Show filters
Vers de nouveaux transistors de puissance
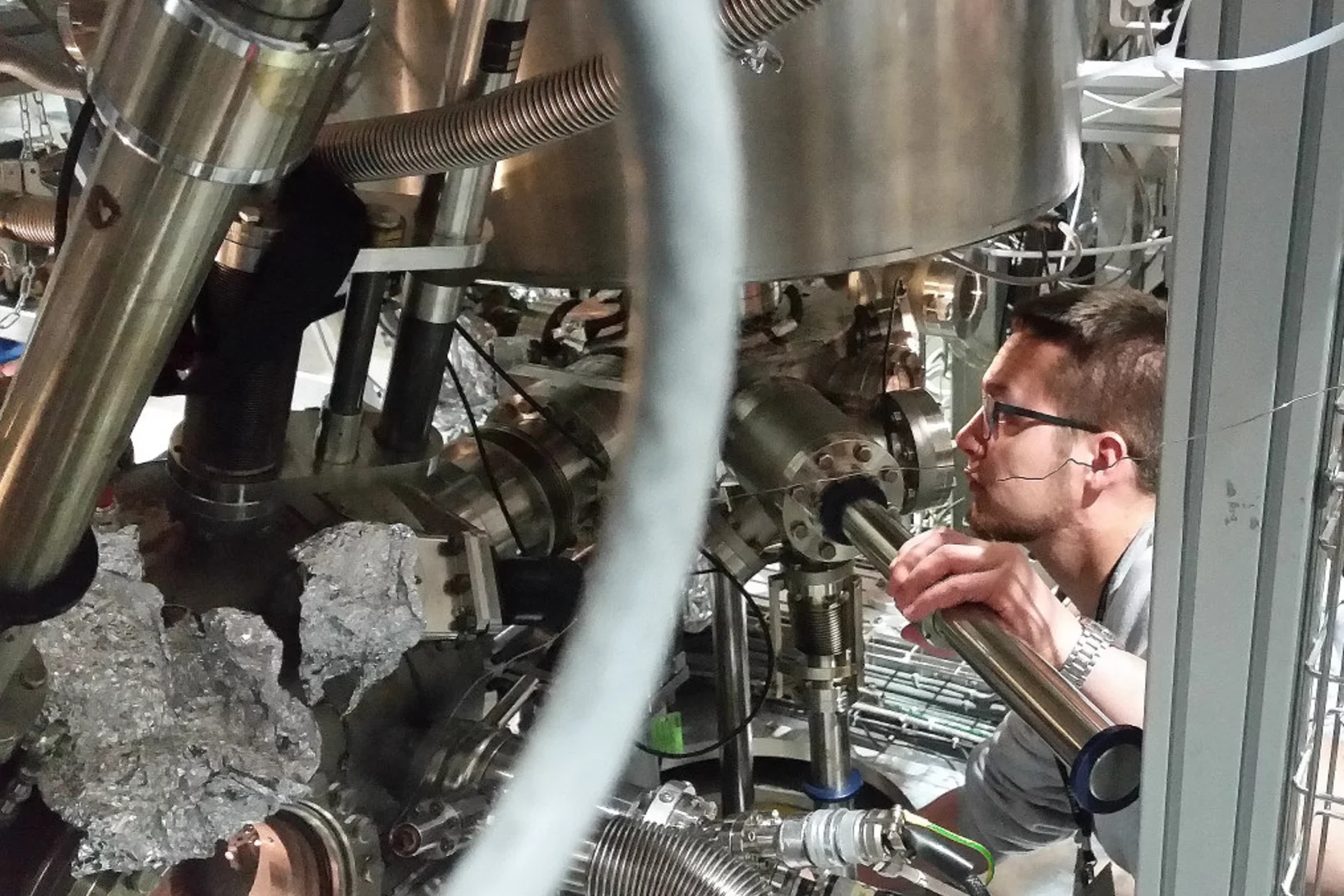
L'industrie de l'électronique attend d'un nouveau type de transistor de puissance en nitrure de gallium qu'il offre des avantages considérables par rapport aux transistors à haute fréquence qui sont utilisés aujourd'hui. Mais de nombreuses propriétés fondamentales du matériau ne sont pas encore connues. Pour la première fois, des chercheurs du PSI ont visionné un flux d'électrons dans le transistor en question. Pour ce faire, ils ont utilisé une des meilleures sources de rayons X mous au monde, qui se trouve à la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS du PSI.
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
HERCULES at the Swiss Light Source
In the week of March 18-23 PSI welcomes 20 PhD students and postdocs taking part in the HERCULES 2018 school on Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation. They will attend lectures and perform two days of practical courses at several beam lines of the Swiss Light Source.
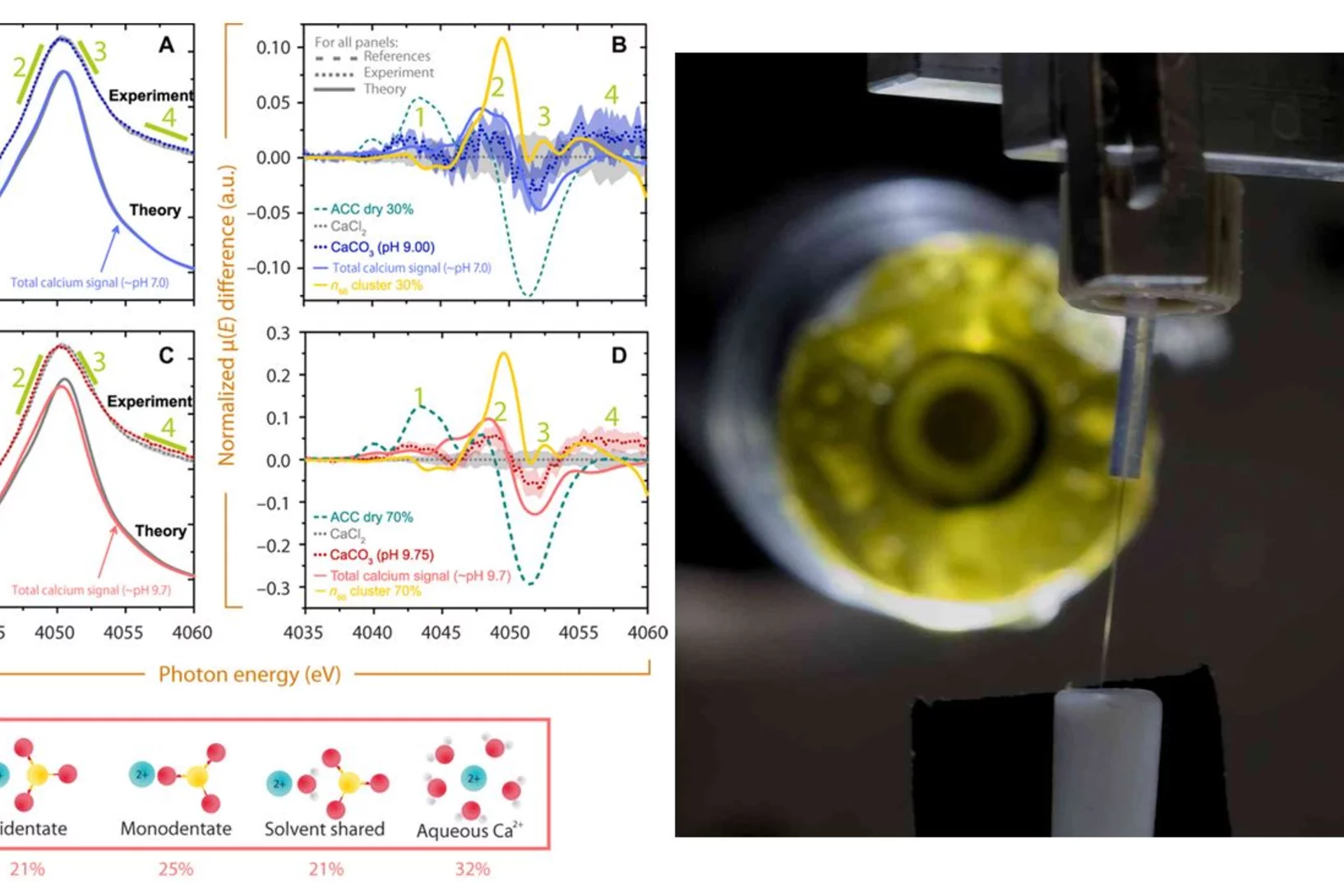
Are supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions classical or non-classical ?
