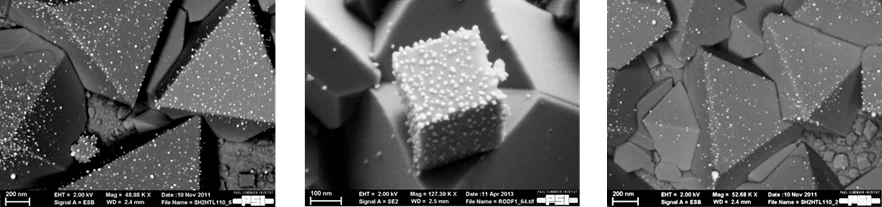
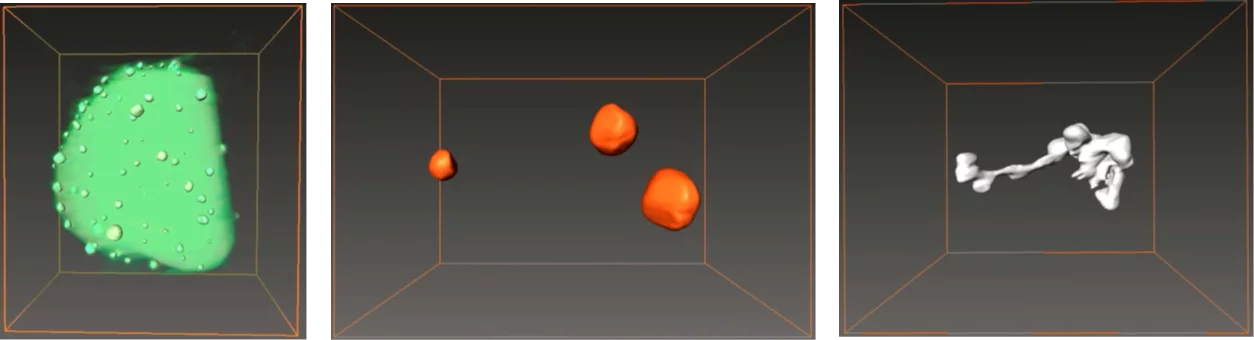
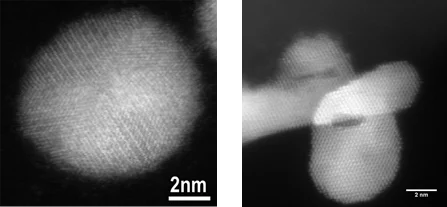
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) in reactor internals and recirculation pipes is one of the major degradation issues in boiling water reactors (BWRs). Efforts to provide mitigation of this cracking have led to the development of noble metal additions (Pt) to the reactor feed water. Under hydrogen water chemistry conditions the Pt nanoparticles, formed in-situ, work as catalysts for the efficient reduction of the oxidizing species formed by radiolysis, and thus lowering the electrochemical corrosion potential, without the negative side-effects of classical hydrogen water chemistry. Noble metal chemical addition is in use in a large number of BWRs worldwide.
To verify and optimise this technology, a research project has been started at PSI/LNM to investigate the deposition and distribution behaviour of Pt in BWRs. The project was financially supported by the Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (ENSI) and by in-kind contributions from nuclear power plants Leibstadt (KKL) and Mühleberg (KKM). The NORA project (phase I: 2010 – 2013, phase II: 2013 – 2016, phase III: 2016 – 2019) provided extremely valuable information with respect to efficiency improvement and validation of this SCC mitigation technology, as well as to possible negative side-effects. The project has been successfully finished, but some small activities in this field are still ongoing.
Some selected publications are available here:
https://www.dora.lib4ri.ch/psi/islandora/object/psi%3A35441
https://www.dora.lib4ri.ch/psi/islandora/object/psi%3A27068