Energy and Environment Research Division
Research at PSI comprises all aspects of human energy use, with the ultimate goal of promoting development towards a sustainable energy supply system. Technologies are being advanced for the utilization of renewable energy sources, low-loss energy storage, efficient conversion, and low emission energy use. Experimental and model-based assessment of these emissions forms the basis of a comprehensive assessment of economic, environmental and social consequences, for both present and future energy supply systems.
Division Head: Prof. Dr. Thomas Justus Schmidt
Energy Briefing Event 2023
The Energy and Environment Division of the Paul Scherrer Institut PSI successfully hosted their second Energy Briefing Event at the Zentrum Paul Klee in Bern. The event focused on the potentials and challenges associated with the production, regulation, and utilization of synthetic fuels. Representatives from WWF, Avenergy, PSI, and BAZL shared their expertise and insights on this topic.
A heartfelt appreciation goes out to Ulrich Koss (Metafuels), Theo Rindlisbacher (BAZL), Christian Bach (Empa), Thomas J. Schmidt (PSI), Thomas Häusler (WWF Switzerland), Daniel Hofer (Avenergy Suisse), and our moderator Stephan Lendi for their invaluable contributions and insightful perspectives.
Energy Briefing Event 2022
On June 28th, 2022, the Energy Divisions (ENE and NES) at PSI hosted their first Energy Briefing Event at the Kursaal in Bern. Knowledgeable voices from industry, research and government shared insights in a dialogue on the feasibility of the Net Zero goal and what next steps are required to achieve this collectively.
A big thank you to Daniela Decurtins (GazEnergy), Particia Sandmeier (Hitachi Energy), Martin Naef (ABB), Pascal Previdoli (BFE), Thomas Schmidt (PSI), Christian Verhoeven (GE), Peter Richner (Empa), Andreas Pautz (PSI) and our Moderator Stephan Lendi for their valuable contributions and insights!
Highlights & News
Aerosol distribution in rooms and the importance of proper ventilation
Urs Baltensperger explains the background why it is absolutely necessary to wear masks in order to reduce the risk of beeing infected with Covid-19.
In the following you find the presentation and summary
Einfache Experimente zeigen: so gut schützen uns Masken und andere Materialien
Spätestens seit Corona ist der Maskengebrauch auch in der Schweiz im Alltag präsent. Doch wie gut können wir uns und andere mit verschieden Materialien vor kleineren und grösseren Partikeln schützen? Das alljährlich durchgeführte PSI Feriencamp bietet Kindern einen spannenden Einblick in die faszinierende Welt der Forschung. In diesem Jahr gingen Kinder an einer Projektstation genau dieser Frage nach. Dabei untersuchten sie, wie gut verschiedene Materialien die im Labor generierten Partikel zurückhalten. Es wurden Textilmasken (im Handel erhältlich, wiederverwendbar, nicht FFP2-zertifiziert), Chirurgenmasken (Einwegmasken, FFP2-zertifiziert), Teefilter, Kaffeefilter, Papiertaschentuch und WC-Papier getestet, und es wurde klar, Maske ist nicht gleich Maske.
Online ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry for the molecular analysis of the atmosphere
Atmospheric aerosols are considered the single largest uncertainty in assessing the human contribution to global warming and amongst the top five health risks worldwide. Our ability to investigate aerosol sources, their formation processes in the gas-phase, and their societal impacts is largely governed by our capability to measure their molecular constituents in real-time. Researchers at PSI have combined for the first time ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry with high time resolution and sensitivity for the molecular analysis of aerosols.
Newly discovered rapid particle growth rates may be the answer to the mystery of aerosol formation in urban smog
Aerosols, suspended particles or droplets, play a key role in Earth’s atmosphere’s energy balance. They can also result in smog formation in cities, which leads to low visibility and serious health risks for the population. A recent study published in Nature outlines a newly discovered mechanism that may play a key role in the continued survival of particles in wintertime smog.
Around Antarctica in 90 days to study the pristine atmosphere
PSI researchers have designed and equipped a laboratory container for operation on research ships to undertake comprehensive studies of the chemistry and microphysics of the atmosphere. The floating laboratory was first deployed during the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition (ACE) with the aim of characterizing aerosol processes that are relevant for climate change in an atmosphere, which is hardly influenced by human emissions of air pollutants other than greenhouse gases.
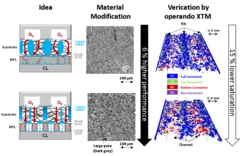
Fast operando X-ray tomographic microscopy improves polymer electrolyte fuel cells
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC) are a key technology for the decarbonization of automotive mobility. In collaboration with Toyota, it is shown by dynamic, operando X-ray tomographic microscopy, how the liquid water saturation in modified gas diffusion layer materials is reduced.
The imaging data supports the understanding of the underlying mechanisms and explains improved cell performance. Novel instrumentation at the TOMCAT beamline further improves imaging time resolution and allows for scan times as short as 0.1 s.
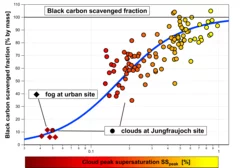
Cloud droplet formation on soot particles
PSI researchers went to the Jungfraujoch research station and applied in situ measurement techniques in real clouds to investigate the ability of soot particles to form cloud droplets. This is a key process determining the atmospheric life-cycle of soot particles, which are primarily emitted by combustion engines and which have a warming effect on climate by absorbing solar radiation.
A third dimension for the nanoscale
Researchers of the Laboratory for Catalysis and Sustainable Chemistry (LSK) from PSI have designed uneven probe supports, which reveal the hidden site of nanocrystals.
Their simple approach allows transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) complete access to the atomic structure of nanomaterials without the need for cumbersome experimental effort.
Giulia Stefenelli wins Swiss Aerosol Award 2019
Award conferred by SwissLung.org during the award ceremony in Berne, Switzerland