Search
Battery Materials and Diagnostics Group
Our goal is to develop novel materials and to improve existing materials for Li-ion, Li-S, and exotic (Na, Mg, Ca, etc...) batteries. We apply different synthetic routes, such as sol-gel chemistry, mechanosynthesis, solid state synthesis under various controlled atmospheres, and microwave synthesis to control the morphology and obtained the most promising electrochemical performances of a dedicated systems.
Study of Graphite Cycling in Sulfide Solid Electrolytes
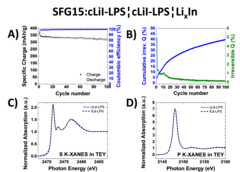
Nowadays, most of the commercial Li-ion batteries employ graphite as the active material in negative electrodes. In the race for the next-generation Li-ion batteries, tremendous research efforts in academia and industry are carried out to replace the current flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid electrolyte, which could improve both, the batteries safety and energy density. Our study investigates two different sulfide-based solid electrolytes, 0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5 (LPS) and 0.3LiI-0.7(0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5), in combination with graphite and discloses the stability of the graphite-solid electrolyte interface. Optimizing the electrode morphology is the key to enhance the rate capability of all-solid-state cells. Using the special tender X-ray range allows chemical characterization of sulfur, phosphor and iodine.
Post mortem/operando XPEEM: for studying the surface of single particle in Li-ion battery electrodes
X-ray photoemission electron microscopy (XPEEM) with its excellent spatial resolution is a well-suited technique to elucidate the complex electrode-electrolyte interface reactions in Li-ion batteries. It provides element-specific contrast images and enables the acquisition of local X-ray absorption spectra on single particles. Here we demonstrate the strength of post mortem measurements and we show the first electrochemical cell dedicated for operando experiments in all-solid-state batteries.
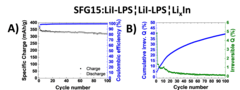
Excellent cycling stability of graphite in all-solid-state battery using sulfide solid electrolyte
All-solid-state lithium ion batteries represent a promising battery technology for boosting the volumetric energy density and promising a superior safety. In this study excellent cycling stability of graphite anode material have been demonstrated in combination with sulfide-based solid electrolyte. Furthermore we evaluated the stability of the graphite-electrolyte interface by analyzing the normalized cumulative irreversible charge during cycling experiments.
Basic course in Electrochemistry (Prof. Dr. Petr Novák, ETHZ)
The basic course in Electrochemistry (given in German) will start in the room HPT C 103 (ETH Campus Hönggerberg) on Monday, September 23, 2019 at 08:45. For further information, please contact PD Dr. Lorenz Gubler, E-mail: Lorenz.Gubler@psi.ch. Download the slides of the lectures here (password-protected): Vorlesung Elektrochemie.
LEC Seminar Archive
Die Seminare finden im Raum ODRA/111 jeweils am Mittwoch um 11:00 Uhr statt. Externe Gäste (ausserhalb des PSI) sind willkommen, werden aber gebeten, sich im Labor-Sekretariat bei Frau Cordelia Gloor unter Tel.: +41 56 310 2919 oder per e-mail anzumelden. Lectures take place in room ODRA/111 on every Wednesday at 11:00 am. External guests (from outside PSI) are welcome, but are requested to register with our secretary Cordelia Gloor at phone: +41 56 310 2919 or via e-mail.