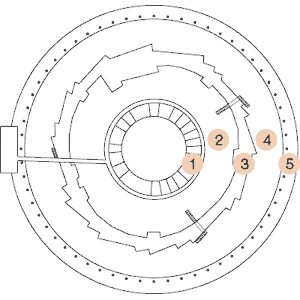
The SLS building has the shape of a doughnut with an outer diameter of 138 m, an inner diameter of 32 m and a height of 14 m.
The whole building is "floating" on a 12m thick layer of gravel, formed during the last glacial period. The wooden roof of the building, as well as a 16 ton crane, is supported at the outside by 60 steel pillars and at the inside by the office building.
The SLS building has 5 different radial zones, starting from the inside:
- office building with control room, labs and offices for 80 people on 3 levels;
- technical gallery with power supplies and RF-stations ;
- tunnel with concrete shielding walls, housing the storage ring, the linac and the booster;
- beamline area;
- outer ring with the 60 pillars, transport lane and air inlet system.
In order to ensure stable conditions for the electron beam and the photon beamlines, it was necessary to fulfil two important boundary conditions:
- mechanical separation of the 40 cm thick concrete floor, supporting the tunnel and the beamlines, from the roof and the walls of the building. To acchieve this, a 3 cm cut was made in the floor between areas 2 and 3 and between areas 4 and 5. Changing weather conditions, like wind and temperature, are thus hardly effecting the tunnel and the beamlines.
- stable temperature in the tunnel and the beamline area. A powerful air conditioning system, with 6 units placed just outside the building, together with a good isolation of the roof and the walls, keep the temperature inside the building at 23°±0.5° in winter and at 25°±0.5° in summer. Inside the accelerator tunnel 150 air jets produce a helical air stream, which enforces a stable temperature distribution, avoiding any hot spots. The average temperature in the tunnel is kept constant at 24° with a tolerance of only ±0.05°.
- An array of small windows lets some daylight into the building. These windows are strongly slanted however, to make sure that no direct sunlight is falling onto the floor.
- An auxiliary building houses the bulky equipment of the technical infrastructure, like pumps and storage tanks for the cooling system and the primary distribution of the electrical power.