NUM division - Publication Highlights
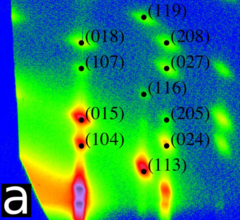
Superlattice growth and rearrangement during evaporation-induced nanoparticle self-assembly
Understanding the assembly of nanoparticles into superlattices with well-defined morphology and structure is technologically important but challenging as it requires novel combinations of in-situ methods with suitable spatial and temporal resolution.
Pressure-induced magnetic order in FeSe: A muon spin rotation study
The magnetic order induced by the pressure was studied in FeSe by means of muon spin rotation (μSR) technique.
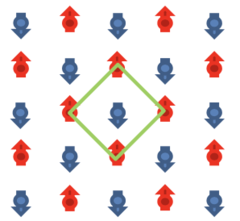
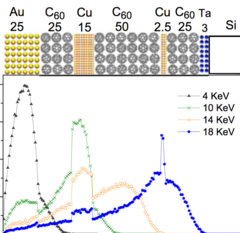
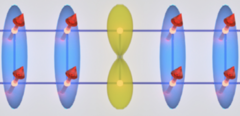
Emergent magnetism at transition-metal-nanocarbon interfaces
Interfaces are critical in quantum physics, and therefore we must explore the potential for designer hybrid materials that profit from promising combinatory effects. In particular, the fine-tuning of spin polarization at metallo–organic interfaces opens a realm of possibilities, from the direct applications in molecular spintronics and thin-film magnetism to biomedical imaging or quantum computing.
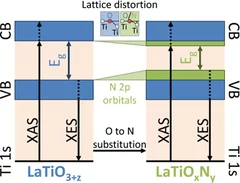
Determination of Conduction and Valence Band Electronic Structure of LaTiOxNy Thin Films
The nitrogen substitution into the oxygen sites of several oxide materials leads to a reduction of the band gap to the visible-light energy range, which makes these oxynitride semiconductors potential photocatalysts for efficient solar water splitting. Oxynitrides typically show a different crystal structure compared to the pristine oxide material.
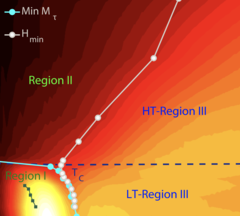
Unconventional magnetic order in the conical state of MnSi
In the temperature-magnetic field phase diagram, the binary metallic compound MnSi exhibits three magnetic phases below Tc ≈ 29K.An unconventional helicoidal phase is observed in zero field. At moderate field intensity a conical phase sets in. Near Tc, in an intermediate field range, a skyrmion lattice phase appears.
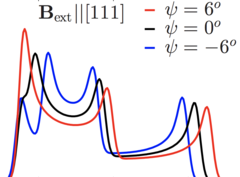
Anomalous Thermal Conductivity and Magnetic Torque Response in the Honeycomb Magnet α-RuCl3
We report on the unusual behavior of the in-plane thermal conductivity κ and torque τ response in the Kitaev-Heisenberg material α-RuCl3. κ shows a striking enhancement with linear growth beyond H = 7T, where magnetic order disappears, while τ for both of the in-plane symmetry directions shows an anomaly at the same field.
Bound States and Field-Polarized Haldane Modes in a Quantum Spin Ladder
The challenge of one-dimensional systems is to understand their physics beyond the level of known elementary excitations. By high-resolution neutron spectroscopy in a quantum spin-ladder material, we probe the leading multiparticle excitation by characterizing the two-magnon bound state at zero field.
Amyloid fibril systems reduce, stabilize and deliver bioavailable nanosized iron
Iron-deficiency anaemia (IDA) is a major global public health problem. A sustainable and cost-effective strategy to reduce IDA is iron fortification of foods, but the most bioavailable fortificants cause adverse organoleptic changes in foods. Iron nanoparticles are a promising solution in food matrices, although their tendency to oxidize and rapidly aggregate in solution severely limits their use in fortification.
Doping Dependence of Collective Spin and Orbital Excitations in the Spin-1 Quantum Antiferromagnet La2-xSrxNiO4 Observed by X-Rays
We report the first empirical demonstration that resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) is sensitive to collective magnetic excitations in S=1 systems by probing the Ni L3 edge of La2-xSrxNiO4 (x=0, 0.33, 0.45). The magnetic excitation peak is asymmetric, indicating the presence of single and multi-spin-flip excitations.