NUM division - Publication Highlights
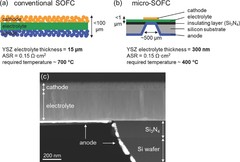
Low-Temperature Micro-Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Partially Amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ Cathodes
Partially amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ (LSC) thin-film cathodes are fabricated using pulsed laser deposition and are integrated in free-standing micro-solid oxide fuel cells (micro-SOFC) with a 3YSZ electrolyte and a Pt anode. A low degree of crystallinity of the LSC layers is achieved by taking advantage of the miniaturization of the cells, which permits low-temperature operation (300–450 °C).
Correlated Decay of Triplet Excitations in the Shastry-Sutherland Compound SrCu2(BO3)2
The temperature dependence of the gapped triplet excitations (triplons) in the 2D Shastry-Sutherland quantum magnet SrCu2(BO3)2 is studied by means of inelastic neutron scattering. The excitation amplitude rapidly decreases as a function of temperature, while the integrated spectral weight can be explained by an isolated dimer model up to 10 K.
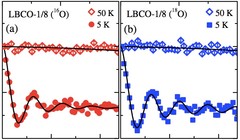
Negative Oxygen Isotope Effect on the Static Spin Stripe Order in Superconducting La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) Observed by Muon-Spin Rot
Large negative oxygen-isotope (16O and 18O) effects (OIEs) on the static spin-stripe-ordering temperature Tso and the magnetic volume fraction Vm were observed in La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) by means of muon-spin-rotation experiments. The corresponding OIE exponents were found to be αTso=-0.57(6) and αVm=-0.71(9), which are sign reversed to αTC=0.46(6) measured for the superconducting transition temperature Tc. This indicates that the electron-lattice interaction is involved in the stripe formation and plays an important role in the competition between bulk superconductivity and static stripe order in the cuprates.
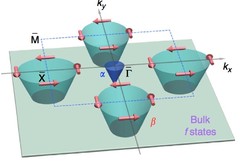
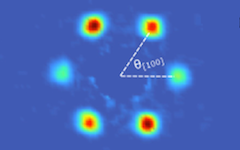
Direct observation of the spin texture in SmB6 as evidence of the topological Kondo insulator
Topological Kondo insulators have been proposed as a new class of topological insulators in which non-trivial surface states reside in the bulk Kondo band gap at low temperature due to strong spin–orbit coupling. In contrast to other three-dimensional topological insulators, a topological Kondo insulator is truly bulk insulating. Furthermore, strong electron correlations are present in the system, which may interact with the novel topological phase. By applying spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, here we show that the surface states of SmB6 are spin polarized. The spin is locked to the crystal momentum, fulfilling time reversal and crystal symmetries.
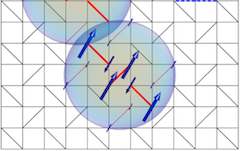
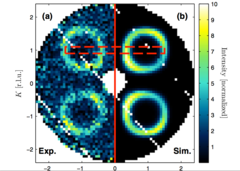
Small-angle neutron scattering study of the mixed state of Yb3Rh4Sn13
Using the small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique we investigated the vortex lattice (VL) in the mixed state of the stannide superconductor Yb3Rh4Sn13. We find a single domain VL of slightly distorted hexagonal geometry for field strengths between 350 and 18 500 G and temperatures between T=0.05 and 6.5 K. We observe a clear in-plane rotation of the VL for different magnetic field directions relative to the crystallographic axes.
Spin-Wave Spectrum of the Quantum Ferromagnet on the Pyrochlore Lattice Lu2V2O7
Neutron inelastic scattering has been used to probe the spin dynamics of the quantum (S=1/2) ferromagnet on the pyrochlore lattice Lu2V2O7. Well-defined spin waves are observed at all energies and wave vectors, allowing us to determine the parameters of the Hamiltonian of the system.
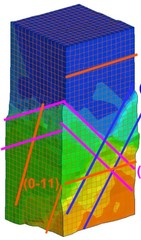
Origin of Anomalous Slip in Tungsten
Low-temperature deformation of body-centered cubic metals shows a significant amount of plastic slip on planes with low shear stresses, a phenomenon called anomalous slip. Despite progress in atomistic modeling of the consequences of complex stress states on dislocation mobility, the phenomenon of anomalous slip remained elusive. Using in situ Laue microdiffraction and discrete dislocation dynamics in micrometer sized tungsten single crystals, we demonstrate the occurrence of significant anomalous slip. It occurs as a consequence of cross kinks, topological configurations generated by prior dislocation interactions.
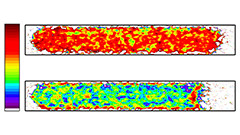
Identification of transitions between liquid water and ice with dual spectrum neutron imaging
The ability to start up at sub-zero Celsius temperatures is a prerequisite for the use of fuel cells in automotive applications, but specific measures need to be taken to prevent the product water to freeze and block the gas supply pathways. In this context, a method for imaging the distribution of liquid water and ice from neutron imaging experiments was developed.
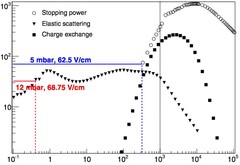
Muon Cooling: Longitudinal Compression
A 10 MeV/c positive muon beam was stopped in helium gas of a few mbar in a magnetic field of 5T. The muon 'swarm' has been efficiently compressed from a length of 16cm down to a few mm along the magnetic field axis (longitudinal compression) using electrostatic fields. The simulation reproduces the low energy interactions of slow muons in helium gas. Phase space compression occurs on the order of microseconds, compatible with the muon lifetime of 2μs. This paves the way for the preparation of a high- quality low-energy muon beam, with an increase in phase space density relative to a standard surface muon beam of 107. The achievable phase space compression by using only the longitudinal stage presented here is of the order of 104.