Show filters
Not Rocket Science, just Nuclear Rocket Science
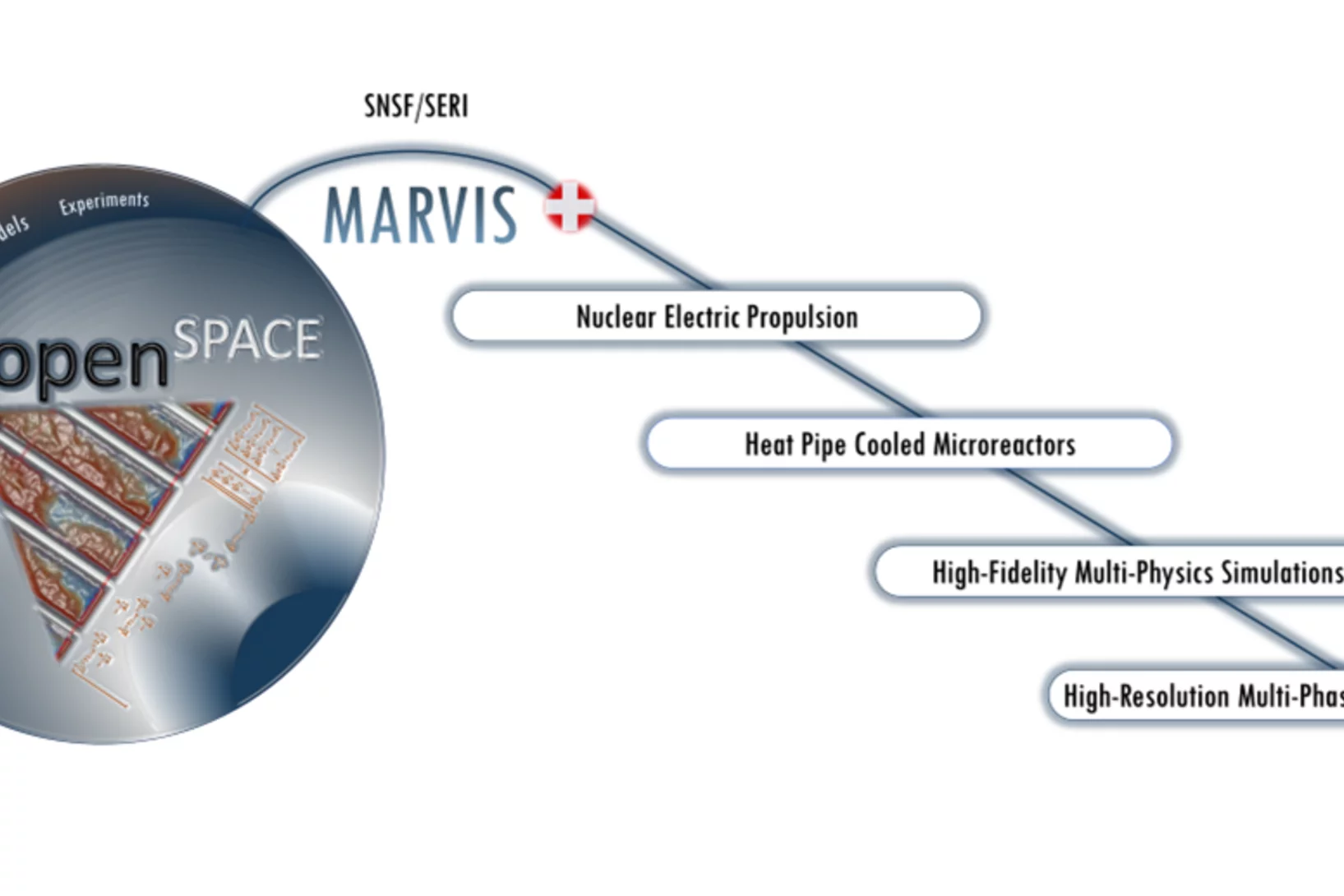
The PSI Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT) conducts computational and experimental research with focus on the safety of nuclear reactors and systems. In recent years, it established the EPSILON program to coordinate and consolidate its research activities on nuclear space applications. Among other things, developments were initiated towards an open-source European platform for high-fidelity simulations and experiments dedicated to space nuclear reactors. Referred to as the openSPACE platform, its underlying concepts are a) to include not only solvers but also reference simulation models as well as experimental validation data; b) to make all of these available to the broader and combined nuclear- and space communities for usage and/or further developments. Through this, the goal is thus not only to facilitate collaborative research in this area but also to enable effective support to the European Space Agency for thorough design, safety and performance evaluations of nuclear reactor systems for in-space propulsion and/or surface power. A first development phase focused on nuclear electric propulsion was proposed and retained among the two projects selected in 2023 by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) for its MARVIS call (Multidisciplinary Advanced Research Ventures in Space) and funded by the Swiss Secretariat for Research and Innovation (SERI). This project, to be conducted via four inter-connected PhD theses, was launched in October 2024 and this marks thus a key milestone for the propulsion of PSI nuclear research towards space.
