Show filters
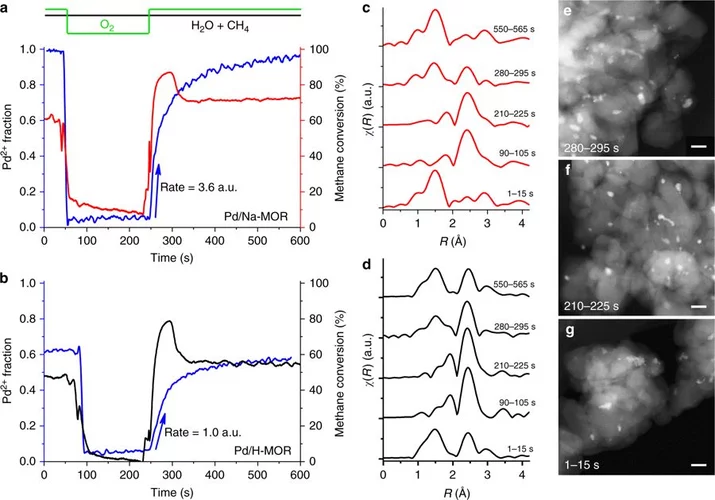
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Using targeted synthesis and in situ characterization a palladium catalyst with improved stability against sintering during methane oxidation was prepared.
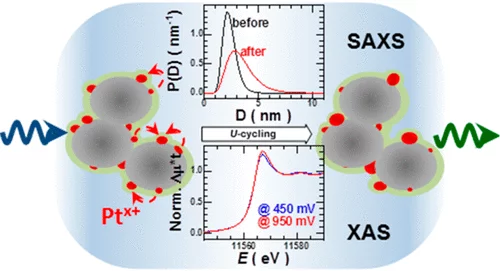
Combining SAXS and XAS To Study the Operando Degradation of Carbon-Supported Pt-Nanoparticle Fuel Cell Catalysts
In the last two decades, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) have evolved into two well-established techniques capable of providing complementary and operando information about a sample’s morphology and composition, respectively. Considering that operation conditions can often lead to simultaneous and related changes in a catalyst’s speciation and shape, herein we introduce a setup that combines SAXS and XAS in a configuration that allows optimum acquisition and corresponding data quality for both techniques.
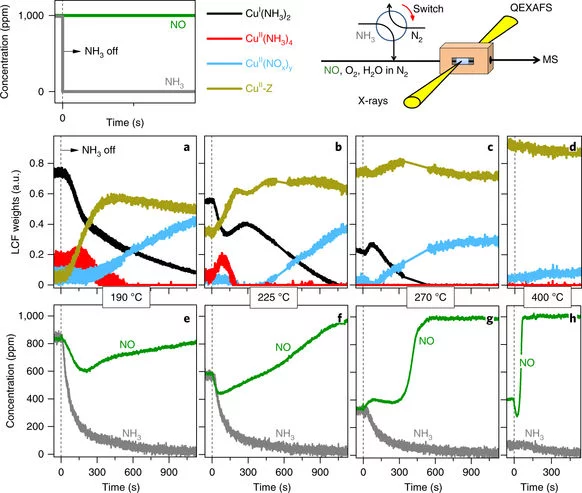
Time-resolved copper speciation during selective catalytic reduction of NO on Cu-SSZ-13
Through the combination of time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy and transient experimentation, we were able to capture an ammonia inhibition effect on the rate-limiting copper re-oxidation at low temperature.
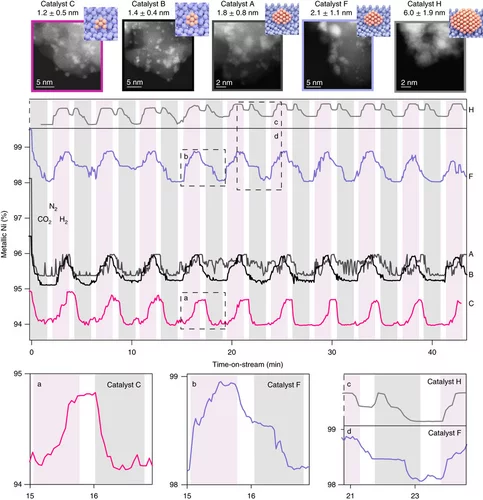
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
Nanomaterial helps store solar energy: efficiently and inexpensively
By combining a scalable cutting-edge synthesis method with time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it was possible to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure during realistic operando conditions for highly active OER perovskite nanocatalysts.