Classical theory predicts that supersaturated carbonate solutions consist mostly of ions and ion pairs, with a small number of larger clusters present in the solution. The population of the different sized clusters in a solution is solely defined by the cluster’s size dependent Free Energy. If clusters are large enough they serve as nucleation germs for a new solid phase. The nucleation occurs once the surface free energy barrier posed by the new solid-liquid interface is overcome by the free energy win from bulk phase growth.
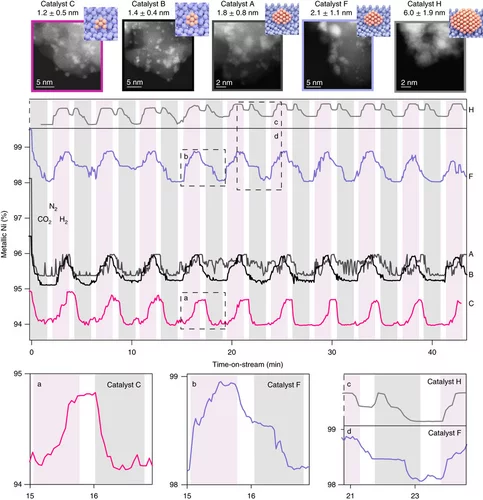
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
La première expérience conduite au SwissFEL a été un succès
Les méticuleuses années de planification et de construction ont porté leurs fruits: la première expérience conduite à la nouvelle grande installation de recherche de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, le laser à rayons X à électrons libres SwissFEL, a été un succès. Ce faisant, deux objectifs ont été atteints: d’un côté l’obtention d’un nouveau résultat scientifique, de l’autre une optimisation de l’interaction entre les nombreux composants de cette installation extrêmement complexe.
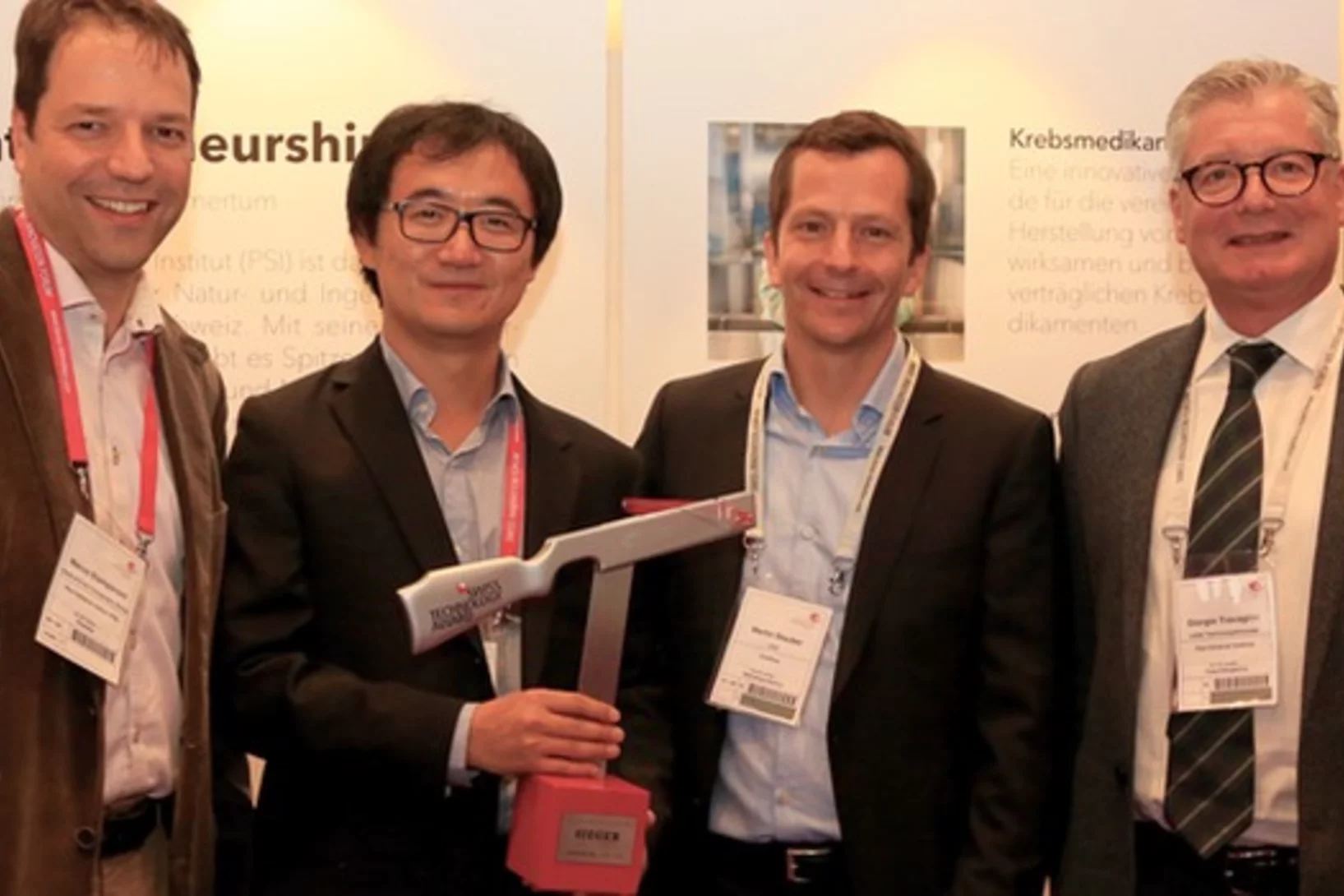
La spin-off du PSI GratXray remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017
Une spin-off du PSI remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017: la jeune entreprise GratXray développe une nouvelle méthode de diagnostic précoce du cancer du sein.
