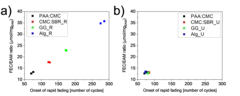Search
Graphite Anodes with Si as Capacity-Enhancing Electrode Additive
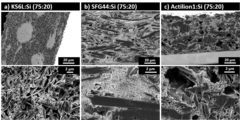
Silicon is a long-standing candidate for replacing graphite as the active material in negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries, due to its significantly higher specific capacity. However, Si suffers from rapid capacity loss, as a result of the large volume expansion and contraction during lithation and de-lithiation. As an alternative to pure Si electrodes, Si could be used as a capacity-enhancing additive to graphite electrodes.
Importance of Identifying Key Experimental Parameters for the Li-ion Battery Performance Testing
The mass loading of Si-graphite electrodes is often considered as a parameter of secondary importance when testing their performance. However, if a sacrificial additive is present in the electrolyte, the electrode loading becomes the battery cycle-life-determining factor. A lower loading was obtained by keeping slurry preparation steps unchanged from binder to binder and resulted in a longer lifetime for some of the binders. When the final loading was kept constant instead, the performance became independent of the binder used.