Project descpription:
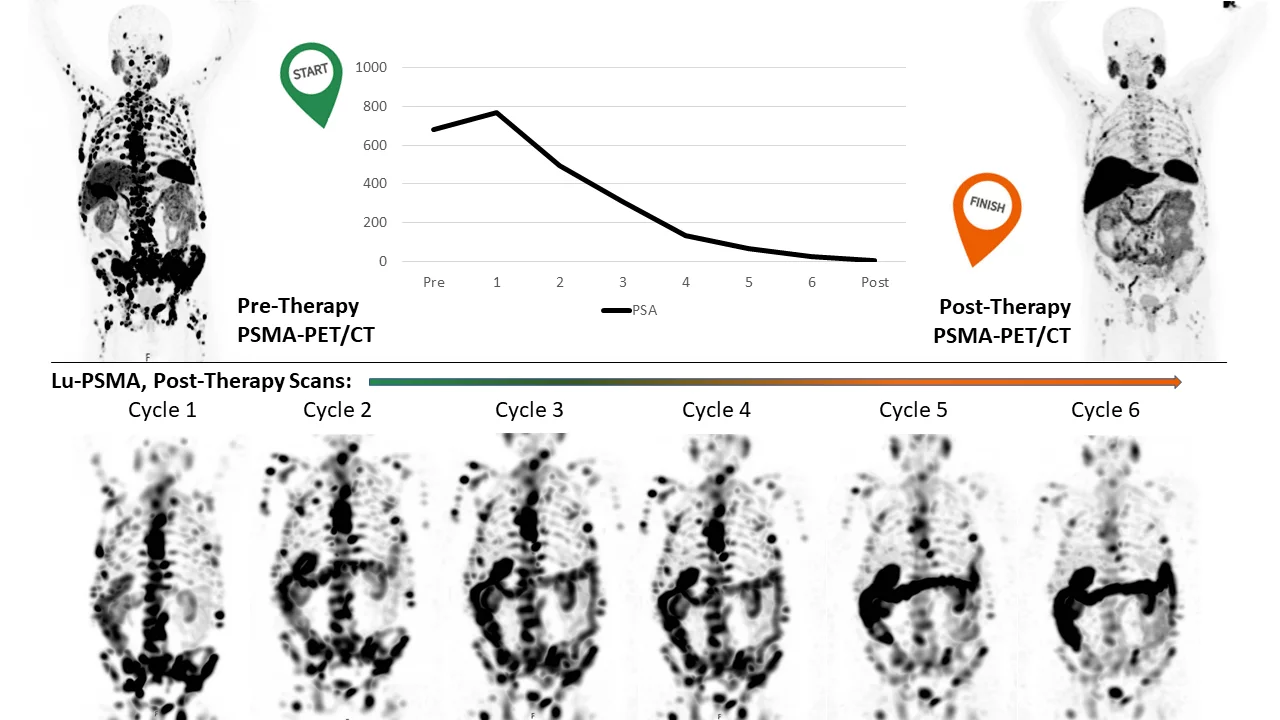
ProSPECT-Q aims to establish a more objective approach to tracking radioligand therapy (RLT) in prostate cancer patients treated with Lutetium-177 (Lu-PSMA), an innovative therapy that targets prostate cancer cells. Lu-PSMA has already shown strong results in extending the survival of patients with advanced prostate cancer, typically as a last-resort option after chemotherapy. However, as the tendency is to introduce Lu-PSMA earlier in the treatment course, a more precise method to assess which patients will benefit from the therapy and to monitor the therapy’s effects over time are required. Currently, assessments rely mainly on visual evaluations and laboratory results, such as Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) levels, which may miss subtle changes in tumoural activity. This project proposes the use of quantitative SPECT/CT imaging, which offers more accurate measurement of tumour volume and response than traditional visual assessments. However, interpreting this data in a clinical context is complex, so ProSPECT-Q seeks to develop new tools for analysing imaging data in combination with clinical information, using artificial intelligence. The project will collect and analyse data from past patients, measuring tumour characteristics, therapy outcomes and side effects. Advanced techniques like machine learning will be used to identify patterns and predict outcomes such as therapy success, defined as therapy completion or serious adverse effects, like bone marrow damage or decrees of renal function. By creating models that predict these risks early, doctors could better balance the risks and benefices of the treatment, helping patients avoid unnecessary side effects and improving their long-term outcomes.
About Sabin-George Pop:
Sabin-George Pop is currently a resident in nuclear medicine at the Kantonsspital Baden (KSB). During his medical studies, he developed a keen interest in the application of machine learning solutions to clinical challenges, and was further immersed in the subject through the KTH Institute's HelloAI programme. All this deepened his passion for AI applications in medical imaging and materialised in his thesis on "Automatic Assessment of Bone Age using Artificial Intelligence" and further in the current project ProSPECT-Q, which aims to combine nuclear medicine expertise with the power of machine learning to improve the risk-benefit assessment and enable more personalised treatment for patients suffering from prostate cancer.
Involved institutions: