Show filters
Predicting component lifetimes in nuclear facilities
For 30 years, experiments have been providing unique insight into how metals and ceramics degrade under high-energy proton bombardment.
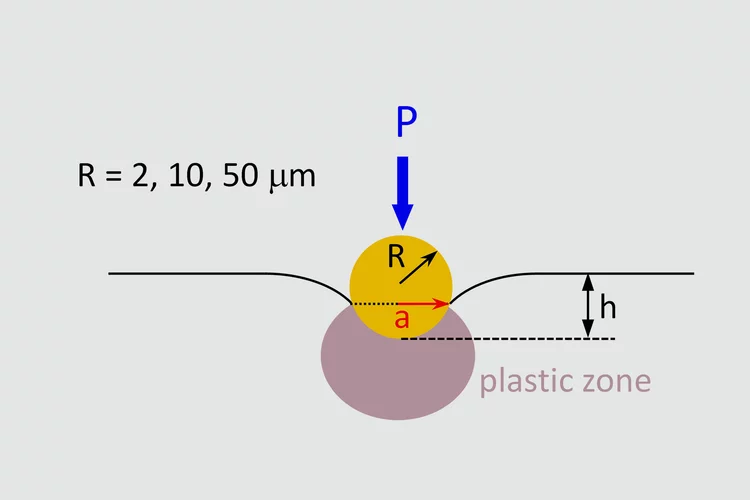
Investigations of the irradiation hardening on a ferritic model alloy from spherical nano-indentations
The objective of this project was to determine the contribution from a variety of obstacles to moving dislocations to the nano-indentation stress necessary to initiate plastic flow. The obstacles are characterized by different length scales. Among these characteristic lengths, there are those associated with the material microstructure such as grain size, dislocations density, irradiation-induced defects, and those related to the size of the plastic zone beneath the indenter, or equivalently to the size of the indent. Thus, we can classify the size effects into two categories: structural size effect and indentation size effect (ISE). The underlying idea is to quantify and separate these two effects on the unirradiated material first to be able to properly isolate the contribution of the irradiation defect on the measured hardness from the tests on irradiated materials.
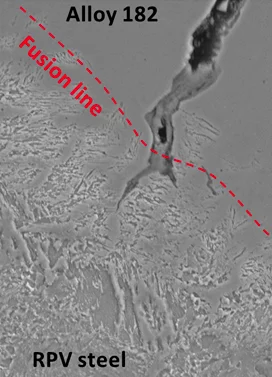
Assessment of stress corrosion cracking incidents in Alloy 182 – reactor pressure vessel dissimilar metal welds
Several stress corrosion cracking (SCC) incidents recently occurred in Alloy 182 - reactor pressure vessel (RPV) dissimilar metal welds in boiling water reactors (BWR). These SCC cracks tend to grow towards the RPV due to weld microstructure and residual stress profiles and might grow into the RPV. They thus represent a serious potential safety concern. PSI has evaluated under which conditions such cracks could grow into the RPV and also developed SCC crack growth disposition curves for the RPV steels that can be used for safety assessments of such cracks. With these curves that were recently accepted as a new Code Case N-896 in the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, sufficient safety margins could be demonstrated for such crack configurations with the current inspection intervals of the periodic in-service inspection.
Les gaines de crayons combustibles et leurs propriétés
Johannes Bertsch travaille au PSI dans la division de recherche Energie nucléaire et sûreté, où il étudie les gaines qui enrobent le combustible exploité dans les centrales nucléaires.
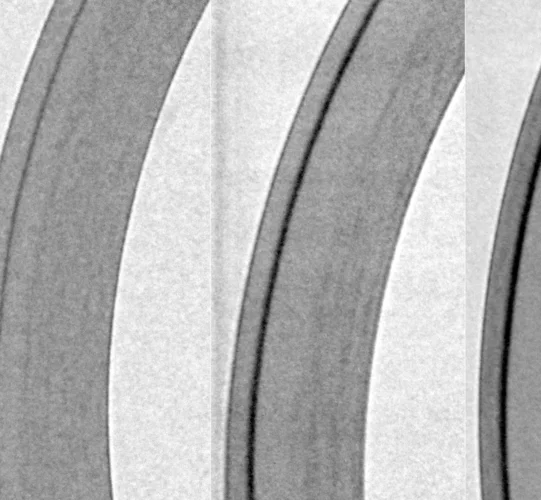
Neutron radiography of detrimental hydrogen in nuclear fuel claddings
Hydrogen is at the source of degradation mechanisms affecting mechanical properties of many structural metal materials. In nuclear power plants, zirconium alloy fuel cladding tubes take up a part of the hydrogen from coolant water due to oxidation. Because of the high mobility of hydrogen interstitial atoms down temperature and concentration gradients and up stress gradients, hydrogen distribution in fuel claddings can often be non-uniform, arising the risk for the integrity of spent fuel rods under mechanical load. At the Laboratory of Nuclear Materials (LNM) in collaboration with the Laboratory of Neutron Scattering and Imaging (LNS), hydrogen redistribution in zirconium alloys was quantified by neutron radiography using the state-of-the-art detector of PSI Neutron Microscope, and the concentration was computed based on thermodynamics, to predict hydrogen diffusion and precipitation for used nuclear fuel.
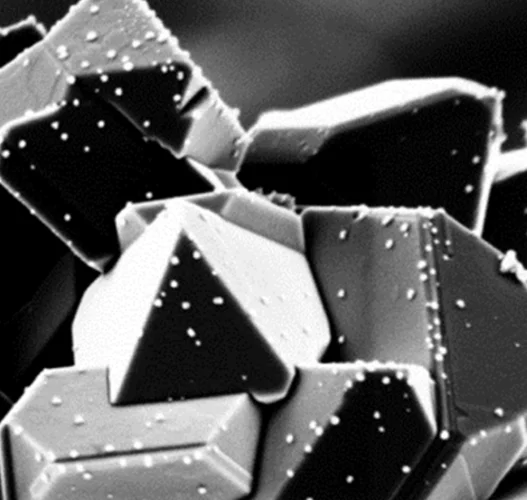
Pt nanoparticles: The key to improved stress corrosion cracking mitigation in boiling water reactors
The formation and growth of cracks by stress corrosion cracking (SCC)in reactor internals and recirculation pipes due to the highly oxidising environment is a serious issue in boiling water reactors. At first, SCC mitigation was attempted by injecting H2 into the feed water, where the injected H2 recombines with the H2O2 and O2 to water and reduces the electrochemical corrosion potential, and consequently the SCC susceptibility. Several disadvantages of the injection of high amounts of H2, have led to the development of noble metal additions to the reactor feed water. With injection of a much smaller amount of H2, the noble metal particles of a few nanometres in size, formed in-situ, work as catalysts for the efficient reduction of the oxidizing species formed by radiolysis, and thus lower the ECP and SCC susceptibility.
L’hydrogène: un cheval de Troie dans la gaine du crayon combustible
Dans un réacteur nucléaire, l’eau se sépare en oxygène et en hydrogène au contact de la gaine contenant les pastilles de combustible, alors à haute température. Cet hydrogène peut pénétrer dans la gaine qui enrobe le combustible proprement dit, et la fragiliser mécaniquement. A l’aide de neutrons et de rayonnement synchrotron, des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) étudient le mécanisme de pénétration de l’hydrogène dans la gaine et l’effet qu’il peut y déployer.