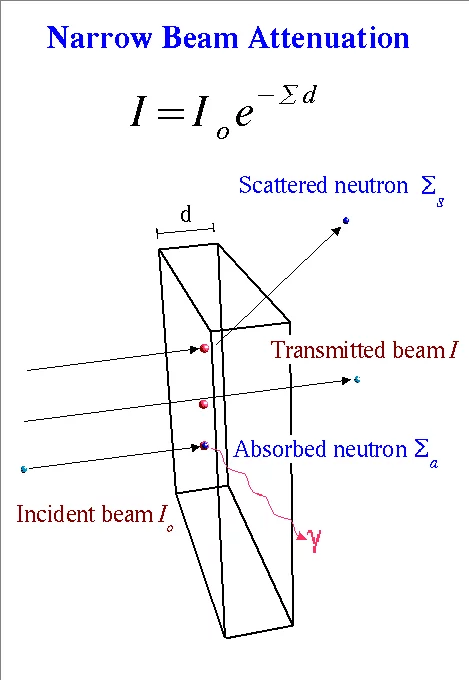
Since the neutron is electrically neutral, it interacts only weakly with matter into which it can penetrate deeply. Contrary to X-rays, which interact dominantly with the electron shell of the atom, the neutron does on the level of the nucleus. Therefore the neutron is quite sensitive to light atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, etc. which have much higher interaction probability with neutrons than with X-rays. In contrast to this, metals comparatively show lower interaction probability with neutrons, thus allowing quite high penetration depth. Elements of similar atomic number Z (= number of protons) likewise differentiate easier with neutrons than with X-rays. A comparison of neutron and X-ray attenuation is given in the section Comparison with X-ray. For neutron transmission the universal law of attenuation of radiation passing through matter (Beer-Lambert law) is valid.
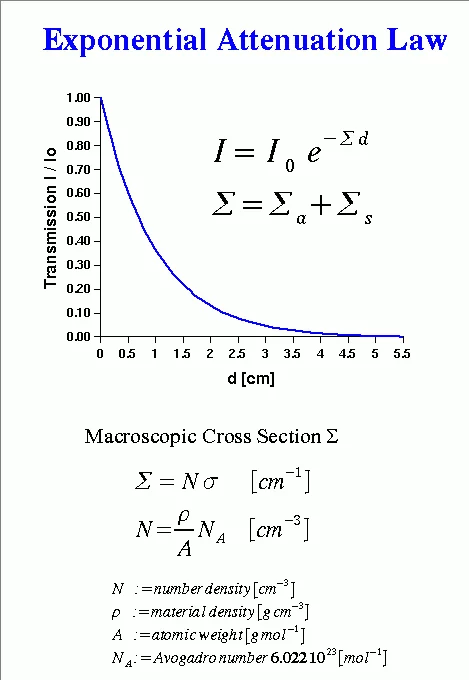
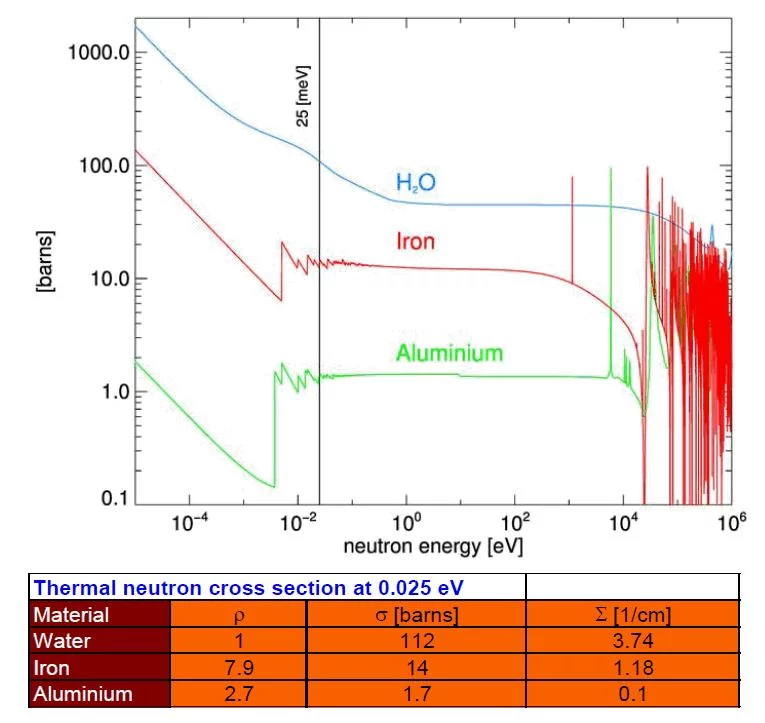
Neutron matter interaction probability is high at thermal or cold energies (see Figure 5). It is given as microscopic cross-section data σ in units of barns i.e. 10-24 cm2, see tables of cross-section data. Neutrons for transmission radiography are therefore extracted from a moderator (e.g. tank containing heavy water), which slows down neutrons produced in a spallation source or a research reactor in the MeV energy range. The transmission behavior of a mono-energetic narrow neutron beam can be described by the basic law of radiation attenuation in matter (See Figure 3 and 4). The ratio between the emerging neutron flux I and incident flux Io is called transmission T. Quantitative data about the material composition (e.g. hydrogen content), can be derived from neutron transmission measurements in the case of known sample shape and dimension d. Hereby the relation defining the macroscopic neutron interaction cross section and the evaluated neutron cross section data are taken from a database. The simple exponential attenuation law does not hold for all situations. Thick samples or strongly scattering (e.g. hydrogen) or absorbing materials (e.g. containing strong absorbers like boron, gadolinium. …) show a deviation, due to multiple scattering effects or the need to take the changing neutron energy spectrum into account.