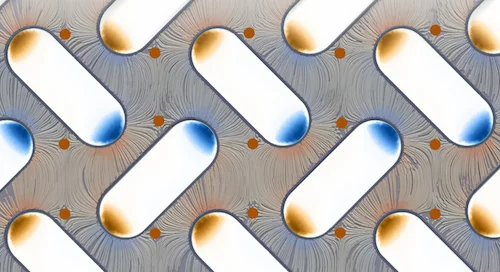
Magnetic structures take a new turn
The unexpected finding that in an ‘artificial spin ice’ magnetostatic energy can be transformed into directed rotation of magnetization provides fresh insights into such nano-patterned magnetic structures — and might enable novel applications in nanoscale devices.
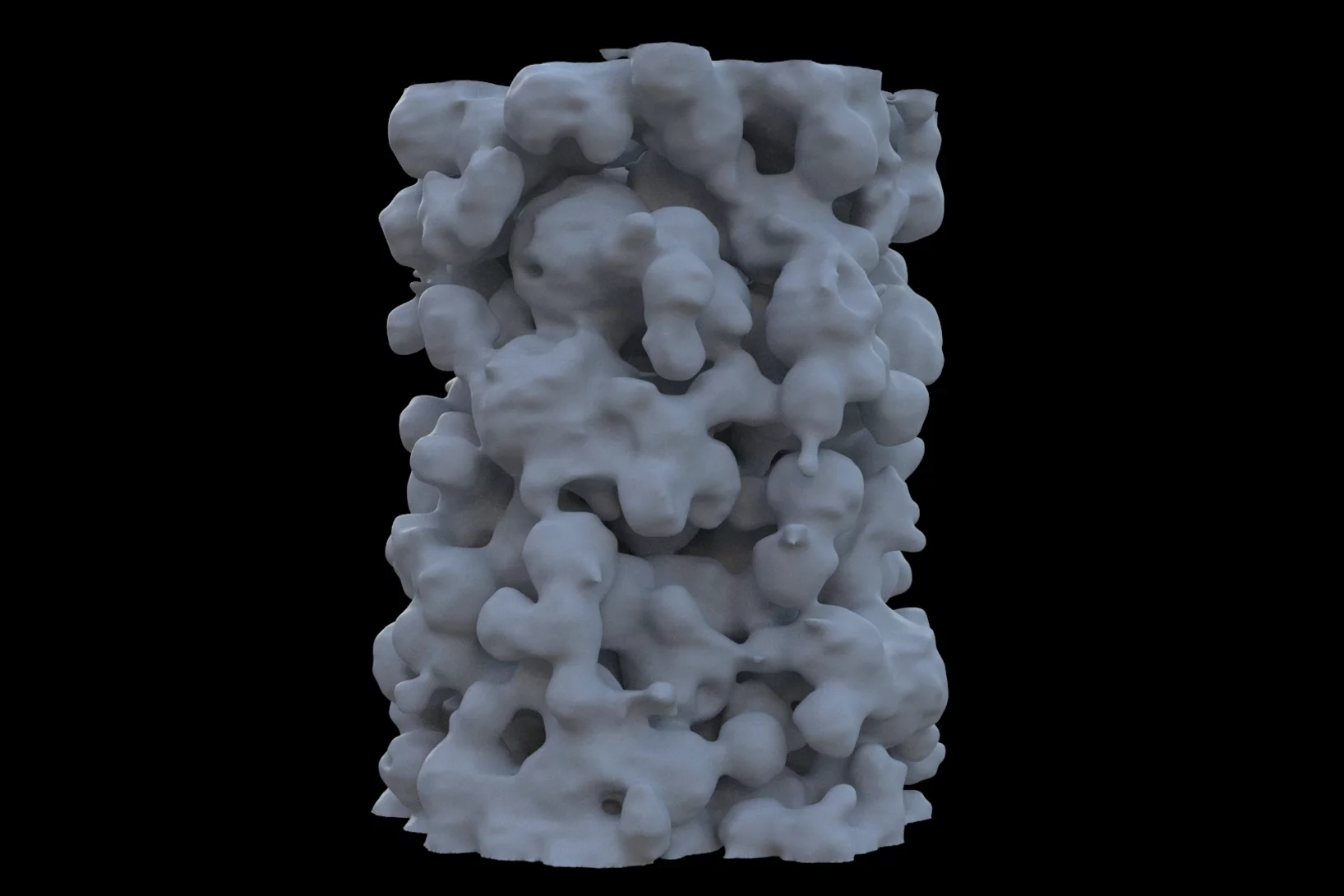
Making the world go round - a look into the structure of a prominent heterogeneous catalyst
Fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, which are composite particles of hierarchical porosity, were examined using ptychographic X-ray tomography. These particles are essential to the conversion of crude oil into gasoline. Examination of catalysts at decreasing levels of catalytic conversion efficacy allowed the detection of possible deactivation causes.
Time- and spatially-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin-orbit torques
Current-induced spin-orbit torques hold a great potential for manipulation of magnetization at ultrafast timescales. Researchers at ETH Zürich have demonstrated, using time-resolved STXM imaging at the Swiss Light Source, the influence of spin-orbit torques on the switching behaviour of Pt/Co/AlOx nanostructured elements.
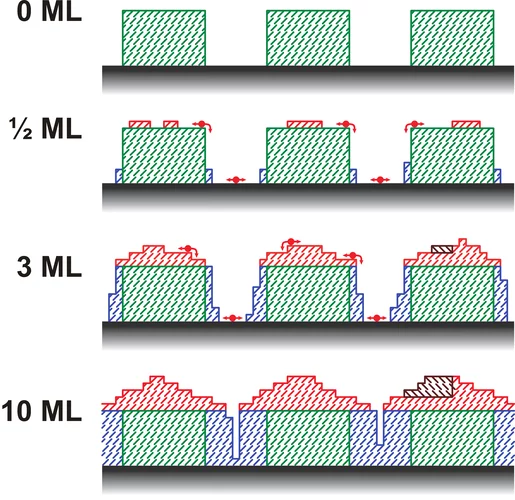
Highly Crystalline C8-BTBT Thin-Film Transistors by Lateral Homo-Epitaxial Growth on Printed Templates
Highly crystalline thin films of organic semiconductors offer great potential for high-performance, low-cost flexible electronics. Researchers at IMEC Belgium have developed a new double-step thin film fabrication process that offers higher performance devices. Soft X-ray spectro-microscopy at the Swiss Light Source was used to prove that the increased performance comes from larger areas of material sharing the same molecular orientation.
