The Neutron Optics (NOP) group’s activities include a wide range of numerical work, in the form of computer simulations.
A big part of NOP's work includes the use of two Monte-Carlo codes (McStas and MCNP) to perform calculations on a variety of different topics. The ray-tracing code McStas is used for: i) design and optimization of neutron lenses for various instruments and experimental set-ups. ii) Development of components (‘plugins’) for the McStas software itself, such as components for neutron lenses’ simulations, gravity component for neutron guides, etc. iii) Performing virtual experiments to accommodate the designing and operational needs of existing and upcoming experimental set-ups at PSI.
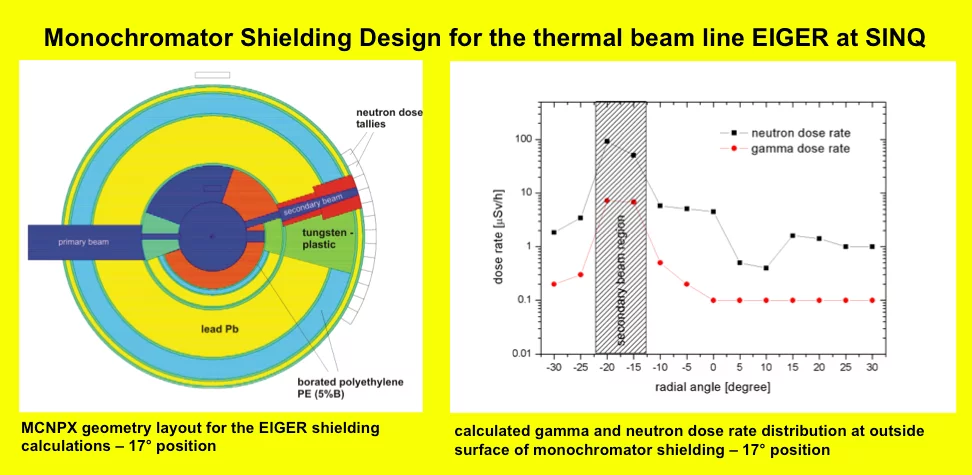
The neutron transport code MCNPX has been extensively used for shielding calculations related to the ESS project, and PSI beamlines and instruments. MCNP has also been used to simulate the behavior of certain materials (sapphire, silicon) as neutron filters. Furthermore, a coupled version of the two software (on whose development NOP has contributed extensively), has been used to perform simulations on the effectiveness of sapphire crystals as fast neutron filters.
An effort to couple SINQ's instrument control system with simulation environments has lead to the development of the Virtual McStas DMC Diffractometer