NUM division - Publication Highlights
Multiferroic Properties of o−LuMnO3 Controlled by b-Axis Strain
Strain is a leading candidate for controlling magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroics. Here, we use x-ray diffraction to study the coupling between magnetic order and structural distortion in epitaxial films of the orthorhombic (o-) perovskite LuMnO3. An antiferromagnetic spin canting in the E-type magnetic structure is shown to be related to the ferroelectrically induced structural distortion and to a change in the magnetic propagation vector.
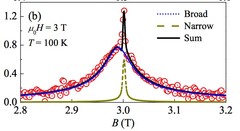
Direct Spectroscopic Observation of a Shallow Hydrogenlike Donor State in Insulating SrTiO3
We present a direct spectroscopic observation of a shallow hydrogenlike muonium state in SrTiO3 which confirms the theoretical prediction that interstitial hydrogen may act as a shallow donor in this material. The formation of this muonium state is temperature dependent and appears below ∼70 K. From the temperature dependence we estimate an activation energy of ∼50 meV in the bulk and ∼23 meV near the free surface. The field and directional dependence of the muonium precession frequencies further supports the shallow impurity state with a rare example of a fully anisotropic hyperfine tensor.
The μ → eγ decay in a systematic effective field
We implement a systematic effective field theory approach to the benchmark process μ → eγ, performing automated one-loop computations including dimension 6 operators and studying their anomalous dimensions. We obtain limits on Wilson coefficients of a relevant subset of lepton-flavour violating operators that contribute to the branching ratio μ → eγ at one-loop.
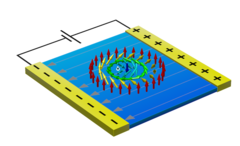
Electric-Field-Induced Skyrmion Distortion and Giant Lattice Rotation in the Magnetoelectric Insulator Cu2OSeO3
Discovering fundamentally new ways to manipulate magnetic spins is crucial for research into advanced technologies. Magnetic Skyrmions, which are topologically stable whirls of magnetic spins, are promising candidates for new device components since those found in metallic host materials can be manipulated using electric currents.
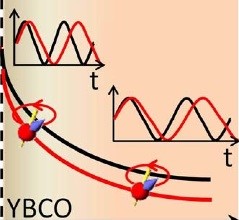
Controlling the near-surface superfluid density in under doped YBa2Cu3O6+x by photo-illumination
The interaction with light weakens the superconducting ground state in classical superconductors. The situation in cuprate superconductors is more complicated: illumination increases the charge carrier density, a photo-induced effect that persists below room temperature. Furthermore, systematic investigations in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6+x (YBCO) have shown an enhanced critical temperature Tc. Until now, studies of photo-persistent conductivity (PPC) have been limited to investigations of structural and transport properties, as well as the onset of superconductivity.
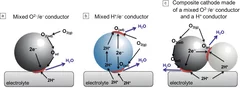
Low-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells based on proton-conducting electrolytes
The need for reducing the operating temperature of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) imposed by cost reduction has pushed significant progress in fundamental understanding of the individual components, as well as materials innovation and device engineering. Proton-conducting oxides have emerged as potential alternative electrolyte materials to oxygen-ion conducting oxides for operation at low and intermediate temperatures.
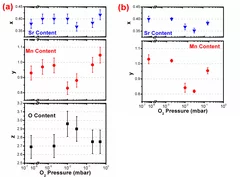
Plasma interactions determine the composition in pulsed laser deposited thin films
Plasma chemistry and scattering strongly affect the congruent, elemental transfer during pulsed laser deposition of target metal species in an oxygen atmosphere. Studying the plasma properties of La0.6Sr0.4MnO3, we demonstrate for as grown La0.6Sr0.4MnO3-δ films that a congruent transfer of metallic species is achieved in two pressure windows: ∼10−3 mbar and ∼2 × 10−1 mbar.
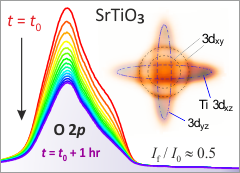
Mixed Dimensionality of Confined Conducting Electrons in the Surface Region of SrTiO3
Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, we show that the recently discovered surface state on SrTiO3 consists of nondegenerate t2g states with different dimensional characters.
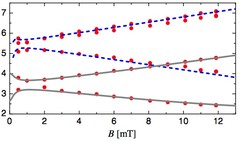
Spin-lattice coupling induced weak dynamical magnetism in EuTiO3 at high temperatures
EuTiO3, which is a G-type antiferromagnet below TN = 5.5 K, has some fascinating properties at high temperatures, suggesting that macroscopically hidden dynamically fluctuating weak magnetism exists at high temperatures. This conjecture is substantiated by magnetic field dependent magnetization measurements, which exhibit pronounced anomalies below 200 K becoming more distinctive with increasing magnetic field strength. Additional results from muon spin rotation experiments provide evidence for weak fluctuating bulk magnetism induced by spin-lattice coupling which is strongly supported in increasing magnetic field.
![Temperature dependence of the (050) reflection from a 200 nm o−LuMnO3 [110]-oriented film. Inset (a): Temperature dependence of the integrated intensity from the (050) structural reflection (black) and the (0qb≈½0) magnetic reflection (red) of this film. Inset (b): The simplest approximation for a distortion producing nonzero intensity for a (0k0) reflection with k odd, depicted for two atoms along the b direction.](/sites/default/files/styles/primer_teaser_square_scale/public/import/num/SHL20141014MultiferroicPropertiesEN/LMO_Strain_Will_PRL_2014.jpg?itok=f8He4m9Q)