The SIM beamline is dedicated to high-spatial resolution x-ray spectroscopy using polarized soft x-rays covering topics ranging from catalysis to battery research, and magnetism. Together with the upgrade of the Swiss Light Source (SLS) to a diffraction limited light source, the design of the SIM beamline has been improved to include two novel UE36knot (APPLE X type) x-ray undulator sources (delivering high intensity x-rays over an extended energy range on the fundamental harmonic) and new stigmatic x-ray optics to provide intense and spatially coherent x-rays with optimized wavefront, ideal for spectroscopy and scattering-based measurements.
The SIM beamline offers several endstations that are open to user via the SLS proposals system:
- A Photo-Emission Electron Microscope (PEEM) (Model: SPELEEM, Elmitec GmbH) as a permanent endstation. The instrument allows one to image samples using the photoelectric effect with very high spatial resolution (50 nm), with chemical and magnetic sensitivity. It is equipped with an energy analyzer for energy-selecting the excited photoelectrons. In addition to excitation by X-rays, illumination by low energy electrons is possible for low energy electron microscopy (LEEM) with additional contrast mechanisms.
- A multipurpose spectroscopy endstation (MultiXAS) - currently being commissioned.
- A soft x-ray ptychography microscope (SOPHIE) operated by the Microspectroscopy Group.
- An open port for user endstations (available after consultation with the beamline scientists).
The SIM beamline is operated by the Microscopy and Magnetism Group.
| Energy range | 260-1600 eV |
|---|---|
| Flux (1 keV) | 1 x 1015 photons/s/0.1%BW/ 0.4 A |
| Focused spot size | 30 µm x 30 µm (V x H) |
| Spectral resolution | > 5000 |
| Polarization | Linear: 0o (horizontal) , ± 45o, and 90o (vertical) Circular: right / left |
| Endstation (ES1) | Photo-emission electron microscope (PEEM) with spatial resolution ~ 50 nm, variable sample temperature: 50 - 1'800 K. |
| Endstation (ES2) | X-ray absorption spectroscopy chamber (MultiXAS) for total electron yield (TEY) and fluorescence (TFY) measurements in applied field (130 mT) and variable sample temperature (10 - 400 K). |
| Endstation (ES3) | Resonant x-ray scattering (RESOXS). Not open for users. Please contact Urs Staub. |
| Endstation (ES4) | Soft x-ray ptychography microscope (SOPHIE) operated by the Microspectroscopy Group. |
| Open port (ES) | External endstations such as near ambient pressure photo-emission (NAPP). These endstations belong to user groups and can only be used in collaboration with them. |
Current Highlights and News
News
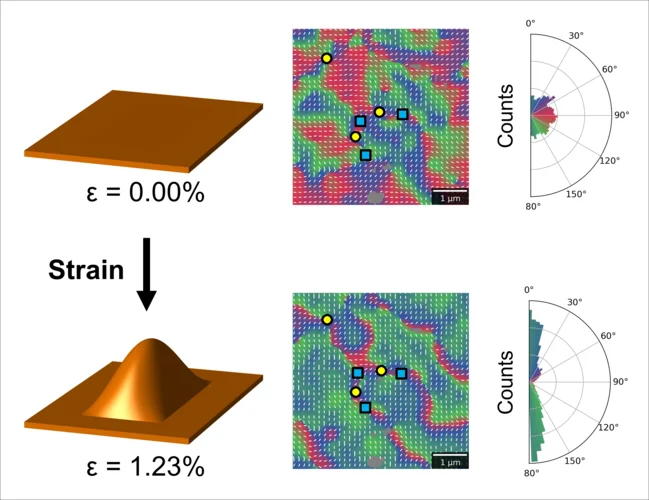
Designing antiferromagnetic domains by stretching membranes in STXM
Researchers from an international collaboration between the United Kingdom and Switzerland have performed imaging of an antiferromagnetic iron oxide membrane using soft X-ray microscopy. By stretching the membranes using a gas cell, the team investigated the modification of domain structures under strain.