Breaking the Drops
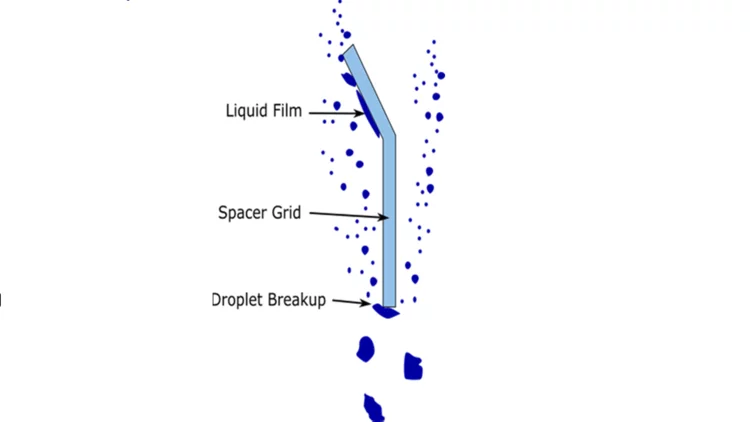
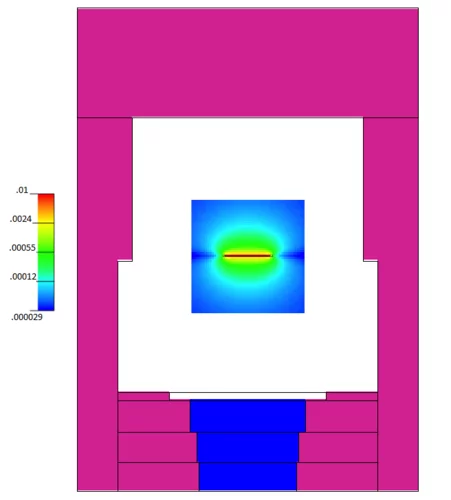
For water-cooled nuclear reactors, a loss of coolant accident constitutes one of the key scenarios to be evaluated for the design of the plant and associated safety systems. Even if these accidents are not expected to occur at all during reactor lifetime, their potential consequences include the heat up of the fuel in the reactor core. For the recovery of the plant to safe conditions, safety systems are in place to inject water in order to reflood the core and to quench the high temperature fuel. The two-phase flow behaviour during this reflooding phase is extremely complex. In particular, the prediction of the behaviour of small liquid droplets generated as the quench front propagates upwards has a significant effect on the fuel temperatures in the upper regions of the reactor core. In collaboration with the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), we have been working to improve our modelling of the droplet behaviour and their impact on key safety parameters.
