The Surface/Interface Spectroscopy (SIS) beamline provides a state-of-the-art experimental set-up to study the electronic band structure of novel complex materials by spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopies. The beamline operates in the energy range from 20 to 800 eV with high flux, high resolution, variable polarization, and low high-harmonic contamination.
The beamline serves two endstations:
- ULTRA (Ultra Low-Temperature high-Resolution ARPES)
for angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES) - COPHEE (Complete PHotoEmission Experiment)
for spin- and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (SARPES)
Users can apply for beamtime with the provided endstations or with their own endstation (after prior consultation with the beamline scientist).
| Energy range | 20 - 800 eV |
|---|---|
| Resolving power (E/Δ E) | 104 |
| Polarization | linear horizontal (20 - 800 eV) linear vertical (40 - 800 eV) circular left/right (50-800 eV) |
| Flux on sample (200 eV) | 2*1013 ph/s/0.1%BW/0.4 A |
| Higher order mode contamination | < 0.1 % |
| Spot size on sample (200 eV) | 50 x 100 µm2 (FWHM) |
Current Highlights and News
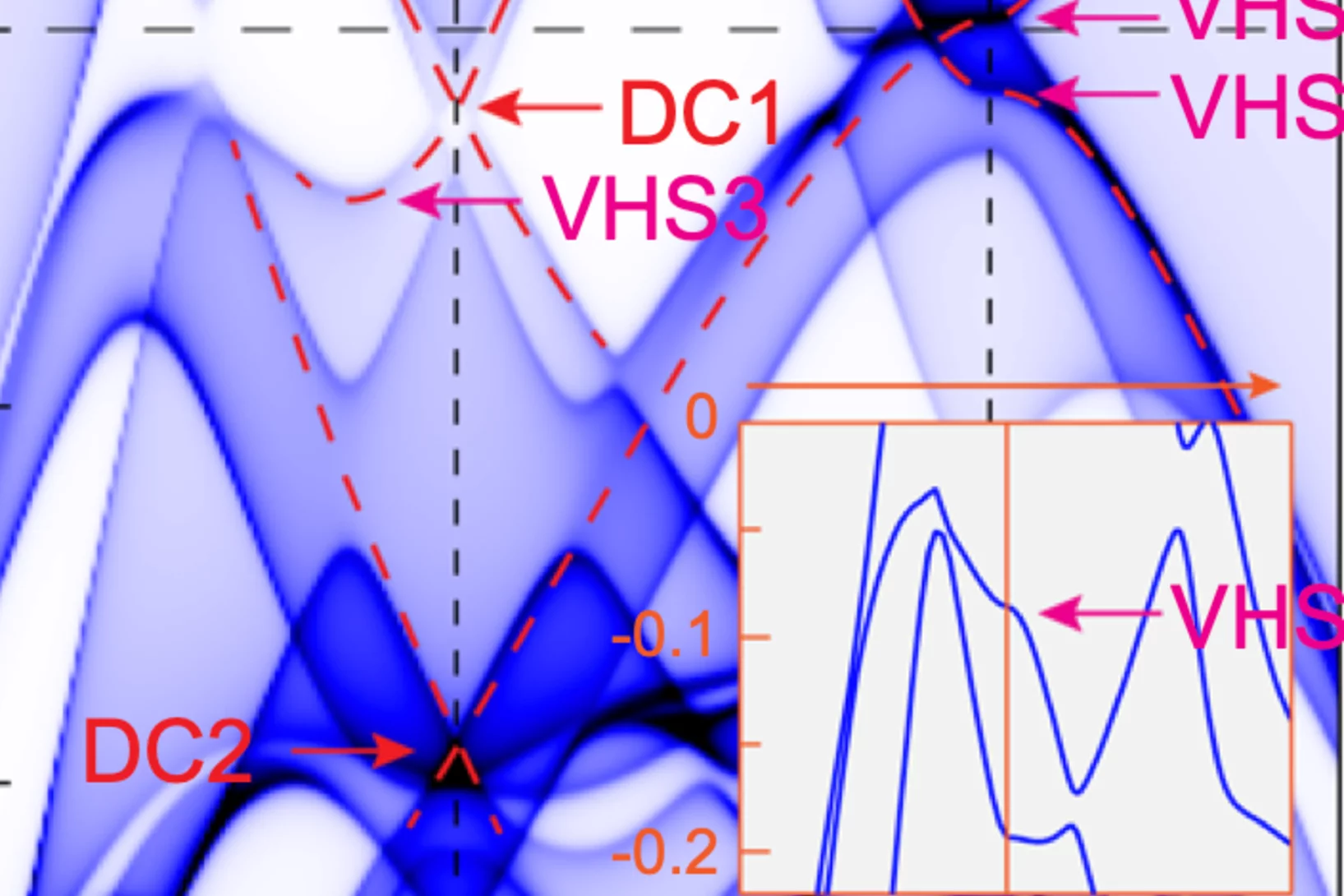
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...
