Energy and Climate
The energy research performed at PSI focuses on processes that can be used in sustainable and safer technologies, ideally with minimal CO2 emissions. The main emphasis is on renewable energy sources. The ESI (Energy System Integration) platform enables research and industry to test solutions for integrating renewables into the existing energy supply. Another focus in this area is the safer use of nuclear energy. These activities are supplemented by analyses giving a comprehensive assessment of energy systems. PSI scientists in the Energy and Environment division study the chemical processes that take place in the atmosphere.
Find out more at: Overview Energy and Climate
Toward better motors with X-ray light
Making Switzerland's road traffic fit for the future calls for research, first and foremost. In the large-scale research facilities of PSI, chemists and engineers are investigating how to improve the efficiency of motors and reduce their emissions.
From the Walkman to the electric car
Three researchers share this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry. They are being honoured for their respective contributions to the development of lithium-ion batteries. Petr Novák of PSI likewise works in this area of research and has known the three laureates personally for decades. In an interview, he tells about sitting directly across from one of them at the crucial moment.
Thirteen months in the Arctic
A PSI research project investigating atmospheric chemistry will be on board the icebreaker Polarstern on 20th September 2019. Researcher Julia Schmale talks about the upcoming expedition and her role in it.
"This is incredibly ambitious"
Every three years, the World Energy Council explores possible developments of the global energy system under different scenarios. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group in PSI’s Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis and one of the lead authors of the study, explains what the individual scenarios mean and how global warming could be mitigated.
Observing solid-state batteries during deformation
PSI researchers have observed mechanical processes in solid-state batteries with unprecedented precision. Using X-ray tomography at the Swiss Light Source SLS, they discovered how fissures inside the batteries propagate. These insights can help to make batteries for electric cars or smartphones safer and more efficient.
Research above – and about – the clouds
At the Jungfraujoch research station, PSI scientists study particulate matter in the atmosphere. And have to deal with the fact that the human body is not made for life at 3,500 metres above sea level.
The energy system of the future and Power-to-X
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI analyse the potential of Power-to-X for Switzerland's energy supply and present their conclusions in a white paper. One finding: The costs for energy from Power-to-X could fall by up to one-third.
In fresh air and in smog
PSI researchers drill through millennia-old glacier ice in the high mountains and analyse the world's highest particulate concentrations in Delhi, India. They are helping to address questions regarding climate change and to reduce air pollution.
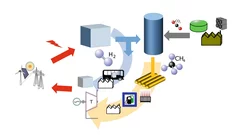
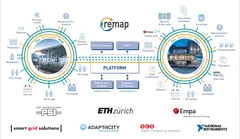
Testing the energy system of the future today, as realistically as possible
With the kick-off of the ReMaP project, companies have another opportunity to test their vision for the energy system of the future now. PSI's ESI platform helps to make better and more intelligent use of renewable energy in the future.
Cladding tubes and their properties
In the Nuclear Energy and Safety Research Division at PSI, Johannes Bertsch focuses on the so-called cladding tubes that are used in nuclear power plants.
Watching electrons and switching bits on
Electronics should get smaller, faster, and above all more energy-efficient. These themes are also present in several research groups at PSI. From incremental improvements to complete rethinking – who is currently working on what?
Why the Little Ice Age ended in the middle of the 19th century
In the first half of the 19th century, a series of large volcanic eruptions in the tropics led to a temporary global cooling of Earth's climate. That Alpine glaciers grew and subsequently receded again during the final phase of the so-called Little Ice Age was due to a natural process. This has now been proven by PSI researchers on the basis of ice cores.
Cleaner emissions thanks to sponge-like structure
PSI researchers have developed a new catalytic converter for cleaning emissions from natural gas engines. It is very active even at low temperatures and remains that way over a long period of time. This allows natural gas to be burned in a cleaner, more climate-friendly way. Thus natural gas and biogas become more attractive as substitutes for petroleum products – for example, as fuel for cars.
Cleaner diesel emissions
PSI researchers have found out why it is harder to control the noxious nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust at low temperatures – and how, in the future, emissions can be cleaned more efficiently depending on the temperature.
Power on demand
If photovoltaic or wind power plants produce more electricity than the network can absorb, valuable energy is lost. At the ESI Platform, PSI researchers are investigating how fuel cells can contribute to making this energy usable in a targeted way through storage.
Profitable for both sides
The young company Swiss Hydrogen is located in Fribourg. Here work is under way on competitive high-performance fuel cells that could be used in environmentally friendly vehicles or deployed as stationary power generators. In the company's collaboration with PSI, as CEO Alexandre Closset explains in this interview, both sides profit.
New technology undergoes real-world testing
The Zurich-based power company Energie 360° provides natural gas, biogas, and wood pellets throughout Switzerland. Now, with the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, it has successfully tested a new Power-to-Gas technology to be implemented in the area of biogas production. The joint project was awarded the Swiss energy prize Watt d'Or 2018. In this interview, division manager Peter Dietiker talks about the collaboration with PSI.
Using what's there
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers are looking for solutions that enable energy from the sun, the wind, or biomass to be efficiently integrated into the Swiss energy system.
Efficient energy from biowaste – Watt d'Or for PSI and Energie 360°
Efficiently producing energy from biowaste: A technology developed at PSI and tested in collaboration with the Zurich-based energy provider Energie 360° makes it possible. It extracts significantly more methane from biowaste than conventional methods. For this important contribution to a sustainable energy supply, PSI and Energie 360° have now been awarded the Watt d'Or 2018 in the Renewable Energy category by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy.
Stress test passed
With a technology developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, around 60 percent more biogas can be produced from bio-waste than with conventional methods. But can it stand the test in practice as well? A 1,000-hour test at the Werdhölzli biowaste digestion and wastewater treatment plant in Zurich was able to answer this question with a clear yes. It was carried out in cooperation with the Zurich-based energy provider Energie 360°. The analysis of the stress test is now available.