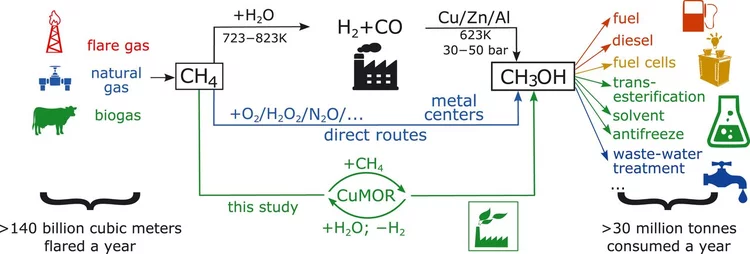
Selective anaerobic oxidation of methane enables direct synthesis of methanol
On the basis of in situ x-ray absorption spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations, it was proposed a mechanism involving methane oxidation at Cu II oxide active centers, followed by Cu I reoxidation by water with concurrent formation of hydrogen.
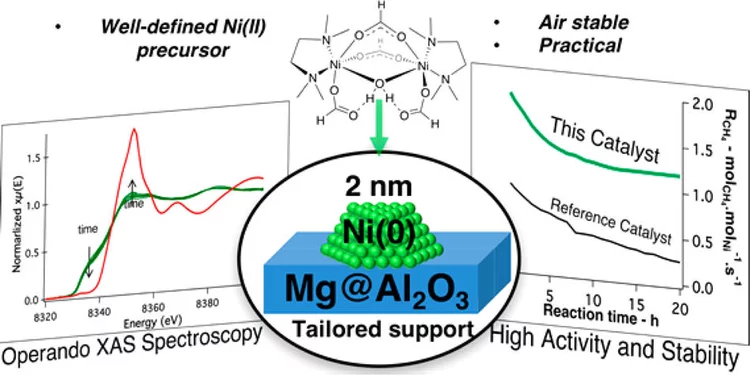
Molecularly Tailored Nickel Precursor and Support Yield a Stable Methane Dry Reforming Catalyst with Superior Metal Utilization
The superior performance of molecularly tailored methane dry reforming catalyst resulted in a maximization of the amount of accessible metallic nickel in the form of small nanoparticles preventing coke deposition. Operando X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy confirms that deactivation largely occurs through the migration of Ni into the support.
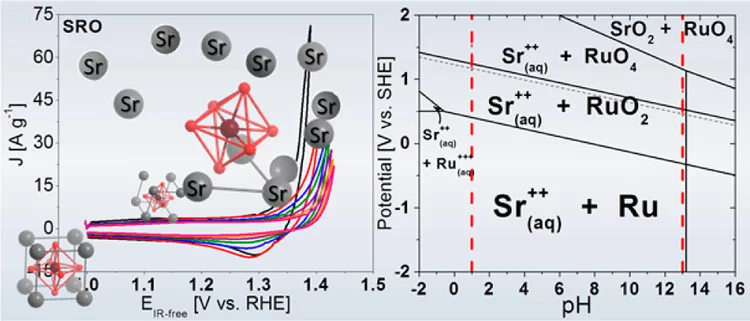
Unraveling Thermodynamics, Stability, and Oxygen Evolution Activity of Strontium Ruthenium Perovskite Oxide
Ru-based perovskites, i.e. SrRuO3 and LaRuO3, have been predicted as active perovskites to exhibit a particularly high oxygen evolution reaction activity. We highlight that understanding the origin of stability under a real operating environment is absolutely essential for the design of a sustainable electrocatalyst with optimal balance between activity and stability.
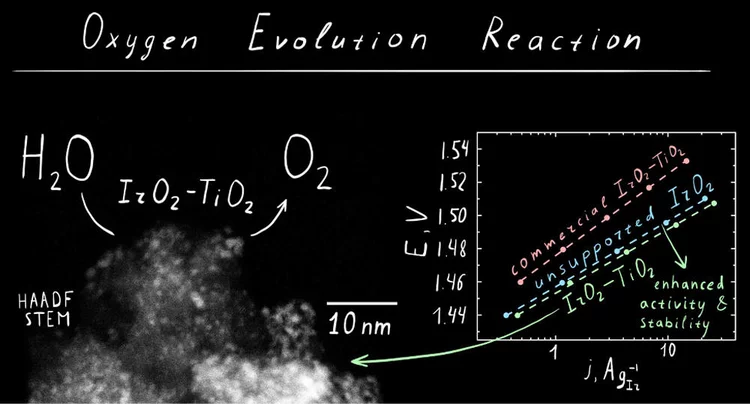
IrO2‑TiO2: A High-Surface-Area, Active, and Stable Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
We have developed a synthetic approach to highsurface-area chlorine-free iridium oxide nanoparticles dispersed in titania (IrO2-TiO2), which is a highly active and stable OER catalyst in acidic media. Operando X-ray absorption studies demonstrate the evolution of the surface species as a function of the applied potential, suggesting the conversion of the initial hydroxo surface layer to the oxo-terminated surface via anodic oxidation.
