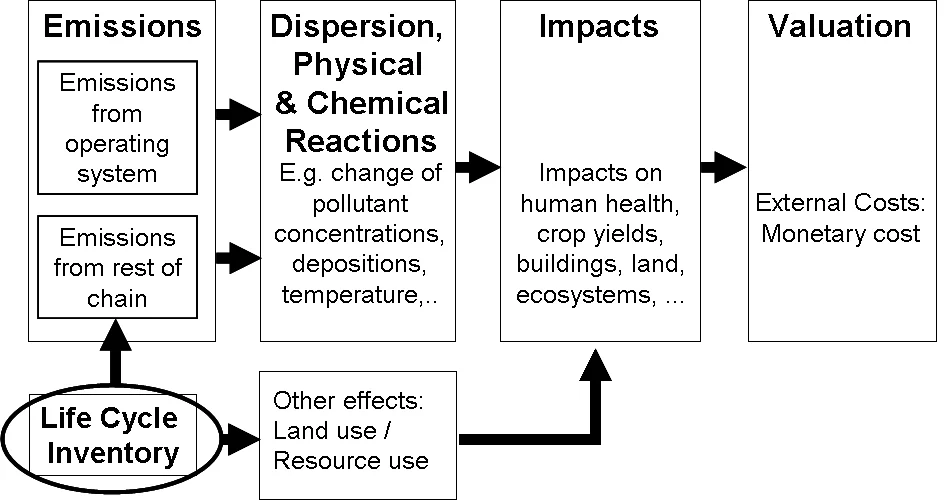
The basis of the environmental impact assessment method is the “impact pathway approach” including life cycle inventory data. The steps are shown in Figure 1.
The assessment starts with the modeling of emissions of the operating system under consideration (e.g. the power plant, or the vehicle). Fine particulates emissions are transported by wind through the air. The inhalation of fine particulate by humans causes health impacts. Not all fine particulates in the air are directly emitted from the combustion system. High temperature combustion processes generate nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions which are (together with other gaseous emissions) precursors for the formation of secondary particulates. Other air pollutants include hazardous metals and organic compounds.
Based on the emission data, the changes of the environment are modeled (e.g. increased air pollutant concentrations). The air quality model applies a 50 km x 50 km grid covering the whole of Europe. Wind carries air pollutants also over the borders. I.e. air emissions in a country cause impacts also in neighboring countries, which are included in the results.
The contributions of the life cycle (e.g. the fuel production, the vehicle production, etc.) to emissions and other burdens (e.g. land-use) are considered as well. For the modelling of the indirect emissions from “rest of chain”, the ecoinvent life cycle inventory database is used.
Exposure-response models are used to estimate the physical impacts on receptors. Impacts on human health include mortality (i.e., the loss of life expectancy) and a variety of morbidity impacts like chronic bronchitis, chronic cough in children, cough in asthmatics, lower respiratory symptoms, congestive heart failure, respiratory hospital admissions, and restricted activity days. In addition to health damages, impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, materials, and climate change are considered.
The last step is the aggregation of different environmental impacts in terms of external costs.
The environmental impact and external costs model is based on the EcoSense model developed in the ExternE project series of the European Union.
The special focus of the TA group is on the combination of environmental impact and external cost assessment with full-scope life cycle inventory analysis.
Selected Publications
Thomas Heck (2019). Advancements of environmental externality modelling of various modes of transportation (Poster). SCCER Mobility 6th Annual Conference, Zürich, Switzerland, ETHZ. https://www.dora.lib4ri.ch/psi/islandora/object/psi:26566
Thomas Heck (2015). Externalities assessment of wood energy in Switzerland. Proceedings of the 23rd European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, 1-4 June 2015, Vienna, Austria, pp. 1393-1401. http://dx.doi.org/10.5071/23rdEUBCE2015-4CO.1.3
Thomas Heck (2014). Health impacts of PM emissions from passenger cars in Europe and reduction potentials due to electric vehicles. Proceedings of the 20th International Transport and Air Pollution Conference, 18-19 September 2014, Graz, Austria. https://www.tapconference.org/assets/files/previous-conferences/proceedings/2014_Proceedings.zip
Thomas Heck and Nickolas K. Meyer (2012): External costs of wood combustion systems in Switzerland. Proceedings of the 20th European Biomass Conference, 18-22 June 2012, Milano, Italy, pp. 2251 – 2256. http://dx.doi.org/10.5071/20thEUBCE2012-5AV.1.25
Nickolas K. Meyer (2011). “Particulate, black carbon and organic emissions from small-scale residential wood combustion appliances in Switzerland” Biomass & Bioenergy, 2011, 36, 31-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.09.023