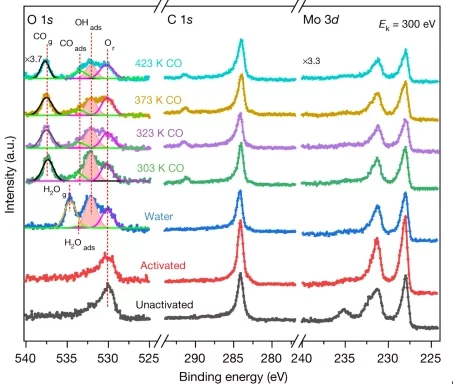
The water–gas shift reaction, leading to the production of hydrogen and carbon dioxide from carbon monoxide and water, is of paramount industrial importance. High activity and stability of the catalysts, typically employed in fuel cells, are important parameter to consider to properly design new materials.
In this work, combining reactivity tests with microscopy and spectroscopy, it has been demonstrated that the co-presence of platinum isolated atoms and nanoclusters supported on molybdenum carbide allows the protection of the support, leading to high stability and high metal-normalized turnover number of 4,300,000 moles of hydrogen per mole of platinum.