Detecting and utilizing minority phases in heterogeneous catalysis
Highly active phases in carbon monoxide oxidation are known, however they are transient in nature. Here, we determined for the first time the structure of such a highly active phase on platinum nanoparticles in an actual reactor.
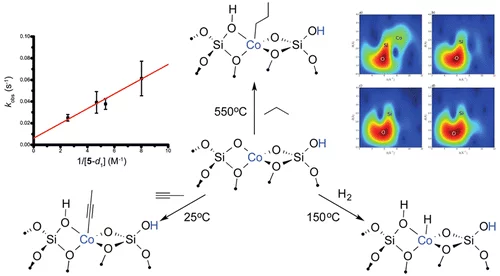
C–H Activation on Co,O Sites: Isolated Surface Sites versus Molecular Analogs
The activation and conversion of hydrocarbons is one of the most important challenges in chemistry. This work shows that isolated Co(II) sites are catalysts for a number of hydrocarbon conversion reactions, such as the dehydrogenation of propane, the hydrogenation of propene, and the trimerization of terminal alkynes. The data are consistent with all of these reactions occurring by a common mechanism, involving heterolytic C–H or H–H activation via a 1,2 addition across a Co–O bond.
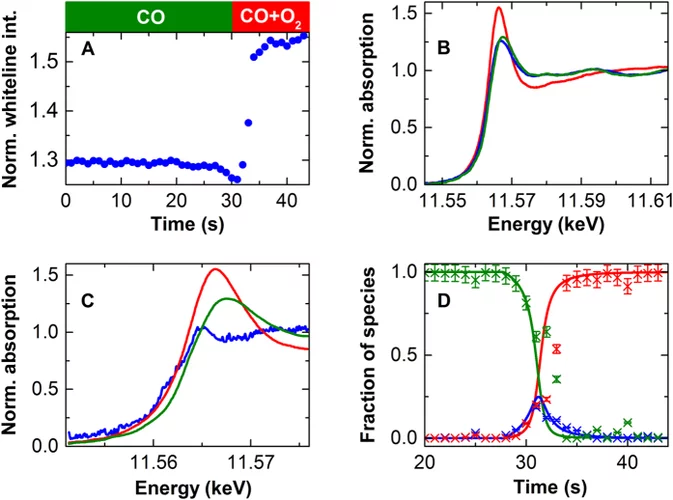
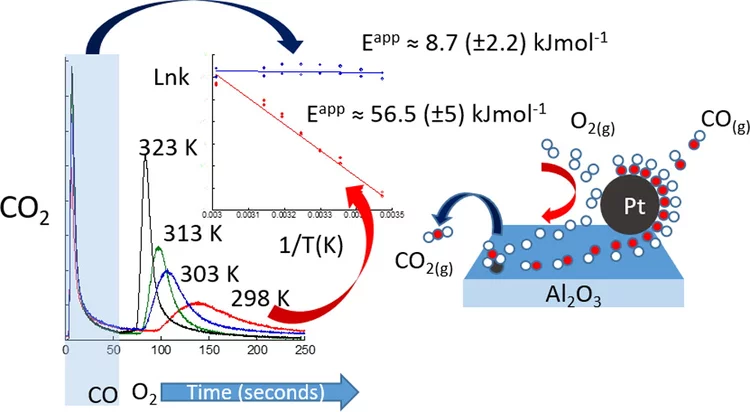
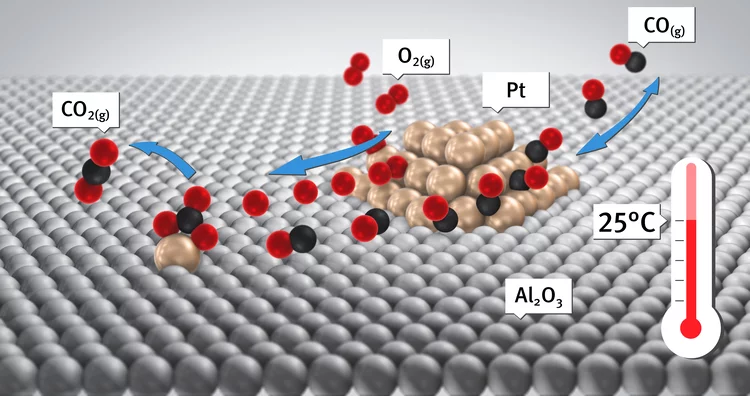
Kinetic studies of the Pt carbonate-mediated, room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 using combined, time-resolved XAFS, DRIFTS, and mass spectrometry
The kinetics involved in novel ambient-temperature mechanism for the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide by oxygen over a Pt/Al2O3 catalyst is evaluated within a periodic redox operation paradigm using combined mass spectrometry (MS), diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy (DRIFTS), and time-resolved Pt L3-edge XAFS. A high-wavenumber (ca. 1690 cm-1) carbonate species are shown to be associated with a room-temperature redox process occurring in a fraction of the Pt atoms present in the catalyst.
