Energy and Climate
The energy research performed at PSI focuses on processes that can be used in sustainable and safer technologies, ideally with minimal CO2 emissions. The main emphasis is on renewable energy sources. The ESI (Energy System Integration) platform enables research and industry to test solutions for integrating renewables into the existing energy supply. Another focus in this area is the safer use of nuclear energy. These activities are supplemented by analyses giving a comprehensive assessment of energy systems. PSI scientists in the Energy and Environment division study the chemical processes that take place in the atmosphere.
Find out more at: Overview Energy and Climate
More than just spilling the beans
Because of their high nitrogen content, spent coffee grounds are a popular garden fertilizer. Recycled in this manner, they already contribute to an environmentally friendly waste management. But they have the potential to deliver much more: a new procedure developed at the PSI allows high quality methane to be formed from spent coffee grounds. PSI researchers involved in a pilot project carried out in cooperation with the Swiss food producer Nestlé were able to show that spent coffee grounds left over during the production of instant coffee can be efficiently re-used elsewhere.
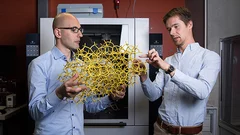
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
Efficient electrolysers are needed in order to store sun and wind energy in the form of hydrogen. Thanks to a new material developed by researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa, these devices are likely to become less costly and more efficient in the future. Researchers were also able to demonstrate that this new material can be reliably produced in large quantities, showing its performance capability in an electrolysis cell—the main component of an electrolyser.
Fuel and chemicals from plant waste
Lignin, as a constituent of many plants, accumulates in large quantities and could theoretically be used as a precursor material for production of fuels and chemicals. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have developed a method with which the processes that take place in the catalytic breakdown of lignin can be observed in detail. The knowledge thus gained could enable targeted improvement of production methods in the future.
Quartz powder for the battery of the future
PSI materials researchers have developed a method that provides crucial insights into the charging and discharging processes of lithium-sulphur batteries. And the method revealed: with quartz powder added to the battery, its available energy increases and the gradual loss of capacity is much weaker.
Making a valuable resource usable with water
In oil extraction sites, gaseous methane is simply burned, even though it could actually be a useful precursor material for fuels and products of the chemical industry. One way to make methane usable is to convert it to methanol. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have now developed a new chemical process that allows this conversion in an efficient and inexpensive way.
Welcome to Esiville
A new visitor’s station at PSI tells the story of a Swiss town that makes the change from a conventional energy supply to one with new renewable energy sources.
How Switzerland could supply its electric power in 2050
The Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI is investigating how Switzerland’s electricity supply might look, up to the year 2050, under a variety of boundary conditions. On the basis of their calculations, the lab’s researchers are able to generate insights on possible future developments of the energy sector, for example, determine how an ambitious reduction in CO2 emissions could be achieved at the lowest possible cost.
Historical copper, trapped in ice
Until now, the onset of copper production in South America was still unclear. Hardly any written records or artefacts from the early high cultures in Peru, Chile, and Bolivia have been preserved. Now, however, researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI in Villigen (Switzerland) have tracked down the evidence. Through analysis of ice from the Illimani glacier in the Bolivian Andes, they found out that copper was being mined and smelted in South America since around 700 BC.
Higher methane yield from bio-waste
Within Switzerland’s bio-waste a huge amount of precious energy is hidden. That’s because valuable methane, the main constituent of natural gas, can be obtained from it. With a technology developed at PSI, the yield of methane from bio-waste could be increased considerably in the future. A long-term test conducted in cooperation with Energie 360° at the Werdhölzli fermentation and wastewater treatment plant is expected to advance this technology further along its path to industrial use.
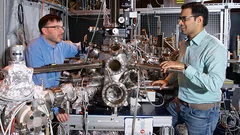
Nanotechnology enables new insights into chemical reactions
Eighty percent of all products of the chemical industry are manufactured with catalytic processes. Catalysis is also indispensable in energy conversion and treatment of exhaust gases. Industry is always testing new substances and arrangements that could lead to new and better catalytic processes. Researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI in Villigen and ETH Zurich have now developed a method for improving the precision of such experiments, which may speed up the search for optimal solutions.
The open-air researcher
Atmospheric scientist Julia Schmale is starting out on a three-month research cruise around the Antarctic. There she will be searching for the cleanest air still to be found on our planet.
Simulations for More Efficient Power Stations
In most cases, electricity is generated when water is heated and transformed into vapour. Vapour bubbles in the water play a decisive role in this process. Using computer simulation, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have succeeded in representing the behaviour of vapour bubbles – and in making their performance more calculable.
The substances that brighten up the clouds
Clouds consist of tiny droplets. These droplets form when water condenses around so-called aerosols – small particles in the atmosphere. To understand how in turn aerosols come into existence scientists have now created a comprehensive computer model simulation based on profound experimental data. This simulation revealed that in addition to sulphuric acid, two other substances are crucially involved in the formation of aerosols: organic compounds and ammonia. These results have now been published in the renowned journal Science.
Molten salt reactors – exploring an alternative
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, a small group of scientists is using theoretical models to explore an alternative for future nuclear reactors: so-called molten salt reactors. This helps to secure Switzerland’s expertise regarding globally relevant questions in the area of nuclear energy and reactor safety, for today and tomorrow.
Renewable energy: Experimental platform ESI is starting up
This fall, the time has come: The Energy System Integration Platform at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI goes into operation. Today, in the framework of the double conference Networked Energy Research Switzerland, it was presented to the media and around 150 representatives from politics, industry, and science.
Sun-Petrol
Despite its great potential, solar energy still faces one big problem: the sun doesn’t always shine and its energy is hard to store. Now, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the ETH Zurich have unveiled a chemical process that uses the sun’s thermal energy to convert carbon dioxide and water directly into high-energy fuels: a procedure developed on the basis of a ground-breaking material combination of cerium oxide and rhodium.
Rechargeable batteries that last longer and recharge more rapidly
Researchers at the Swiss Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and ETH Zurich have developed a simple and cost-effective procedure for significantly enhancing the performance of conventional Li-ion rechargeable batteries. Whether in wristwatches, smartphones, laptops or cars, the use of rechargeable batteries will be optimized in all areas of application, considerably extending storage capacity as well as cutting down charging times.
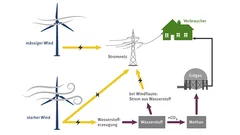
Turning Electricity into Gas – and back into Electricity
As capacities for producing solar and wind energy increase, integrating these into the existing energy system is becoming more of a challenge. The ESI platform is testing methods for successful integration. The answer: storing surplus energy as gas.
High-performance catalytic converters for natural-gas vehicles
Natural-gas vehicles are on the way, and they need catalytic converters for the exhaust too. While work is under way at Empa, the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Testing and Research, to optimise natural-gas engines and catalytic converters, the PSI is specialising in research methods that enable very precise observation of catalytic converters. For this work, the PSI researchers have now developed a universal measurement chamber in which catalytic converters can be studied with a variety of different analytical methods, yet always under the same conditions.
Present-day measurements yield insights into clouds of the past
Researchers have shown how fine particles are formed from natural substances in the atmosphere. These findings will improve our knowledge about clouds in the pre-industrial era and thus will contribute to a more accurate understanding of both the past and future evolution of our climate.