L'atmosphère à la lumière des rayons X
Des chercheurs du PSI ont développé une chambre d’expérience où ils reconstituent certains processus qui se jouent dans l’atmosphère et peuvent étudier ces derniers avec une précision inégalée grâce à de la lumière de type rayons X issue de la SLS. Lors de leurs premières expériences, ils ont étudié la formation du brome, qui joue un rôle essentiel dans la dégradation de l’ozone dans les couches inférieures de l’atmosphère. A l’avenir, cette nouvelle chambre d’expérience sera également mise à disposition de chercheurs d’autres disciplines scientifiques.
Dr. Nan Xu awarded SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics
The SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics, sponsored by IBM, has been awarded to Dr. Nan Xu for his excellent work on topological quantum states. Dr. Nan Xu is a joint postdoc of Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
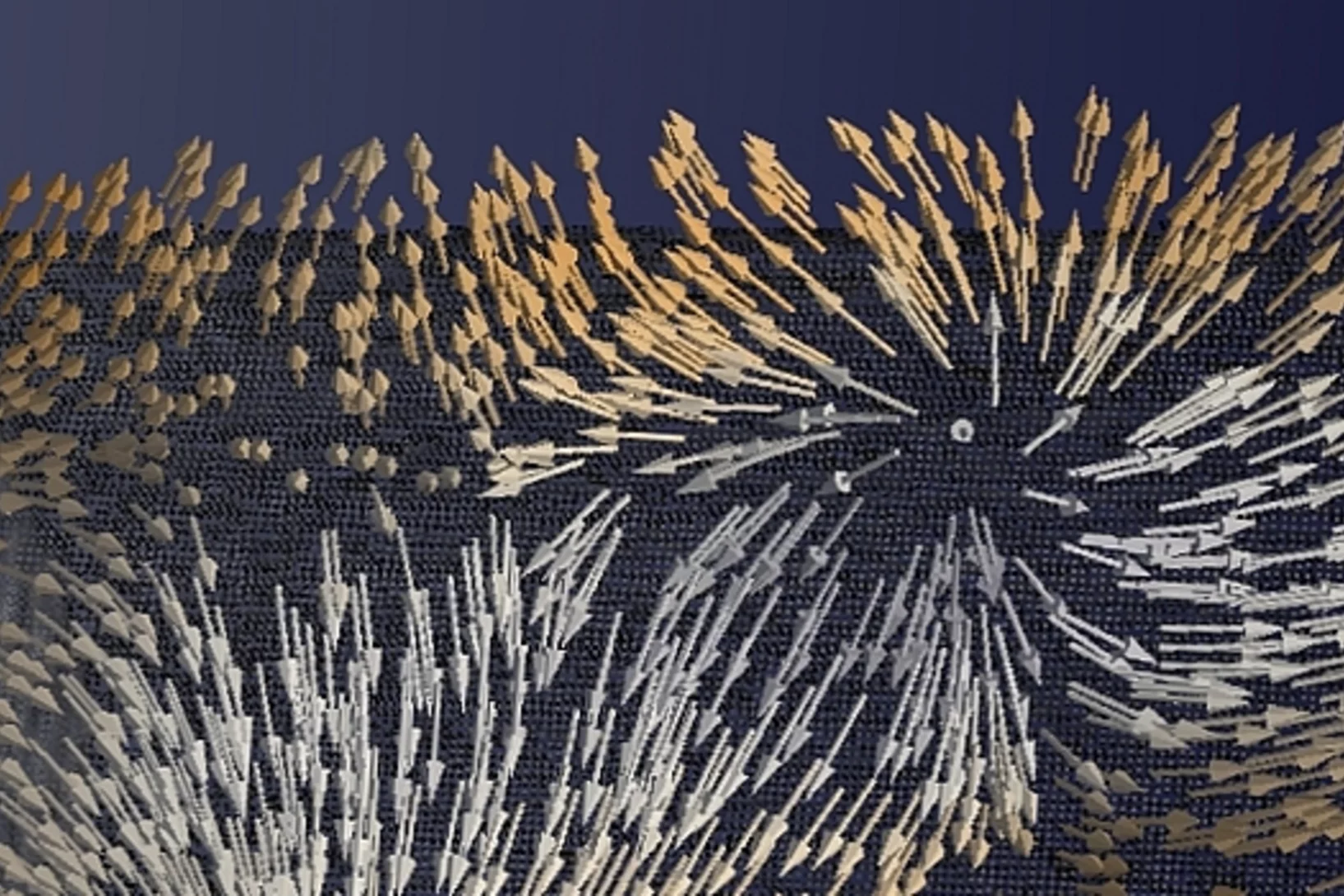
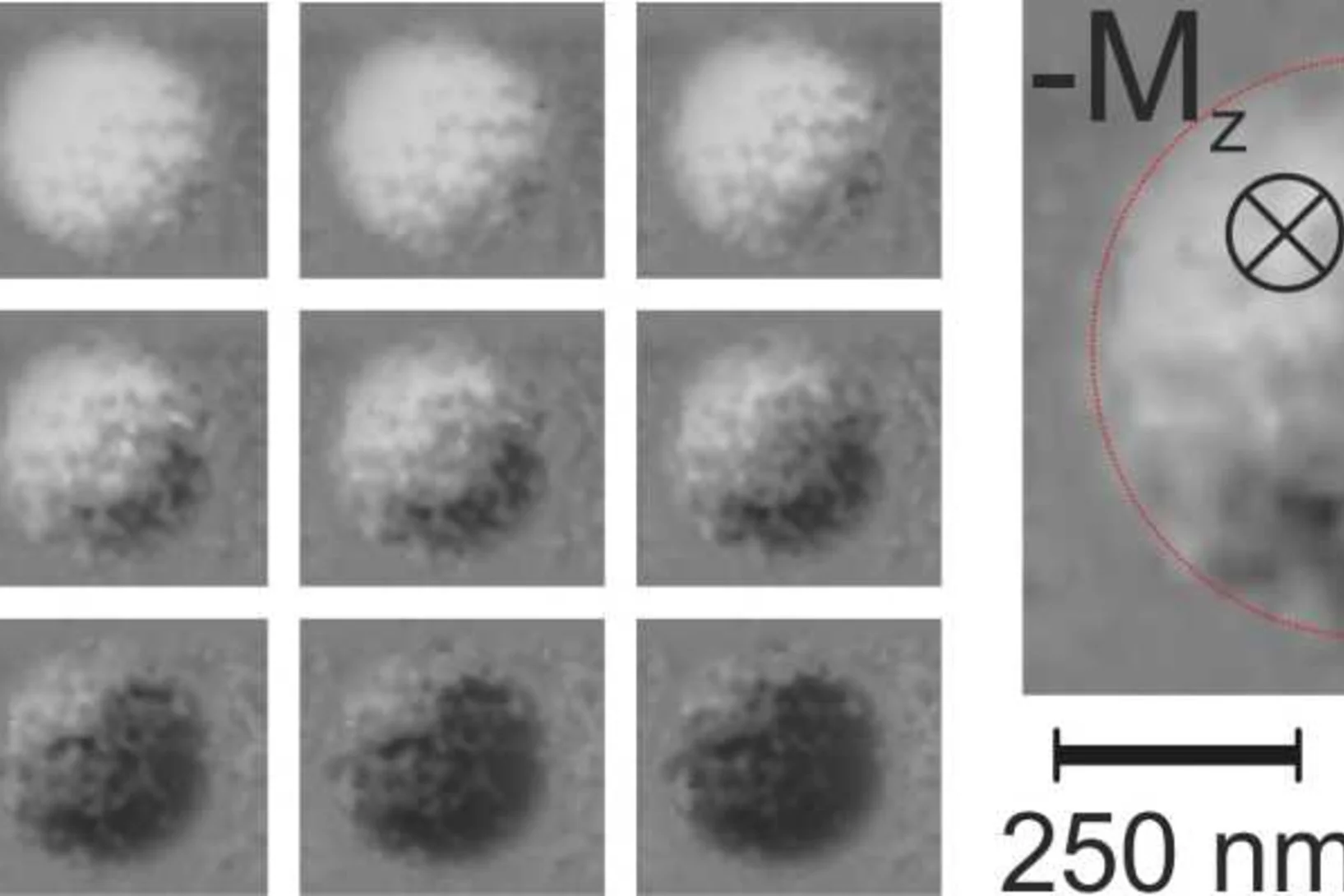
Plongée dans un aimant
Pour la première fois, des chercheurs ont réussi à visualiser les directions de l'aimantation dans un objet magnétique tridimensionnel. Les plus petits détails de leur visualisation mesuraient moins d'un dixième de millième de millimètre. Un type de motif exceptionnel est ressorti dans la structure qu'ils ont fait apparaître: des singularités magnétiques appelées points de Bloch, jusque-là connues uniquement en théorie.