Taking good and safe care of the retired … nuclear fuel
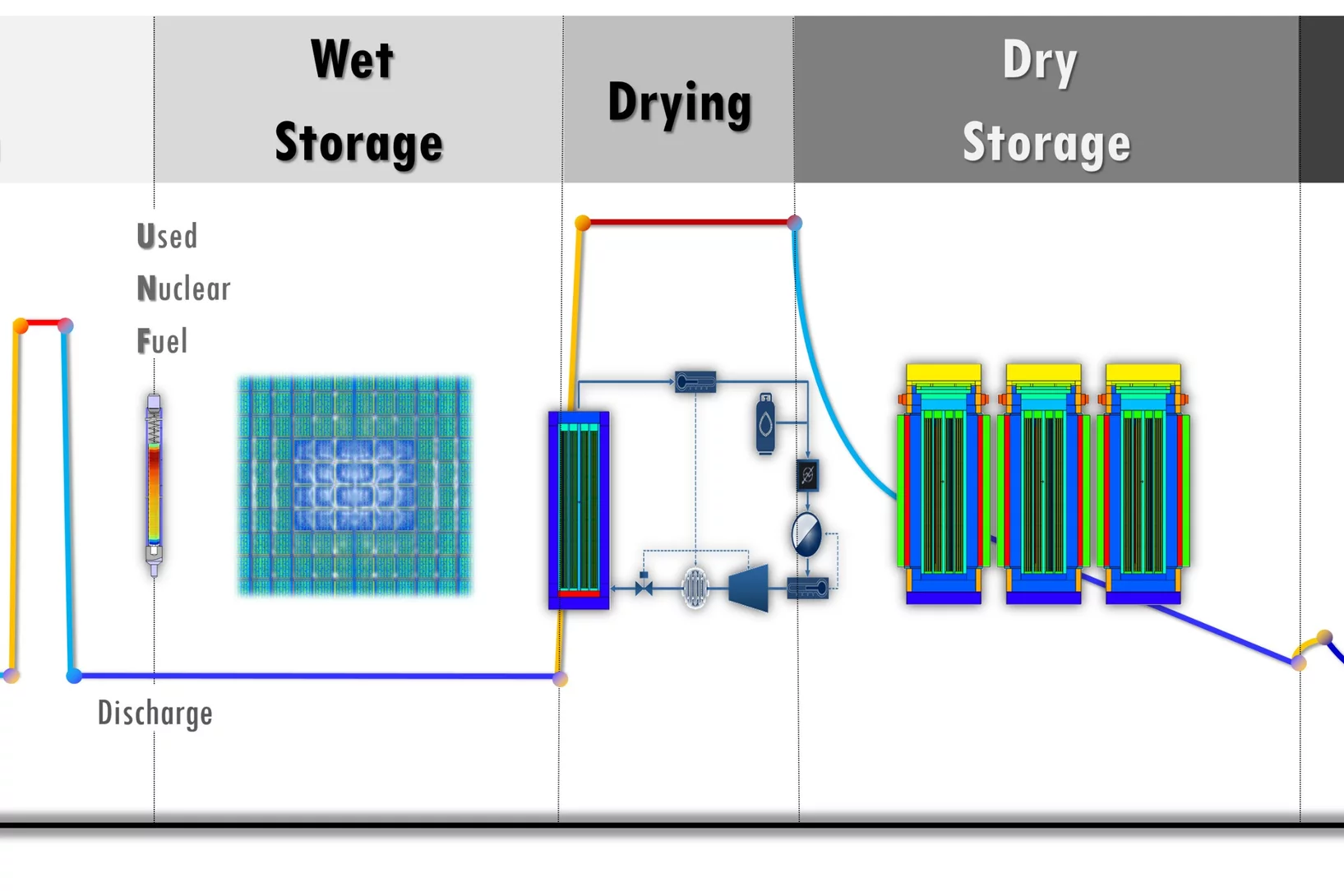
After several years of loyal and reliable services during heavy duty operation in a reactor, nuclear fuel must be discharged and go into retirement. For Switzerland, the final place of retirement is planned to consist of a deep geological repository where the used nuclear fuel will be disposed. Before the repository is constructed, the used fuel will need to be stored in wet pools and/or dry storage casks.
During all this time, safe handling of the fuel will remain the top priority for operators and regulators. To gain better knowledge on the relevant phenomena which could potentially affect the fuel thermo-mechanics and safety characteristics during long storage periods as well as to allow predicting their evolution, simulation models are being developed at PSI within the DRYstars project.
A first milestone was recently achieved with the development of models coupled to state-of-the-art fuel performance codes for each of the three main categories of phenomena considered as having high safety relevance for storage, namely helium behaviour, creep behaviour and hydrogen behaviour.