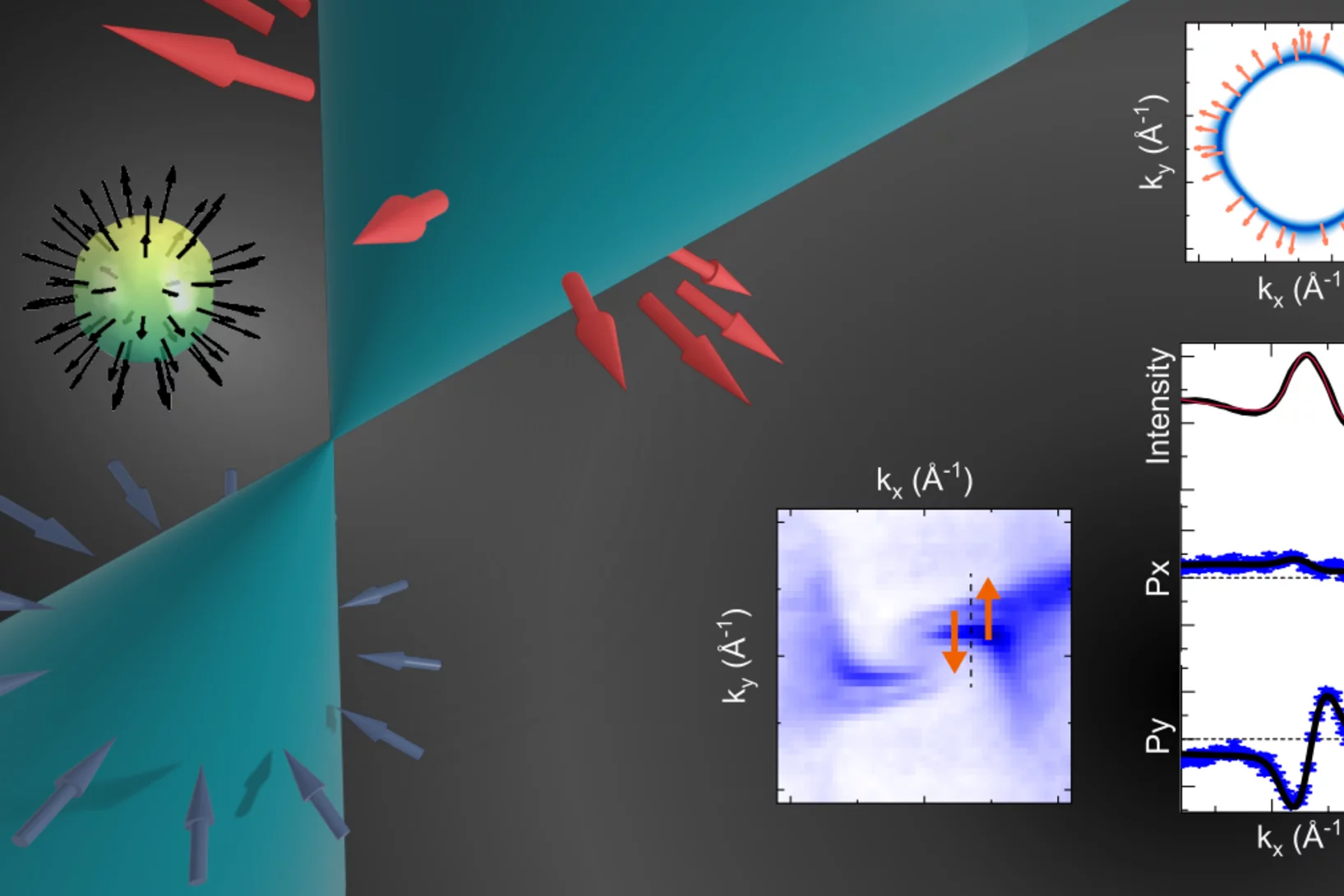
Weyl spin-momentum locking in a chiral topological semimetal
Spin–orbit coupling in noncentrosymmetric crystals leads to spin–momentum locking – a directional relationship between an electron’s spin angular momentum and its linear momentum. Isotropic orthogonal Rashba spin–momentum locking has been studied for decades, while its counterpart, isotropic parallel Weyl spin–momentum locking has remained elusive in experiments. Theory predicts ...
De nouveaux matériaux pour les ordinateurs du futur
Des chercheurs identifient et étudient des compositions de matériaux dont les propriétés particulières pourraient permettre de concevoir des puces d’un genre nouveau.