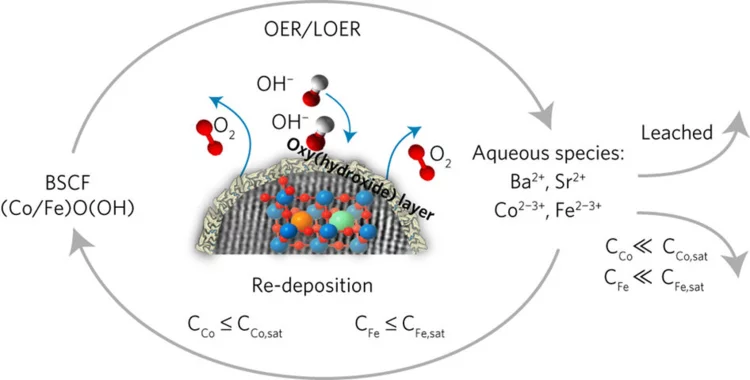
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
By combining a scalable cutting-edge synthesis method with time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it was possible to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure during realistic operando conditions for highly active OER perovskite nanocatalysts.
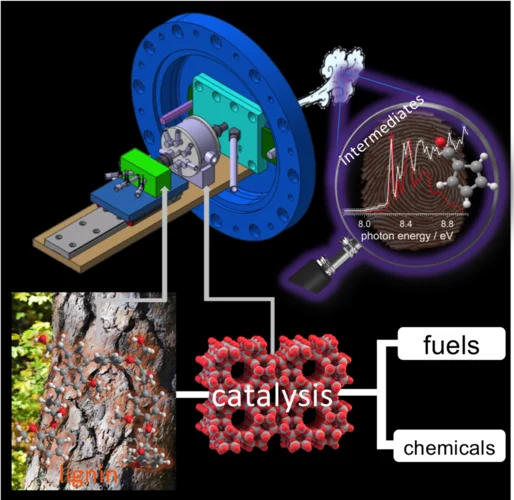
Understanding the reaction mechanism in lignin catalytic fast pyrolysis
Lignin is a major constituent of plants, and may be used as a precursor for fuels and fine chemicals. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignin is one of the most promising approaches. By using vacuum ultraviolet synchrotron radiation and threshold photoelectron spectroscopy we could identify elusive intermediates, which are responsible for the formation of phenol and benzene and could thus tackle this reaction mechanism. Mechanistic understanding could enable targeted improvement of production methods in the future, beyond the currently used "cook-and-look" approach.
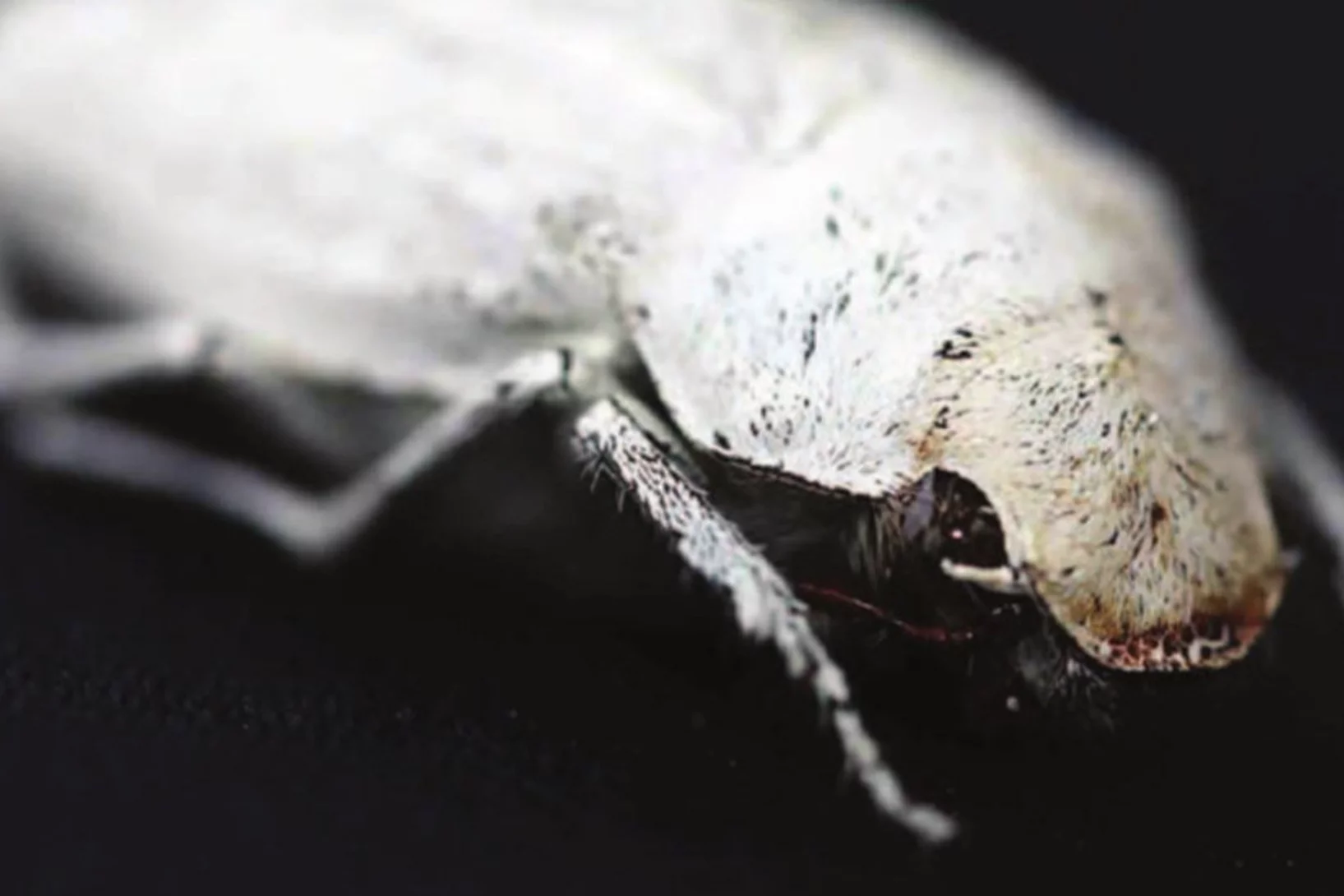
Photonic structure of white beetle wing scales: optimized by evolution
A very thin layer on this beetle’s wings exhibits a complicated structure on the nanoscale that gives them a bright white color. X-ray nanotomography acquired at the Swiss Light Source provides a faithful image of this structure in three dimensions with which scientists can confirm its evolutionary optimization: just enough material for an efficient reflection of white light.