Elusive multiferroicity in RNiO3 perovskites
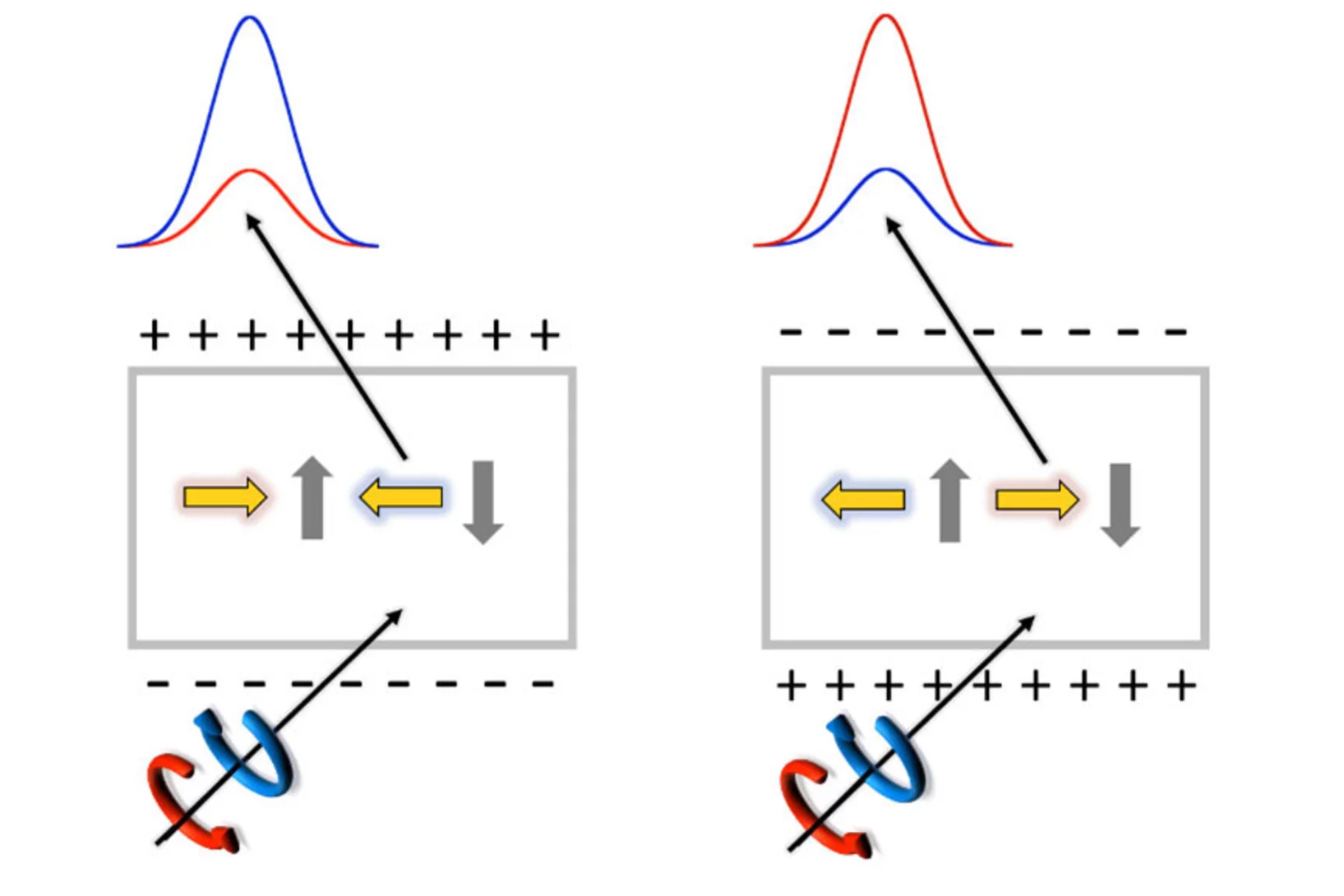
In our recent paper we examined YNiO3 and proved that the RNiO3 type material known for its metal-insulator transition is in fact a type II multiferroic. We provide direct evidence of an electric-field-driven switch of the noncolliear magnetic state finally confirming the proposed type II multiferroic nature of YNiO3.
Mechanism For All-Optical Magnetization Switching
X-rays reveal a non-collinear magnetic state as the base for all-optical magnetization switching.
Call schedule
| Call for proposals II-26 | |
|---|---|
| Experimental Period | II-26 |
| Call | 09 February 2026 |
| Submission deadline | 16 March 2026 (midnight, 23:59 CET) |
| Start period | 01 July 2026 |
| End period | 14 December 2026 |
| Notification of outcome | 26 May 2026 |