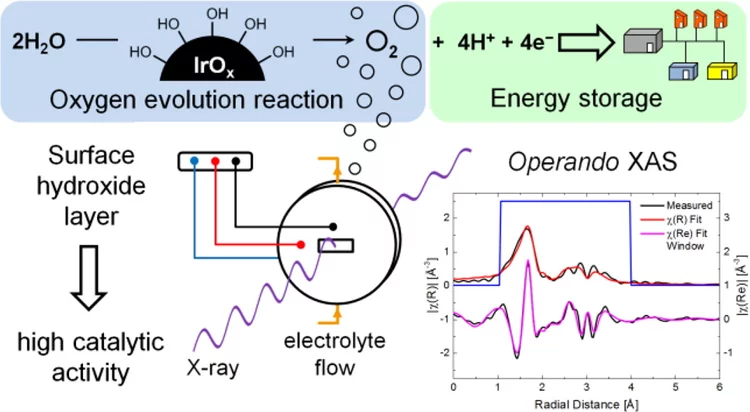
Iridium Oxide for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Correlation between Particle Size, Morphology, and the Surface Hydroxo Layer from Operando XAS
A simple and scalable method for preparation of well-defined chlorine–free iridium oxide nanoparticles active for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) was developed. Operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicate that OER activity is strongly related to the presence of iridium hydroxo (Ir–OH) species on the surface of iridium oxide nanoparticles.
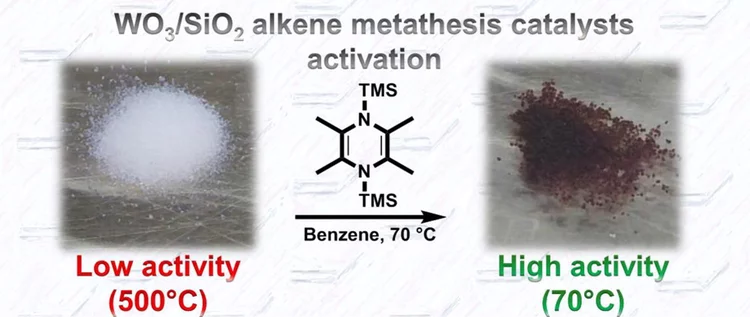
Low temperature activation of supported metathesis catalysts by organosilicon reducing agents
Industrial alkene metathesis processes rely on silica-supported tungsten oxide catalysts, which operate at high temperatures (>350 °C) due to the difficulty in generating active sites (carbenes or metallacyclobutanes). We report here a low temperature activation process of well-defined metal oxo surface species using organosilicon reductants, which generate a large amount of active species at only 70 °C (0.6 active sites/W).