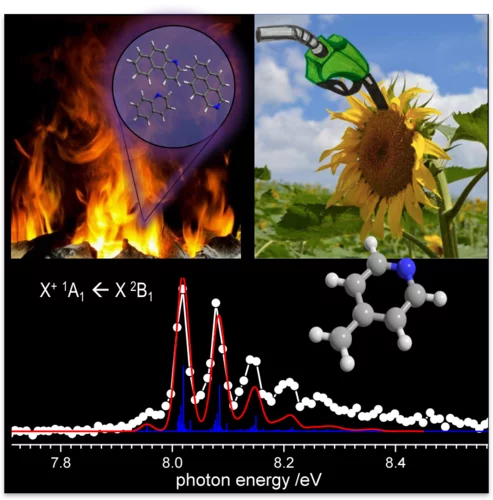
Isomer-Selective Generation and Spectroscopic Characterization of Biofuel Intermediates
Online combustion analysis relies heavily on spectral data to detect reactive intermediates isomer-selectively to establish e.g. kinetic flame models. Due to the difficulty to generate these species cleanly, spectral data are rather scarce. Here we report on the selective generation of three picolyl radical isomers (C5H4N-CH2*) by deamination of aminomethylpyridines. Picolyl radicals are relevant in biofuel combustion, and could now be characterized by threshold photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation. Vibrationally resolved bands and distinct ionization energies allow for isomer-specific detection of these elusive species in complex environments and permit us to explore new avenues in soot- and NOx formation kinetics.
Towards understanding of human betacoronavirus HKU1 life cycle
Researchers from China and USA join forces with Swiss Light Source (SLS) macromolecular crystallography (MX) beamline scientists in a study, which aims at understanding an important step in the life cycle of the human betacoronavirus HKU1.
La radiographie en 3D permet de visualiser les moindres détails d’une puce informatique
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont réalisé des radiographies détaillées en 3D d’une puce informatique usuelle. Dans le cadre de leur expérience, ils ont analysé une petite portion de puce qu’ils avaient préalablement découpée. Durant la mesure, cet échantillon est resté intact. Pour les fabricants, déterminer si la structure de leurs puces est conforme aux normes représente un défi. Ces résultats constituent donc une possibilité d’application importante pour un procédé spécifique de tomographie à rayons X que les chercheurs du PSI développent depuis quelques années.
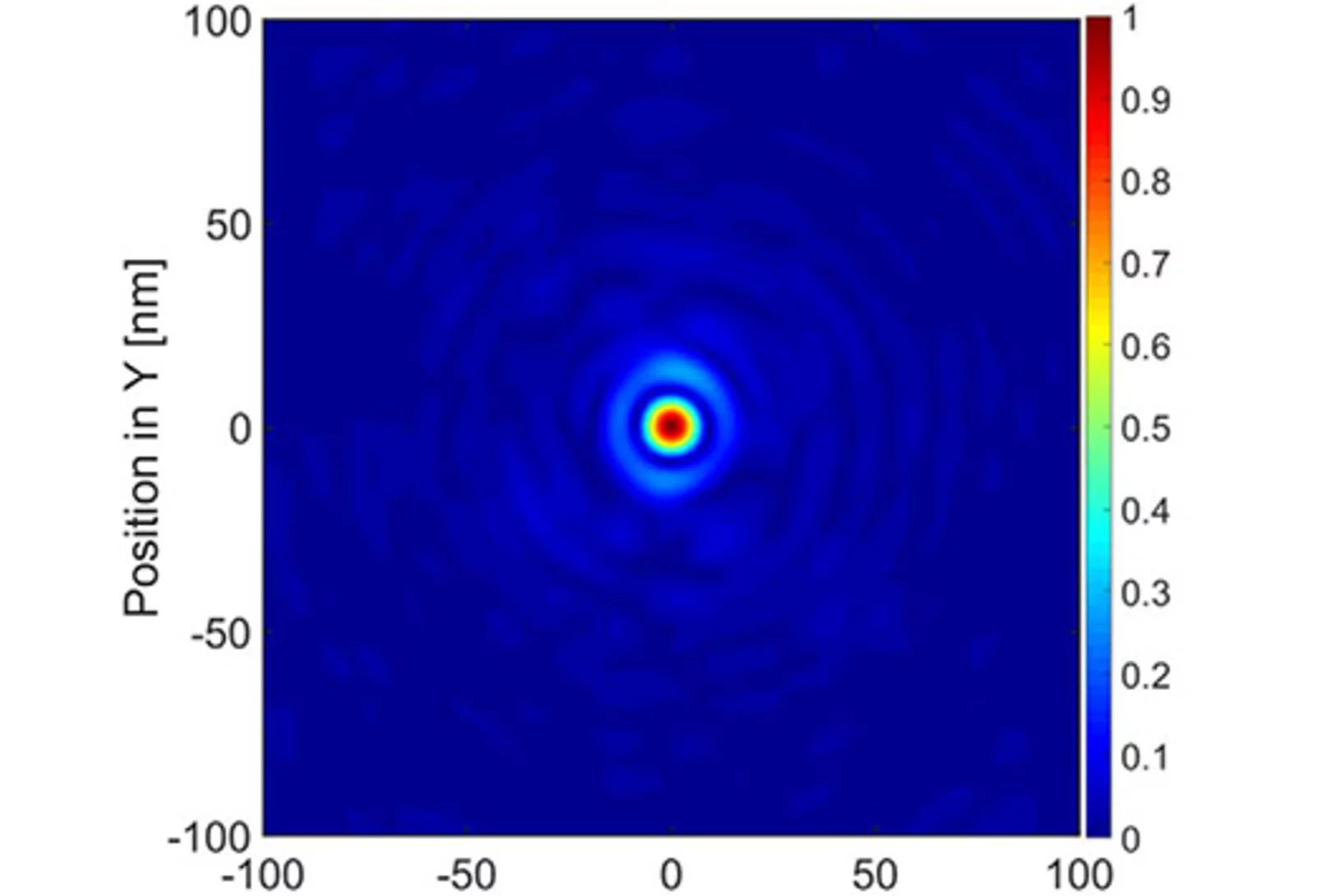
Interlaced zone plates push the resolution limit in x-ray microscopy
A novel type of diffractive lenses based on interlaced structures enable x-ray imaging at resolutions below 10 nm. The fabrication method and the test results of these novel x-ray lenses have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
De nouvelles approches des réactions chimiques grâce aux nanotechnologies
80 % des produits de l’industrie chimique sont fabriqués par recours à la catalyse. Ce procédé est également indispensable dans la conversion énergétique et l’épuration des gaz d’échappement. L’industrie teste donc continuellement de nouvelles substances et de nouvelles configurations susceptibles de déboucher sur de nouveaux procédés catalytiques plus performants. Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI à Villigen et de l’ETH Zurich ont à présent développé une méthode qui permet d’améliorer nettement la précision de tels essais, ce qui devrait accélérer la recherche de solutions optimales.
