News & Events
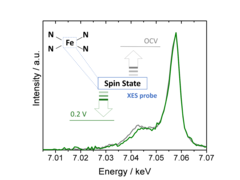
Using X-ray emission spectroscopy to study the electronic properties of single atom catalysts
Single atom catalysts hold great promise as O2- or CO2-reduction electrocatalysts, but a deeper understanding of their active sites’ structure and electronic properties is needed in order to render them sufficiently active and stable. To this end, we have used X-ray emission spectroscopy to determine these catalysts’ electronic configuration, and performed in situ measurements that unveil the effect of potential on this key feature.
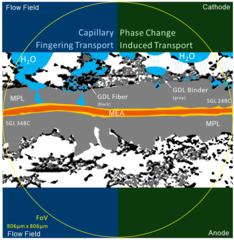
Temperature Dependent Water Transport Mechanism
Subsecond and submicron operando X-ray tomographic microscopy (XTM) was applied to reveal the water dynamics inside the gas diffusion layer (GDL) of polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC). Utilizing the instrumental advancements in operando XTM of PEFCs the contribution of capillary-fingering and phase-change-induced flow on water transport in GDLs was quantified, for the first time during fuel cell startup at different operation temperatures.
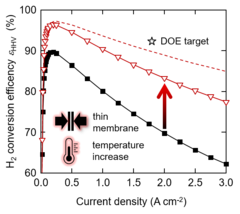
Efficient Water Electrolysis at Elevated Temperature using Commercial Cell Components
Decarbonization of the energy system across different sectors using power-to-X concepts relies heavily on the availability of low-cost hydrogen produced from renewable power by water electrolysis. Polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE) is a promising technology for hydrogen (and oxygen) production for distributed as a well as centralized operation. The total cost of hydrogen is dominated by the electricity cost. Therefore, increase of conversion efficiency is pivotal in improving the commercial viability of electrolytically produced hydrogen. In this study, we investigate the prospects of improving conversion efficiency by reducing the membrane thickness from 200 to 50 micron and increasing the cell temperature from 60 to 120°C.
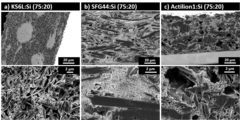
Graphite Anodes with Si as Capacity-Enhancing Electrode Additive
Silicon is a long-standing candidate for replacing graphite as the active material in negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries, due to its significantly higher specific capacity. However, Si suffers from rapid capacity loss, as a result of the large volume expansion and contraction during lithation and de-lithiation. As an alternative to pure Si electrodes, Si could be used as a capacity-enhancing additive to graphite electrodes.
LEC Contribution to the SCCER Mobility Project
Two groups from the Electrochemistry Laboratory, together with a team from ZHAW and EPFL have developed a novel evaporative cooling concept for polymer electrolyte fuel cells from the material to the cell level.
The 5 min movie explains and summarizes the development.
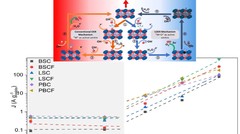
Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity and Underlying Mechanism of Perovskite Electrocatalysts at Different pH
PSI researchers have studied the how the electrolyte pH values influence the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity and stability of different promising perovskite oxide catalysts for application as anodic electrodes in alkaline water electrolyzers. The OER activity and stability decreased decreasing the electrolyte pH values. By combining electrochemical studies and operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it has been suggested that different reaction mechanisms dominate in alkaline and near-neutral electrolyte pH region.
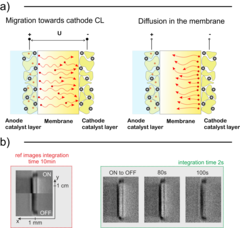
Analysis of cation contamination of polymer electrolyte water electrolysers (PEWEs)
With the help of in situ PEWE regeneration methods, we can potentially enable the treatment of degraded cells without the necessity of stack disassembly, saving operation costs of the plant. In this context, we observed the movement of cations in a PEWE cell using neutron imaging and compared it with a model. This model is expected to be useful for the early detection of cation contamination problems in PEWEs, and the monitoring of in situ regeneration.
Post mortem/operando XPEEM: for studying the surface of single particle in Li-ion battery electrodes
X-ray photoemission electron microscopy (XPEEM) with its excellent spatial resolution is a well-suited technique to elucidate the complex electrode-electrolyte interface reactions in Li-ion batteries. It provides element-specific contrast images and enables the acquisition of local X-ray absorption spectra on single particles. Here we demonstrate the strength of post mortem measurements and we show the first electrochemical cell dedicated for operando experiments in all-solid-state batteries.
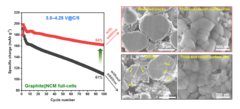
Improved Interfacial Stability of Ni-rich Oxide Full-Cells
PSI researchers have identified a novel electrolyte additive, allowing extended voltage range of Ni-rich oxide full-cells, while keeping excellent performance. The instability of cathode–electrolyte interface causes the structural degradation of cathode active material and the electrolyte consumption, resulting in a rapid capacity fading and shortening battery life-time. The PSI-identified additive help to alleviate these problems and extend battery life-time.