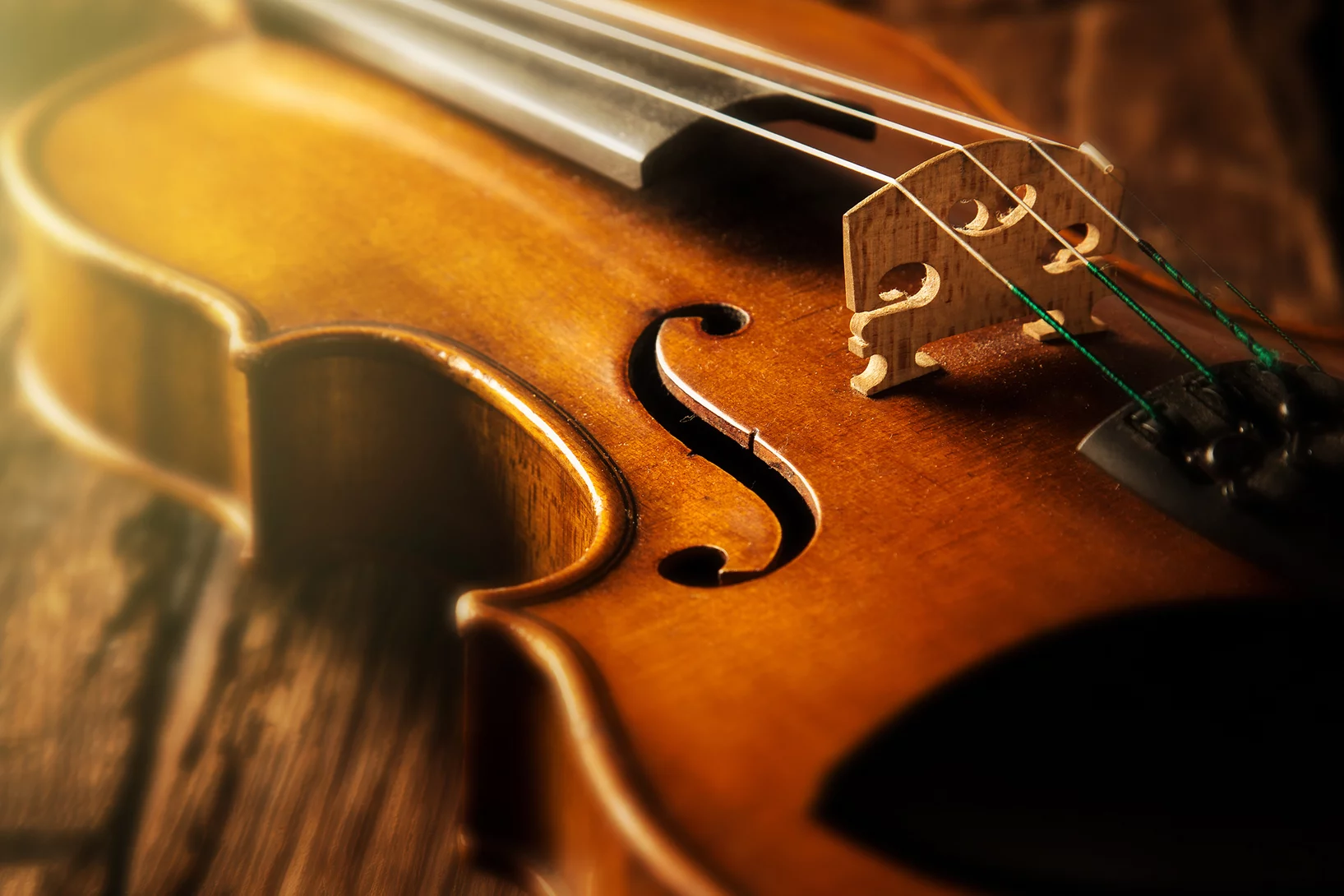
Le secret des Stradivarius dévoilé
Comme l’a découvert une équipe internationale de chercheurs, les anciens maîtres luthiers Stradivari et Guarneri utilisaient des adjuvants chimiques inattendus pour leurs violons.
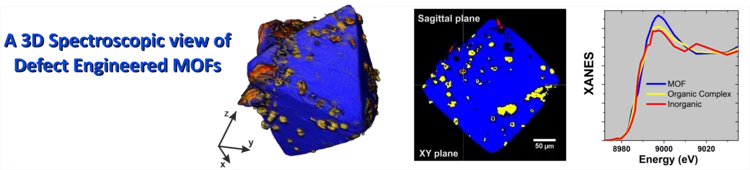
Full-field X-ray absorption tomography reveals the chemical structure of defects in metal-organic frameworks
Cryo-full-field XANES computed tomography was used to visualize the presence and distribution of a second coordination polymer of reduced copper coordination within defect-engineered HKUST-1 MOF crystals. Observations encourage a revisitation of the structure-property relationships of defect-engineered MOFs.
Comment les catalyseurs vieillissent
La structure du matériau utilisé dans les catalyseurs en industrie chimique se modifie au fil des ans. Des chercheurs du PSI ont étudié ce phénomène au moyen d’une nouvelle méthode.
Important elementary reactions of lignin catalytic pyrolysis revealed
To develop sustainable lignin valorization strategies, a solid understanding of the underlying reaction mechanism is critical. By detection of highly reactive and elusive intermediates, new light could be shed on one of the most basic elementary reactions in lignin catalytic fast pyrolysis.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
Insights into the world’s oldest pile carpet
High-resolution XRF imaging of the specific metal distribution within wool fibers at the PHOENIX beamline gives insights into traditional oriental dyeing procedures.