Used Nuclear Fuel: from Better Characterization to Better Optimization
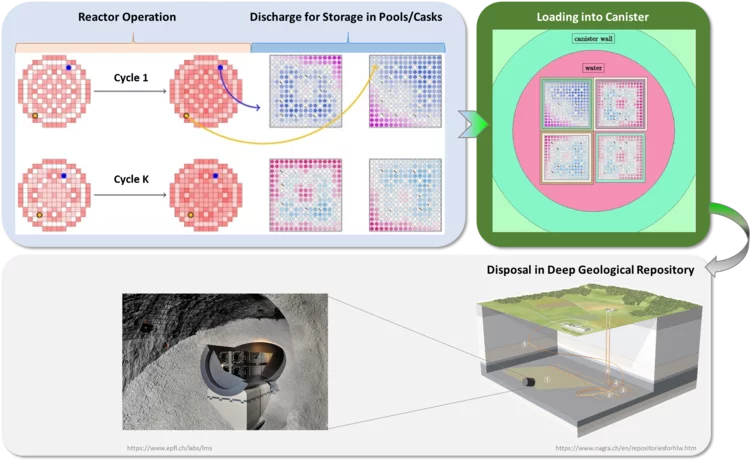
A safe, economical and environmental friendly disposal of used nuclear fuel represents an essential objective of relevance for all. This guides the approach under development at the laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics. Establish higher resolution simulation methods to gain more detailed knowledge on the content of each single nuclear fuel rod ever irradiated in a reactor. Thereafter, use this knowledge to explore optimization approaches that could potentially enlarge the range of disposal options allowing to fulfill the highest level of safety standards while reducing economical costs and geological footprints at the same time.
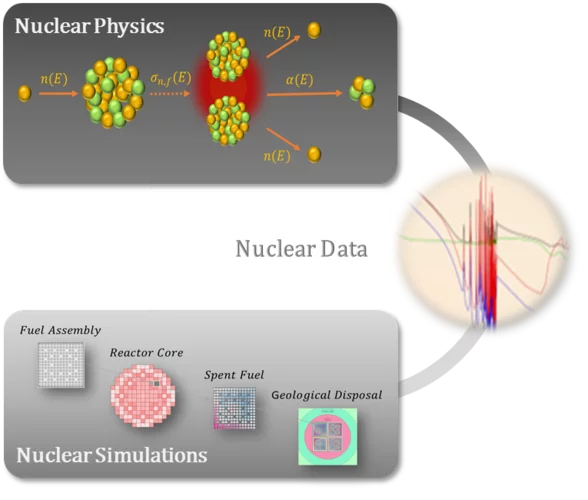
Nuclear Data – Towards a Stronger Link between Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Simulations
All matter in the universe is made of atoms and all atoms are made of particles. Spontaneous changes within atoms as well as collisions between atoms and surrounding particles are nuclear reaction processes guided by nuclear physics laws. To simulate these processes using computer models, probabilities for the various involved nuclear reactions are required. This is precisely the role of nuclear data: supply the computational models with evaluated quantities representing these nuclear reaction probabilities.
Through this, nuclear data can effectively be seen as the fundamental link between nature and any computer simulation involving nuclear reactions. It is thus of primary importance to continuously improve knowledge on nuclear data. In that context, researchers at the laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics have recently focused on the development and application of Bayesian frameworks combining both differential and integral experiments for the improvement of nuclear data. By considering the different experiments together, the aim is to achieve enhancements of the nuclear data evaluations while preserving the basic nuclear physics sum rules.
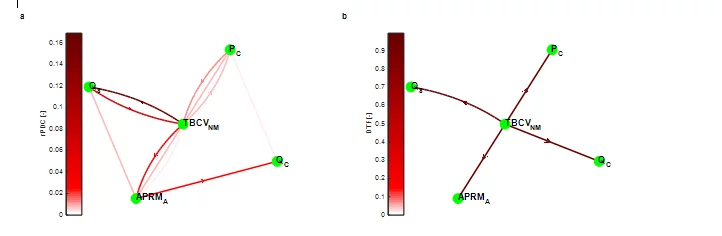
Identifying a disturbance root-cause from ... noise!
Nuclear reactors are complex systems with inherent stochastic behaviour. In simple words, the behaviour of various reactor processes are continuously fluctuating over their mean values, even under normal operation and steady-state conditions. The detailed and systematic analysis of this noisy behaviour can reveal valuable information about the operating status of the studied nuclear reactor. More importantly, designed modifications of the reactor’s operation or even unexpected deviations from the normal performance can be identified using advanced signal analysis techniques. The STARS program, at the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT) in PSI, based on a tight collaboration with the Swiss nuclear industry, has developed a well-established signal analysis methodology, being continuously improved since more than two decades. The latest enhancements of the PSI signal analysis methodology allow a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive the reactor’s operation, and can provide better insight on the root-cause of possible disturbances or malfunctions. Recently, the latest STARS activities in advanced signal analysis techniques were culminated by an international recognition through a special distinction from the AIP Chaos Journal.
