NUM division - Publication Highlights
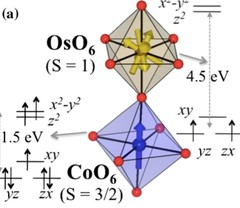
Lattice-Site-Specific Spin Dynamics in Double Perovskite Sr2CoOsO6
Magnetic properties and spin dynamics have been studied for the structurally ordered double perovskite Sr2CoOsO6. Neutron diffraction, muon-spin relaxation, and ac-susceptibility measurements reveal two antiferromagnetic (AFM) phases on cooling from room temperature down to 2 K. In the first AFM phase, with transition temperature TN1=108K, cobalt (3d7, S=3/2) and osmium (5d2, S=1) moments fluctuate dynamically, while their average effective moments undergo long-range order. In the second AFM phase below TN2=67K, cobalt moments first become frozen and induce a noncollinear spin-canted AFM state, while dynamically fluctuating osmium moments are later frozen into a randomly canted state at T≈5K.
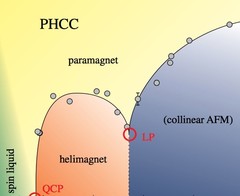
Quantum and classical criticality in a dimerised quantum antiferromagnet
A quantum critical point (QCP) is a singularity in the phase diagram arising due to quantum mechanical fluctuations. The exotic properties of some of the most enigmatic physical systems, including unconventional metals and superconductors, quantum magnets, and ultracold atomic condensates, have been related to the importance of the critical quantum and thermal fluctuations near such a point.
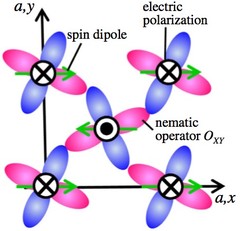
Spin-Nematic Interaction in the Multiferroic Compound Ba2CoGe2O7
We demonstrate the existence of the spin-nematic interactions in an easy-plane type antiferromagnet Ba2CoGe2O7 by exploring the magnetic anisotropy and spin dynamics. The combination of neutron scattering and magnetic susceptibility measurements reveals that the origin of the in-plane anisotropy is an antiferro-type interaction of the spin-nematic operator. The relation between the nematic operator and the electric polarization in the ligand symmetry of this compound is presented. The introduction of the spin-nematic interaction is useful to understand the physics of spin and electric dipole in multiferroic compounds.
Hydride ions in oxide hosts hidden by hydroxide ions
The true oxidation state of formally ‘H?-’ ions incorporated in an oxide host is frequently discussed in connection with chemical shifts of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, as they can exhibit values typically attributed to H+. Here we systematically investigate the link between geometrical structure and chemical shift of H- ?ions in an oxide host, mayenite, with a combination of experimental and ab initio approaches, in an attempt to resolve this issue.
Bipartite magnetic parent phases in the iron oxypnictide superconductor
High-temperature superconductivity appears as a consequence of doping charge carriers into an undoped parent compound exhibiting antiferromagnetic order; therefore, ground-state properties of the parent compound are highly relevant to the superconducting state. On the basis of this logic, spin fluctuations have been considered as the origin of pairing of the superconducting electrons in the cuprates.
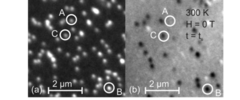
Direct Observation of Magnetic Metastability in Individual Iron Nanoparticles
Studying the magnetization of individual iron (Fe) nanoparticles by magnetic spectromicroscopy reveals that superparamagnetic (SPM) and ferromagnetic blocked (FM) nanoparticles can coexist in the investigated size range of 8-20 nm.
Comprehensive study of the spin-charge interplay in antiferromagnetic La2-xSrxCuO4
The origin of the pseudogap and its relationship with superconductivity in the cuprates remains vague. In particular, the interplay between the pseudogap and magnetism is mysterious. Recent low-temperature angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) experiments on the underdoped cuprate superconductors indicate the presence of a fully gapped Fermi surface (FS); even in the antiferromagnetic phase.
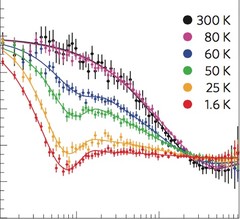
Pressure-Induced Quantum Critical and Multicritical Points in a Frustrated Spin Liquid
The quantum spin-liquid compound (C4H12N2)Cu2Cl6 is studied by muon spin relaxation under hydrostatic pressures up to 23.6 kbar. At low temperatures, pressure-induced incommensurate magnetic order is detected beyond a quantum critical point at Pc ∼ 4.3 kbar. An additional phase transition to a different ordered phase is observed at P1 ∼ 13.4 kbar. The data indicate that the high-pressure phase may be a commensurate one. The established (P-T) phase diagram reveals the corresponding pressure-induced multicritical point at P1, T1 = 2.0 K.
Strong Meissner screening change in superconducting radio frequency cavities due to mild baking
We investigate 'hot' regions with anomalous high field dissipation in bulk niobium superconducting radio frequency cavities for particle accelerators by using low energy muon spin rotation (LE-μSR) on corresponding cavity cutouts. We demonstrate that superconducting properties at the hot region are well described by the non-local Pippard/BCS model for niobium in the clean limit with a London penetration depth λL=23+/-2 nm . In contrast, a cutout sample from the 120C baked cavity shows a much larger λ>100nm and a depth dependent mean free path, likely due to gradient in vacancy concentration. We suggest that these vacancies can efficiently trap hydrogen and hence prevent the formation of hydrides responsible for rf losses in hot regions.