NUM division - Publication Highlights
Waves on circular paths
Just as electrons flow through an electrical conductor, magnetic excitations can travel through certain materials. Such excitations, known in physics as "magnons" in analogy to the electron, could transport information much more easily than electrical conductors. An international research team has now made an important discovery on the way towards such components, which could be highly energy-efficient and considerably smaller.
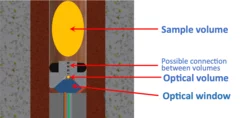
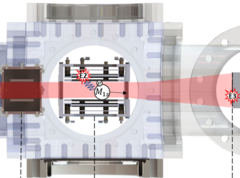
Optical Setup for a Piston-Cylinder Pressure Cell: A Two-Volume Approach
Measurement of the absolute value of the applied pressure in high-pressure muon and neutron experiments is a complicated task. It often requires the presence of a calibration material inside the sample volume, and could also cause additional time to obtain the response of the calibrant. Here we describe the use of optical calibrants for precise determination of the pressure value inside the piston-cylinder clamp cells.
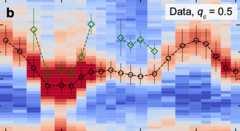
Antiferromagnetic excitonic insulator state in Sr3Ir2O7
Excitonic insulators are usually considered to form via the condensation of a soft charge mode of bound electron-hole pairs. This, however, presumes that the soft exciton is of spin-singlet character. Early theoretical considerations have also predicted a very distinct scenario, in which the condensation of magnetic excitons results in an antiferromagnetic excitonic insulator state. Here we report resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) measurements of Sr3Ir2O7.
New insight into unconventional superconductivity
Signatures for a novel electronic phase that enables charge to flow spontaneously in loops have been observed in a kagome superconductor. The findings are published today in Nature.
Muon spin spectroscopy
Muons are particles with a spin of 1⁄2 that can be implanted into a wide range of condensed matter materials to act as a local probe of the surrounding atomic environment. Measurement of the muon’s precession and relaxation provides an insight into how it interacts with its local environment. From this, unique information is obtained about the static and dynamic properties of the material of interest ...
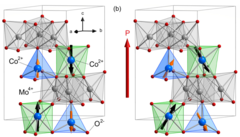
Confirming the trilinear form of the optical magnetoelectric effect in the polar honeycomb antiferromagnet Co2Mo3O8
Magnetoelectric phenomena are intimately linked to relativistic effects and also require the material to break spatial inversion symmetry and time-reversal invariance. Magnetoelectric coupling can substantially affect light–matter interaction and lead to non-reciprocal light propagation. Here, we confirm on a fully experimental basis, without invoking either symmetry-based or material-specific assumptions, that the optical magnetoelectric effect in materials with non-parallel magnetization (M) and electric polarization (P) generates a trilinear term in the refractive index...
Precision Measurement of the Lamb Shift in Muonium
We report a new measurement of the n=2 Lamb shift in Muonium. Our result of 1047.2(2.3)stat(1.1)syst MHz comprises an order of magnitude improvement upon the previous best measurement. This value matches ...
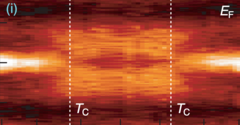
Signatures of Weyl Fermion Annihilation in a Correlated Kagome Magnet
The manipulation of topological states in quantum matter is an essential pursuit of fundamental physics and next-generation quantum technology. Here we report the magnetic manipulation of Weyl fermions in the kagome spin-orbit semimetal Co3Sn2S2, observed by high-resolution photoemission spectroscopy. We demonstrate the exchange collapse of spin-orbit-gapped ferromagnetic Weyl loops into paramagnetic Dirac loops under suppression of the magnetic order.
The world’s most powerful neutron microscope
PSI scientists help construct the new European Spallation Source ESS