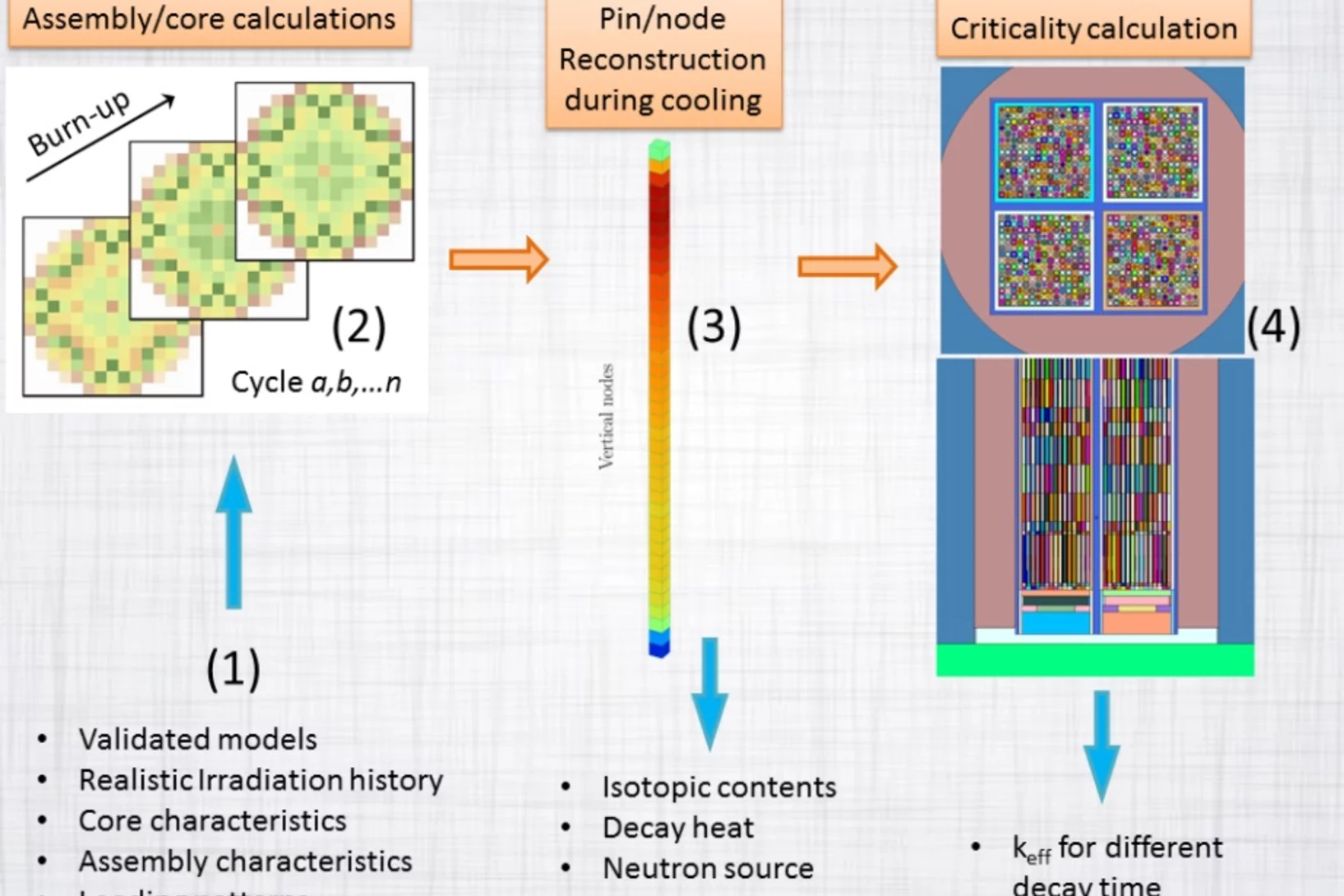
Consistent criticality and radiation studies of Swiss spent nuclear fuel: The CS2M approach
Spent fuel management is becoming one of the major concerns in many countries with a nuclear program. The radiation aspect as well as the safe and economical part of the long-term storage of the spent nuclear fuel has to be evaluated with a high degree of confidence. To assist such project from the neutronic simulation side, a new method is proposed to systematically calculate at the same time canister loading curves and radiation sources, based on the inventory information from an in-core fuel management system.