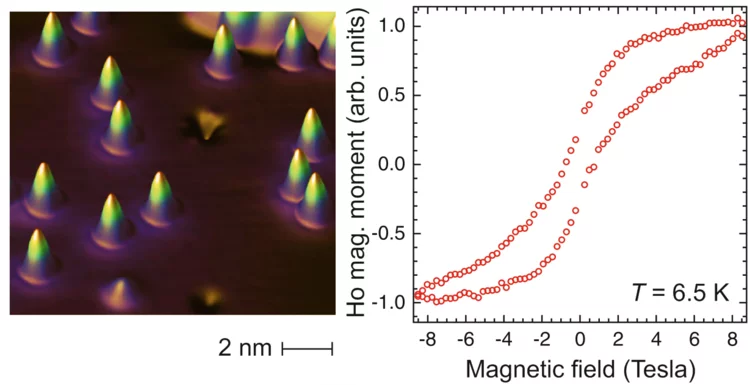
The Smallest Magnet
Single holmium atoms adsorbed on few monolayers of magnesium oxide are extraordinarily stable magnets. They retain a significant fraction of their magnetization when the external magnetic field is switched off. This has been shown recently in a study combining x-ray magnetic circular dichroism performed at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) as well as scanning tunneling microscopy. The results open perspectives of storing and processing information at ultrahigh density.
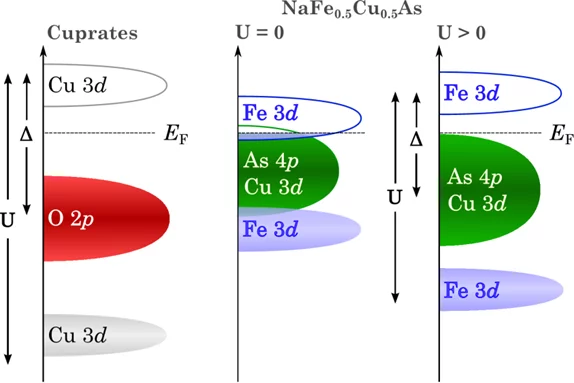
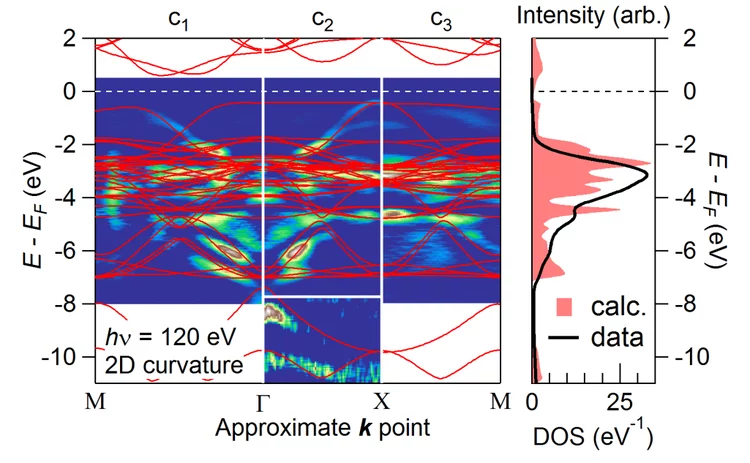
Novel insulating phase in iron-pnictide materials
The first example of an insulating phase which is close to the superconducting phase in an iron-pnictide system has been recently observed in heavy Cu-doped NaFe1-xCuxAs (x > 0.3). A combined study by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that on-site Coulomb repulsion and enhanced Hund’s rule coupling are responsible for the insulating behavior. The results show that the insulating phase in NaFe0.5Cu0.5As resembles the situation in the parent compounds of the high-Tc cuprate superconductors.
Conducteur d'électricité ou isolant, au choix
L’oxyde de néodyme-nickel est un matériau qui, suivant la température, est soit un métal, soit un isolant. Cette transition peut être commandée par l’application d’une tension électrique, ce qui fait de ce matériau un candidat potentiel pour les transistors dans les appareils électroniques modernes. Des chercheurs à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont utilisé un développement perfectionné et sophistiqué de la diffusion de rayons X et réussi à saisir la cause de cette transition: la réorganisation des électrons autour des atomes d’oxygène.
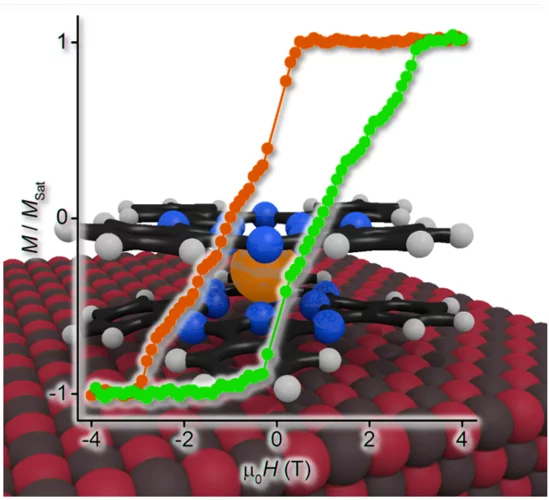
Magnesium Oxide Boosts the Hysteresis of Single-Molecule Magnets
Researchers from PSI and EPFL have demonstrated that the magnetization hysteresis and remanence of TbPc2 single-molecule magnets drastically depends on the substrate on which they are deposited. If a few atomic layers thick magnesium oxide film grown on a silver substrate is used, a record wide hysteresis and record large remanence can be obtained. Single-molecule magnets are attractive for molecular spintronics applications such as information processing or storage.
