Search
Grüne Treibstoffe für den Flugverkehr
In einer neuen Initiative wollen PSI und Empa gemeinsam einen Prozess entwickeln, um Kerosin aus erneuerbaren Ressourcen herzustellen.
“More objectivity would be helpful”
The current energy debate could do with more facts and less gut feeling – argue Thomas J. Schmidt, renewables expert, and Andreas Pautz, nuclear energy specialist.
Wie wichtig ist Wasserstoff für die Energiewende?
Einordnungen von Thomas J. Schmidt, Energieexperte des PSI
Switzerland’s path to the net-zero target
The ETH institutions are pooling their expertise in pursuit of the net-zero target.
Zukünftige Computerchips mit "elektronischem Blutkreislauf"
Im Rahmen des Sinergia-Programms fördert der Schweizerische Nationalfonds das dreijährige Forschungsvorhaben REPCOOL. Unter der Leitung von IBM Research à Zürich arbeiten in diesem Projekt Wissenschaftler der ETH Zürich, des Paul Scherrer Instituts in Villigen und der Università della Svizzera italiana in Lugano gemeinsam an der Erforschung eines elektronischen Blutkreislaufs für zukünftige 3D-Computerchips. Vom menschlichen Gehirn inspiriert, entwickeln die Forscher ein Mikrokanalsystem mit einer elektrochemischen Flussbatterie, die 3D-Chipstapel gleichzeitig kühlen und mit Energie versorgen. Ultimatives Ziel ist die Entwicklung eines Supercomputers in PC-Grösse.This news release is only available in German.
Five times less platinum: fuel cells could become economically more attractive thanks to novel aerogel catalyst.
Fuel cells that convert hydrogen into power and only produce pure water as a by-product have the potential to lead individual mobility into an environmentally friendly future. The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) has been researching and developing such low-temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells for more than 10 years and initial field tests have already demonstrated the successful use of these fuel cells in cars and buses. However, further research is still required to improve the durability and economic viability of the technology. An international team of researchers involving the PSI has now manufactured and characterised a novel nanomaterial that could vastly increase the efficiency and shelf-life of these fuel cells à as well as reduce material costs.
Mit Röntgenlicht zu besseren Antrieben
Um den Strassenverkehr der Schweiz zukunftsfähig zu machen, ist vor allem Forschung gefragt. In den Grossforschungsanlagen des PSI untersuchen Chemiker und Ingenieure, wie Antriebe effizienter und abgasärmer werden.
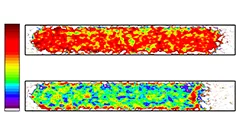
Ice in fuel cells imaged directly for the first time
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have succeeded in imaging the distribution of frozen and liquid water in a hydrogen fuel cell directly for the first time. They applied a new imaging technique that uses successively two beams with different neutron energies to distinguish between areas with liquid water and those with ice extremely reliably. The method therefore opens up the prospect of studying one of the main problems of using fuel cells to power vehicles: ice can clog the pores in the fuel cells and affect their performance. The PSI scientists’ results will be published in the journal Physical Review Letters on 16 June 2014.