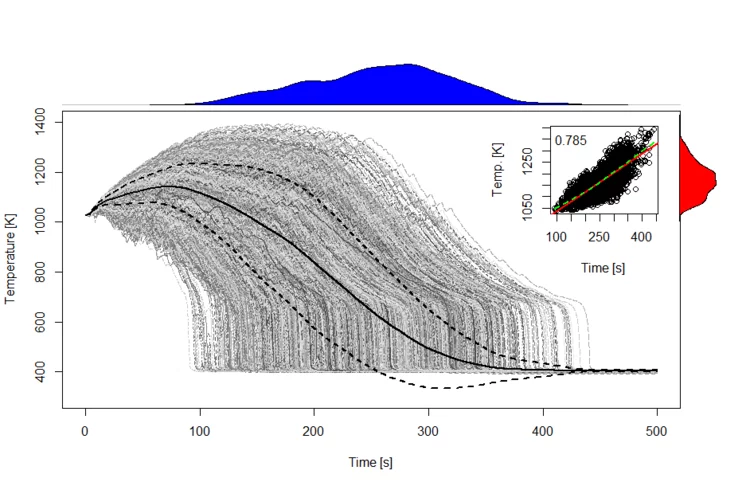
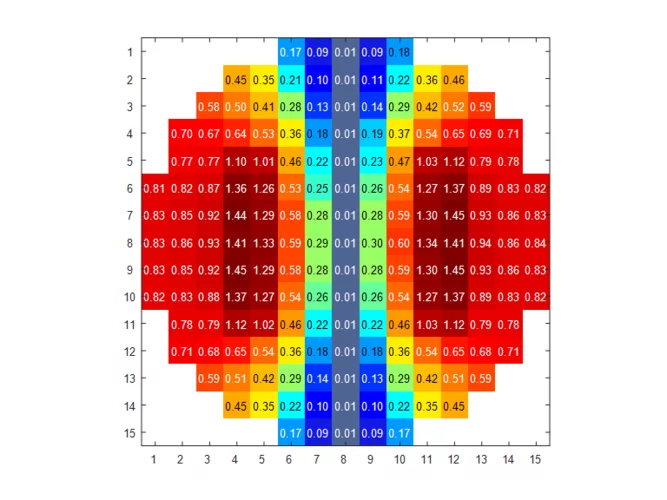
Global Sensitivity Analysis and Registration Strategy for Temperature Profiles of Reflood Experiment Simulations
Global sensitivity analysis (GSA) is routinely applied in engineering to determine the sensitivity of a simulation output to the input parameters. Typically, GSA methods require the code output to be a scalar. In the context of thermal-hydraulic system code, however, simulation outputs are often not scalar but time-dependent (e.g. temperature profile). How to perform GSA on these outputs?
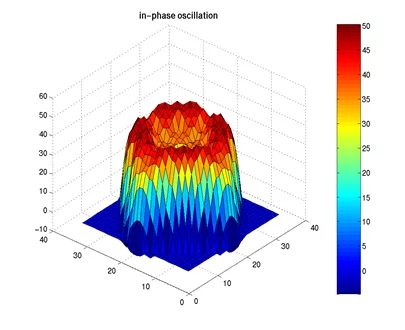
Signal Noise Analysis in Nuclear Reactors: when the disturbing role of noise becomes valuable
Noise appears in many areas of science, and commonly has an unwanted and disturbing nature by deteriorating signals’ quality. Therefore, various techniques have been developed over the years for separating noise from pure signals. However, noise has a key role in signal analysis of nuclear reactors as its’ appropriate assessment can be used not only for exploring the normal and dynamic behaviour of nuclear cores, but also for identifying and detecting possible anomalies of reactor systems. State of the art methods have been recently implemented within the well-established signal analysis methodology of the STARS program, at the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT), for investigating nuclear reactor noise and getting a better insight on analysing reactors’ operation.
