NUM division - Publication Highlights
In situ stress observation in oxide films and how tensile stress influences oxygen ion conduction
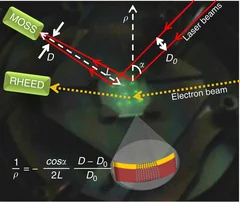
Many properties of materials can be changed by varying the interatomic distances in the crystal lattice by applying stress. Ideal model systems for investigations are heteroepitaxial thin films where lattice distortions can be induced by the crystallographic mismatch with the substrate. Here we describe an in situ simultaneous diagnostic of growth mode and stress during pulsed laser deposition of oxide thin films.
Dramatic pressure-driven enhancement of bulk skyrmion stability
The recent discovery of magnetic skyrmion lattices initiated a surge of interest in the scientic community. Several novel phenomena have been shown to emerge from the interaction of conducting electrons with the skyrmion lattice, such as a topological Hall-effect and a spin-transfer torque at ultra-low current densities.
Coexistence of low-moment magnetism and superconductivity in tetragonal FeS and suppression of Tc under pressure
The family of iron-based superconductors has recently acquired a new member material, FeS. Theoretically, this compound has been shown to have electronic structure similar to that of the superconducting FeSe. However, contradictory ground states have been predicted for FeS. In this work, a collaboration of authors from Switzerland and Germany use muon spin rotation and relaxation to show that weak-moment magnetism microscopically coexists with bulk superconductivity.
Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Interplay of Attractive and Repulsive Interactions in Nanoparticle-Polymer System
The phase behavior of nanoparticle (silica)−polymer (polyethylene glycol) system without and with an electrolyte (NaCl) has been studied. It is observed that nanoparticle−polymer system behaves very differently in the presence of electrolyte. In the absence of electrolyte, the nanoparticle−polymer system remains in one-phase even at very high polymer concentrations.
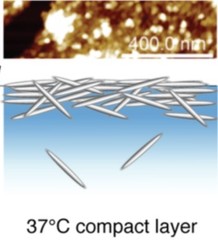
Mechanically Enhanced Liquid Interfaces at Human Body Temperature Using Thermosensitive Methylated Nanocrystalline Cellulose
The mechanical performance of materials at oil/water interfaces after consumption is a key factor affecting hydrophobic drug release. In this study, we methylated the surface of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) by mercerization and dimethyl sulfate exposure to produce thermosensitive biopolymers. These methylated NCC (metNCC) were used to investigate interfacial thermogelation at air/water and medium-chain triglyceride (MCT)/water interfaces at body temperature.
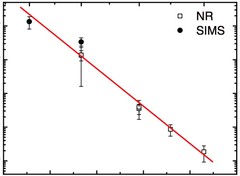
Self-Diffusion in Amorphous Silicon
The present Letter reports on self-diffusion in amorphous silicon. Experiments were done on 29Si/natSi heterostructures using neutron reflectometry and secondary ion mass spectrometry. The diffusivities follow the Arrhenius law in the temperature range between 550 and 700°C with an activation energy of (4.4 ± 0.3) eV.
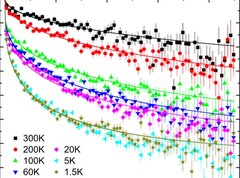
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
The performance and degree of efficiency of industrial transformers are directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). Industrial transformer cores are built of stacks of single HPSLs. While the insulating coating on each HPSL reduces eddy-current losses in the transformer core, the coating also induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
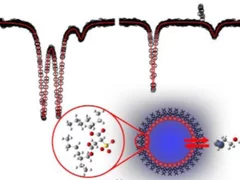
Rate of Molecular Transfer of Allyl Alcohol across an AOT Surfactant Layer Using Muon Spin Spectroscopy
The transfer rate of a probe molecule across the interfacial layer of a water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsion was investigated using a combination of transverse field muon spin rotation (TF-μSR), avoided level crossing muon spin resonance (ALC-μSR), and Monte Carlo simulations. Reverse micro-emulsions consist of nanometer-sized water droplets dispersed in an apolar solvent separated by a surfactant monolayer.
The flip-over effect in pulsed laser deposition: Is it relevant at high background gas pressures?
In pulsed laser deposition the use of a rectangular or elliptical beam spot with a non 1:1 aspect ratio leads to the so called flip-over effect. Here, the longest dimension of the laser spot results in the shortest direction of plasma plume expansion.