Shedding light on the origins of high-Tc superconductivity in bismuth oxides
Researchers have overcome a number of challenges in order to employ an advanced probe in the study of an unusual material, barium bismuth oxide (BaBiO3) – an insulating parent compound of a family of high-temperature superconductors known since the late 80s. In order to finally realize the experiments, the researchers grew and studied thin films of the material completely in situ under ultrahigh vacuum conditions. The results show that superconductivity in bismuth oxides emerges out of a novel insulating phase, where hole pairs located on combinations of the oxygen orbitals are coupled with distortions of the crystal lattice.
Single shot grating interferometry demonstrated using direct conversion detection
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute's Swiss Light Source in Villigen, Switzerland, have developed an X-ray grating interferometry setup which does not require an analyzer grating, by directly detecting the fringes generated by the phase grating with a high resolution detector. The 25um pitch GOTTHARD microstrip detector utilizes a direct conversion sensor in which the charge generated from a single absorbed photon is collected by more than one channel. Therefore it is possible to interpolate to achieve a position resolution finer than the strip pitch.
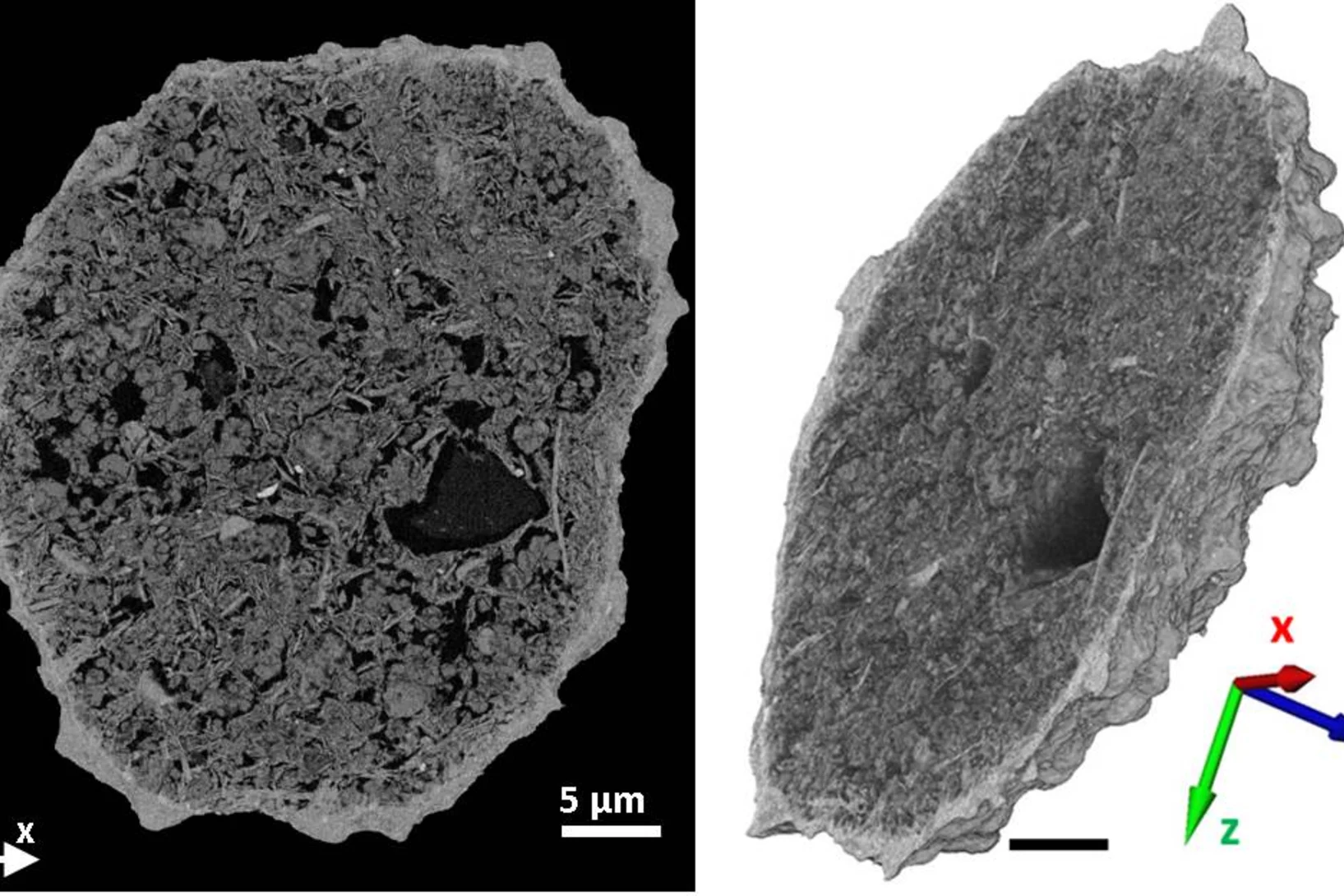
How does food look like on the nanoscale?
The answer to this question could save food industry a lot of money and reduce food waste caused by faulty production. Researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the Paul Scherrer Institut have obtained a 3D image of food on the nanoscale using ptychographic X-ray computed tomography. This work paves the way towards a more detailed knowledge of the structure of complex food systems.
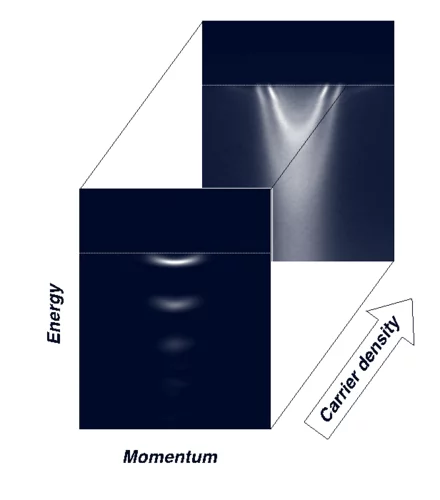
Tailoring Novel Superconductivity
The Angle Resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements performed on 2DEL at STO surface revealed that, at low carrier density, electrons are always accompanied by a quantized dynamic lattice deformation. Together with the electron, these phonon-cloud formed a new composite quasiparticle called Fröhlich polaron.
PSI Scientific Reports
Archive 2006-2012. The Scientific Reports – containing accounts of research topics from all the different areas – provide an impression of the variety of subjects researched at PSI.