Monte Carlo Simulation of Scintillation Detector for Spent Fuel Characterization in a Hot Cell
Spent fuel characterization is necessary to improve nuclear fuel design, optimize core refueling patterns and manage the handling, transport and storage of spent fuel assemblies. The experimental characterization of spent fuels includes measuring their gamma and neutron emissions typically with high-purity Germanium and He-3 detectors. In the past few years, however, efforts to develop efficient and low-cost, fast and thermal, neutron detectors have guided the research to the development of new scintillation detectors. These scintillators offer good efficiency, fast-timing properties, and good pulse shape discrimination capabilities for dual gamma and neutron detection. Within the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT), a preliminary analysis was performed through Monte Carlo simulations to design a measurement unit at the HOTLAB based on new scintillators for the detection of fast neutrons emitted by spent fuel. This semester work of Marianna Papadionysiou was presented at the ANS Student conference in April and received two awards for "Best Detection and Measurement" and "Best Overall Research".
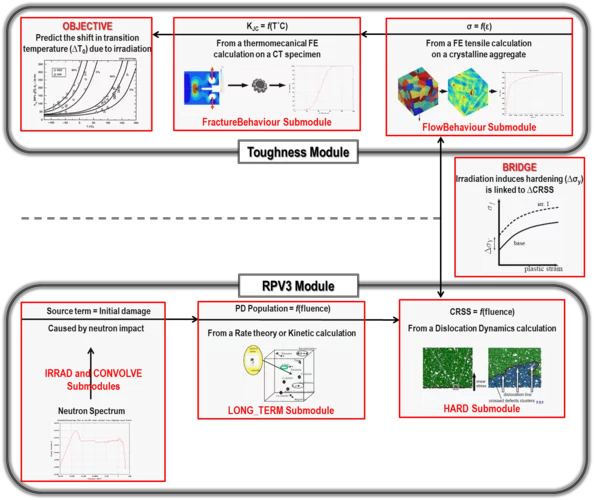
PERFORM-60: Modelling the Ageing of Reactor Vessel Steels
The main threat to the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) operational safety is certainly the radiation damage that hardens and embrittles the steel it is made of. Four decades of research worldwide have allowed understanding and monitoring the phenomena that come into play. At the computational level, a simulation platform, PERFORM-60, has the ambitious aim of predicting the steel evolution for most RPV and operational conditions. It was initially elaborated in the frame of the EU project of the same acronym and is currently further developed to be the end-product of the on-going H2020 EU project SOTERIA. As a contribution of the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Systems Behaviour (LRS) to SOTERIA, the platform has been rigorously assessed for the first time since its release on a real case study of a Swiss RPV. This critical assessment has been acknowledged by the community and serves as basis for improvements and future developments of the platform within SOTERIA.
The Dynamics of Nuclear Reactors
Nuclear reactor dynamics deals with the transient behaviour of nuclear reactors which mostly refers to time changes of the imbalance between heat production and removal. Since the prediction of the dynamic behaviour is crucial for the safety of a reactor, computational models and methodologies have been developed in the framework of the STARS project, at the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT), with the main goal to simulate the complex behaviours of reactors under various conditions with a high level of fidelity.
Une plus grande robustesse grâce aux imperfections
Le dioxyde d’uranium, combustible des centrales nucléaires, résiste mieux aux dégâts causés par les radiations quand sa structure présente des écarts microscopiques par rapport à un agencement idéal.
Simulations informatiques : un pilier essentiel de la sécurité des centrales nucléaires
Sans simulations informatiques, l’exploitation de centrales nucléaires serait pratiquement impossible. Qu’il s’agisse d’intégrer de nouveaux composants, ou de mener des tests et des essais visant à assurer la sécurité : presque tout doit être calculé et analysé par ordinateur au préalable. Au Laboratoire de physique des réacteurs et des comportements des systèmes, on développe à cet effet des modèles de calcul et des programmes informatiques. Les chercheurs du PSI officient dans ce cadre en tant que partenaires de recherche indépendants de l’IFSN (Inspection fédérale de sécurité nucléaire), et fournissent ainsi une contribution importante pour assurer la sécurité des centrales nucléaires suisses.
Quality Management
NES Open positions
Current job openings in the PSI Center for Nuclear Engineering and Sciences