News
ETH CoLab Award for Mohammadhossein Montazerian
Mohammadhossein Montazerian was part of the winning team to secure an ETH CoLab Award. It is an award to help entrepreneurial research to make a first step towards business.
E-MRS 2025 Spring Meeting Young Researcher Award for Mohammadhossein Montazerian
During its recent spring meeting the European Materials Research Society has awarded the E-MRS Young Researcher Award to Mohammadhossein Montazerian from the LMX laboratory in recognition of his "Outstanding contribution to the Symposium L: Solid state batteries - materials, processing and advanced characterization".
Julius Springer Price 2024
Prof. Thomas Lippert, Editor in Chief at Applied Physics A, awards Prof. Boris Chichkov the 2024 Julius Springer Prize for Applied Physics.
Scientific Highlights
Two-dimensional gradients in magnetic properties created with direct-write laser annealing
Across the fields of magnetism, microelectronics, optics, and others, engineered local variations in material properties can yield groundbreaking functionalities that play a crucial role in enabling future technologies. One-dimensional lateral gradients in material properties give rise to a plethora of new effects in thin-film magnetic systems. However, extending such gradient-induced behaviors to two dimensions has been challenging to realize experimentally. Here, we demonstrate the creation of two-dimensional complex patterns with continuous variations in magnetic anisotropy, interlayer exchange coupling, and ferrimagnetic compensation at the mesoscopic scale in numerous application-relevant magnetic materials. We exploit our engineered gradients in material properties to demonstrate novel magnetic functionalities, including the creation of a spin wave band pass filter and an architecture for passively resetting the position of a magnetic domain wall. Our results highlight the exciting new physics and device applications enabled by two-dimensional gradients in thin film properties.
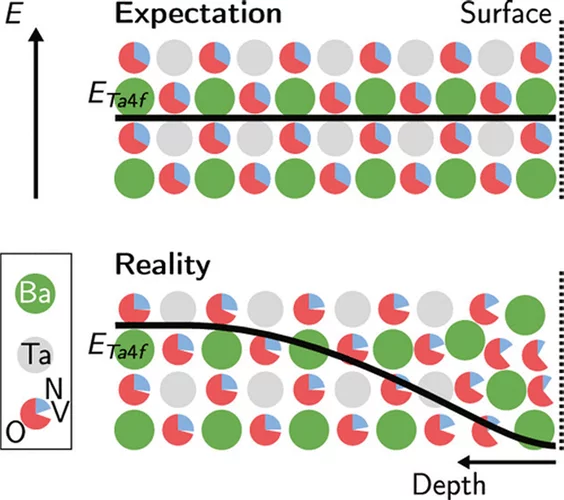
Anionic Disorder and Its Impact on the Surface Electronic Structure of Oxynitride Photoactive Semiconductors
The conversion of solar energy into chemical energy, stored in the form of hydrogen, bears enormous potential as a sustainable fuel for powering emerging technologies. Photoactive oxynitrides are promising materials for splitting water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. However, one of the issues limiting widespread commercial use of oxynitrides is degradation during operation. While recent studies have shown the loss of nitrogen, its relation to reduced efficiency has not been directly and systematically addressed with experiments. In this study, we demonstrate the impact of the anionic stoichiometry of BaTaOxNy on its electronic structure and functional properties. Through experimental ion scattering, electron microscopy, and photoelectron spectroscopy investigations, we determine the anionic composition ranging from the bulk toward the surface of BaTaOxNy thin films. This further serves as input for band structure computations modeling the substitutional disorder of the anion sites. Combining our experimental and computational approaches, we reveal the depth-dependent elemental composition of oxynitride films, resulting in downward band bending and the loss of semiconducting character toward the surface. Extending beyond idealized systems, we demonstrate the relation between the electronic properties of real oxynitride photoanodes and their performance, providing guidelines for engineering highly efficient photoelectrodes and photocatalysts for clean hydrogen production.
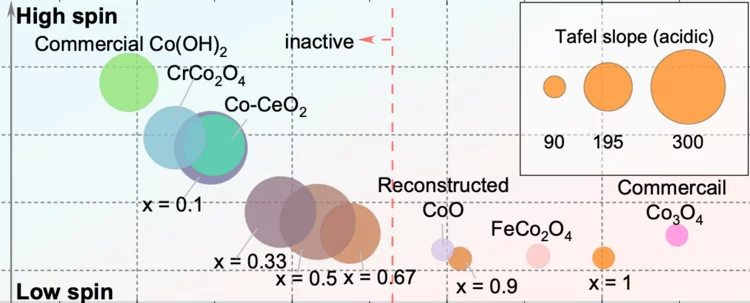
Surface oxidation/spin state determines oxygen evolution reaction activity of cobalt-based catalysts in acidic environment
Co-based catalysts are promising candidates to replace Ir/Ru-based oxides for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysis in an acidic environment. However, both the reaction mechanism and the active species under acidic conditions remain unclear. In this study, by combining surface-sensitive soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy characterization with electrochemical analysis, we discover that the acidic OER activity of Co-based catalysts are determined by their surface oxidation/spin state.