Show filters
Pressure and temperature dependence of the laser-induced plasma plume dynamics
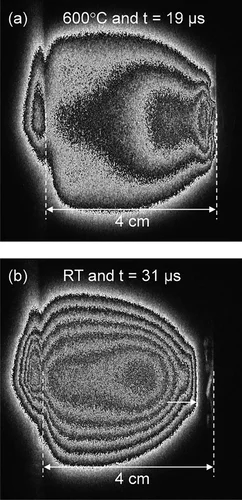
The influence of different background gases and substrate heating on the plasma plume dynamics from silver ablation is investigated by species selected time and space resolved imaging. The results provide a time-resolved understanding on how those process parameters affect the expansion: from a free expansion in vacuum with velocities exceeding 20'000 m/s to a very slow expansion in Ar at 1 × 10−1 mbar with arrival velocities of 280 m/s.
Structure and Conductivity of Epitaxial Thin Films of In-Doped BaZrO3‑Based Proton Conductors
Epitaxial thin films of the proton-conducting perovskite BaZr0.53In0.47O3−δH0.47−2δ, grown by pulsed laser deposition, were investigated in their hydrated and dehydrated conditions through a multitechnique approach with the aim to study the structure and proton concentration depth profile and their relationship to proton conductivity.
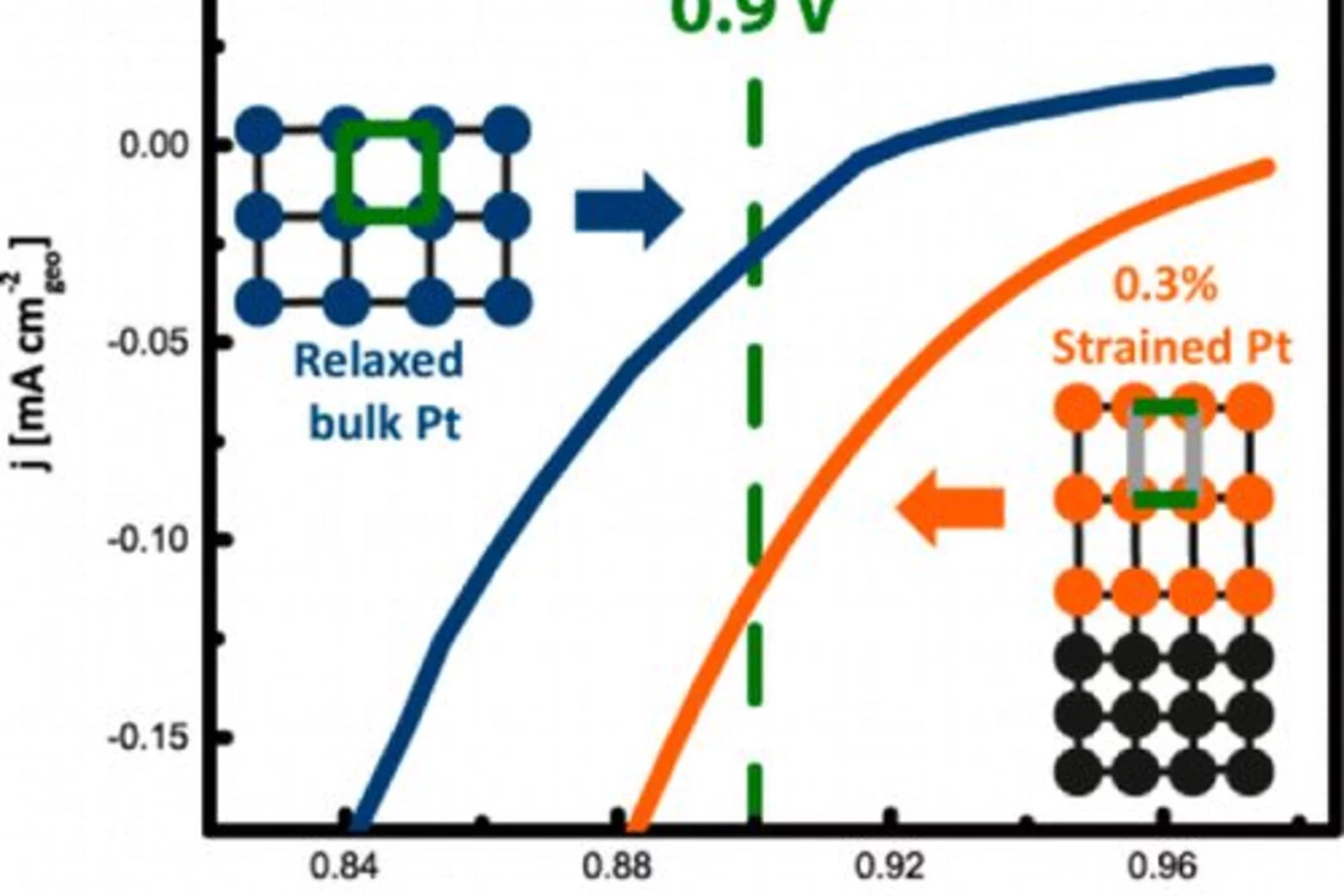
Investigating the Role of Strain toward the Oxygen Reduction Activity on Model Thin Film Pt Catalysts
Environmentally friendly energy conversion devices such as fuel cells are becoming more and more attractive. However, major impediments to large-scale application still arise on the material side, related to the cost and poor performance of the cathode catalyst. State-of-the-art electrocatalysts are all Pt-based materials, suffering from poor electrochemical oxygen reduction kinetics.
