Turbulent natural convection in the containment during severe accidents can affect the depletion of the fission product particles and other nuclear aerosols. The information of the particle concentration in containment atmosphere at different periods of the accident is vital for estimation of the source term if a leakage from the containment or a containment failure occurs.
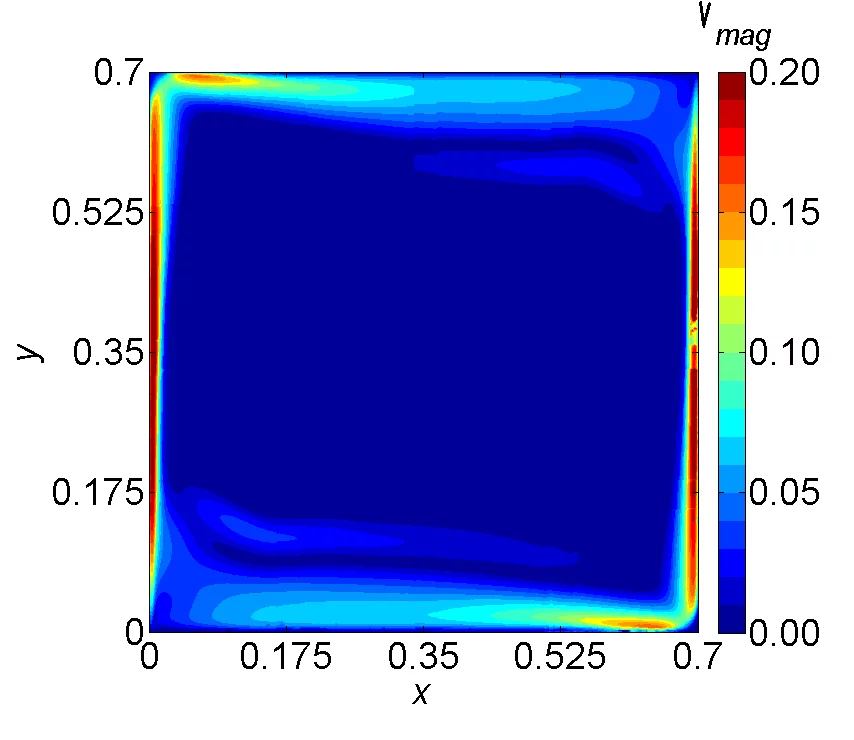
The DIfferentially heated cavity with Aerosol in turbulent NAtural convection (DIANA) facility was used to experimentally investigate the effects of turbulent natural convection on aerosol deposition inside a cubical cavity with two opposing isothermal vertical walls and adiabatic top, bottom, front and back walls with a Rayleigh number approximately 109. The flow field in the mid-plane joining the isothermal walls was investigated using Particle Image Velocimetry. Gas temperature measurements were collected using K-type thermocouple. The deposition of dp = 1 µm and dp = 2.5 µm SiO2 particles was studied in DIANA, using light intensity as well as online mass concentration measurements with Tapered Element Oscillating Microbalance (TEOM).
The flow and temperature data was used to validate a large eddy simulation (LES) model of the cavity using realistic measured temperature boundary conditions at horizontal cavity walls. The LES was able to predict well the mean and fluctuating flow fields and was therefore used in a Lagrangian particle tracking simulation. The particle tracking results matched well with the measurement, showing that with the larger particle size, the deposition was mainly caused by the gravitational settling to the cavity floor. The results indicated that due to the turbulent flow, the particles stayed approximately uniformly distributed in the atmosphere resulting in almost identical deposition rate everywhere in the cavity. However, it was shown that the theoretical stirred settling model, where uniformly distributed particles in a cubic volume settle only through sedimentation, was unable to accurately predict the particle depletion rate with 1 µm particles. It was concluded that the geometry of the flow has a profound effect on the particle deposition rates in the cavity and stirred settling model is too simplified for accurate description of particle deposition in these specific flow conditions.
Experimental Investigation of a Turbulent Particle-Laden Flow Inside a Cubical Differentially Heated Cavity
J.Kalilainen, P.Rantanen, T.M.Lind, A.Auvinen, A.Dehbi
Journal of Aerosol Science 100, 73-87
DOI: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2016.06.001