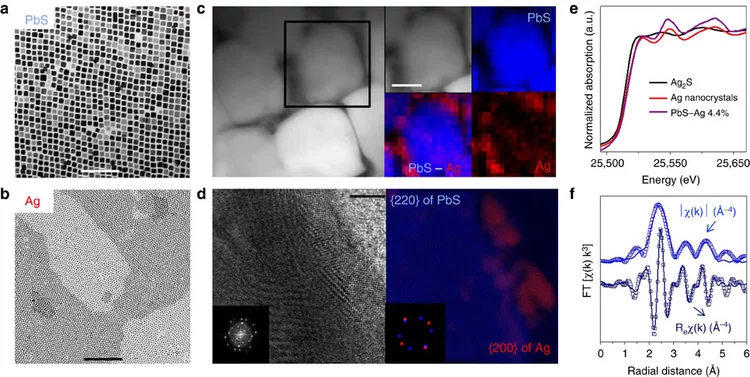
High-performance thermoelectric nanocomposites from nanocrystal building blocks
Using an assembly of colloidal nanocrystals a Ag-PbS nanocomposite was produced with increased thermoelectic figures of merit up to 1.7K at 850 K. EXAFS spectroscopy at the Ag K-edge was essential to show that Ag does not dissolve in PbS nanoparticles but preserved the individual nanodomains. This reduces the PbS intergrain energy barriers for charge transport
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt-Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
A new possibility for the attainment of low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide is demonstrated. Here we report using time-resolved DRIFTS, XAS, and mass spectrometry a platinum carbonate-mediated mechanism for the room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide.
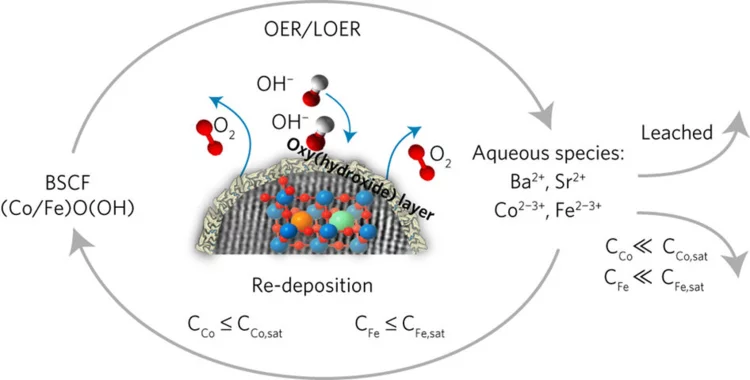
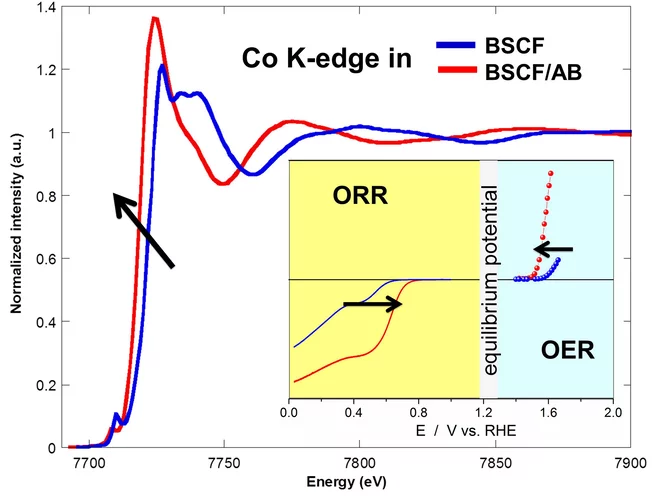
Superior Bifunctional Electrocatalytic Activity of Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ/ Carbon Composite Electrodes: Insight into the Local Electronic Structure
Using XAS it was demonstrated that carbon acts as an activity booster for Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3 oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalyst promoting change of cobalt oxidation state.
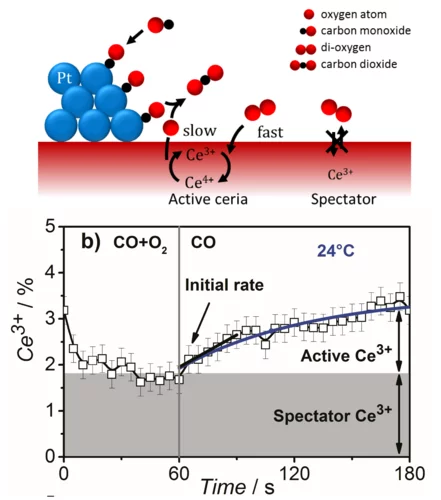
Catalytically Active and Spectator Ce3+ in Ceria-Supported Metal Catalysts
Using time-resolved resonant X-ray emission spectroscopy, we quantitatively correlated the initial rate of Ce3+ formation under transient conditions to the overall rate of CO oxidation under steady-state conditions and showed that ceria reduction is a kinetically relevant step in CO oxidation, whereas a fraction of Ce3+ was present as spectators.