Coexisting multiple order parameters in single-layer LuMnO3 films
Magnetoelectric multiferroics hold great promise for electrical control of magnetism or magnetic control of ferroelectricity. However, single phase ferroelectric materials with a sizeable ferromagnetic magnetization are rare. Here, we demonstrate that a single-phase orthorhombic LuMnO3 thin film features coexisting magnetic and ferroelectric orders.
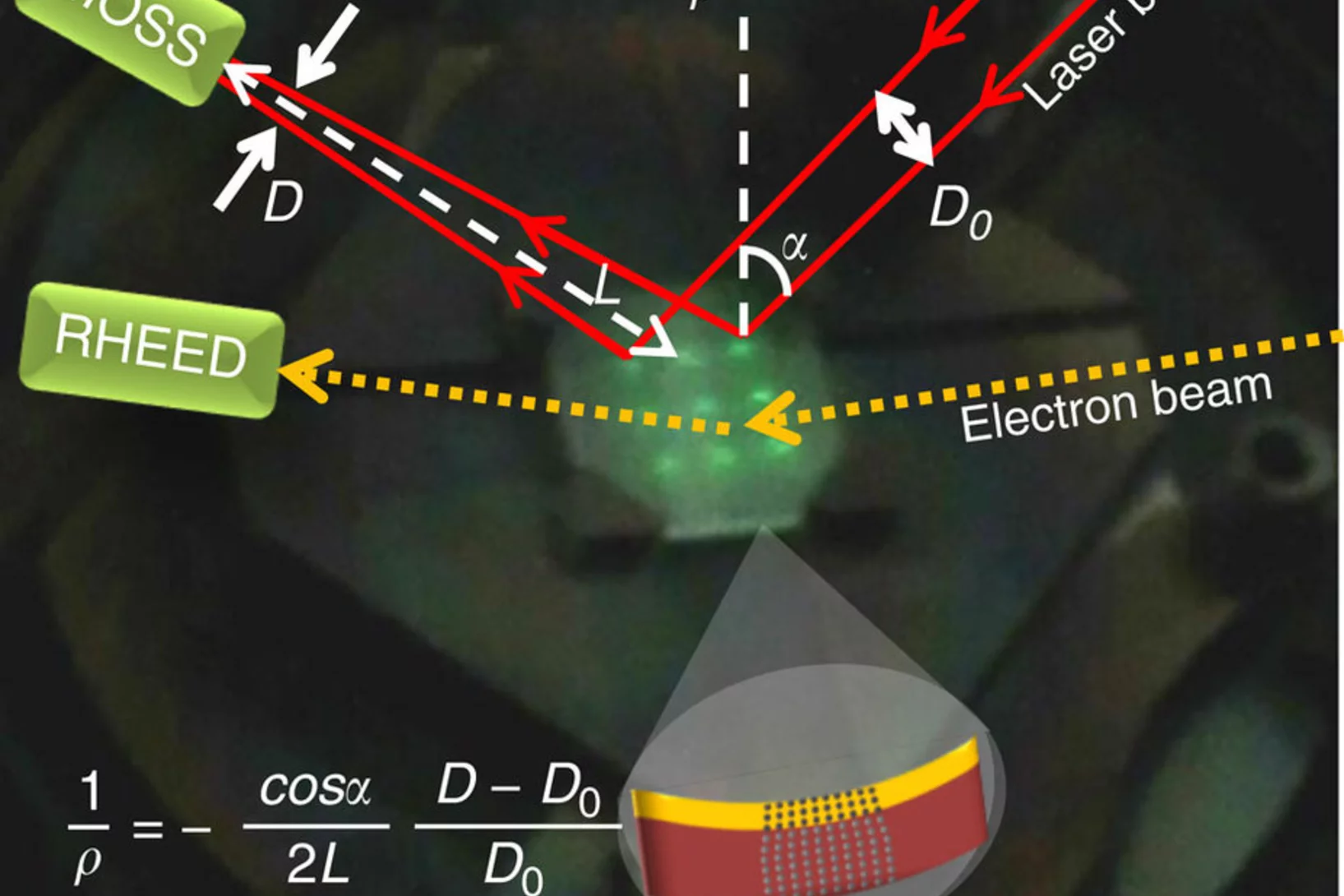
In situ stress observation in oxide films and how tensile stress influences oxygen ion conduction
Many properties of materials can be changed by varying the interatomic distances in the crystal lattice by applying stress. Ideal model systems for investigations are heteroepitaxial thin films where lattice distortions can be induced by the crystallographic mismatch with the substrate. Here we describe an in situ simultaneous diagnostic of growth mode and stress during pulsed laser deposition of oxide thin films.

![Sketch of a ferroic triangle showing the relation and techniques with which the ferroic orders, FM, AFM, and FE, and their mutual coupling have been established. The experimental techniques written in black letters (polarized neutron reflectometry, PNR; resonant soft x-ray diffraction, SXRD; x-ray diffraction, XRD) to identify ferroic properties have been reported elsewhere [22, 24]. Magnetization, susceptibility, μSR, neutron diffraction, and electrical polarization are reported.](/sites/default/files/styles/teaser_grid_3_2_crop_xl/public/import/num/SHL20160822CoexistingEN/CWS_PRB_94_054423_2016.jpg.webp?itok=TybDdEab)