NUM division - Publication Highlights
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
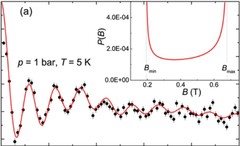
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.
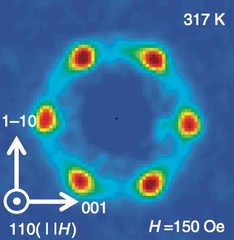
Néel-type skyrmion lattice with confined orientation in the polar magnetic semiconductor GaV4S8
Following the early prediction of the skyrmion lattice (SkL) - a periodic array of spin vortices - it has been observed recently in various magnetic crystals mostly with chiral structure. Although non-chiral but polar crystals with Cnv symmetry were identified as ideal SkL hosts in pioneering theoretical studies, this archetype of SkL has remained experimentally unexplored.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
B. Wehinger et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 305401 (2015). This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass.
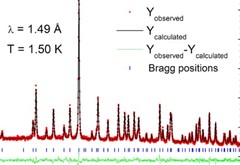
Candidate Quantum Spin Liquid in the Ce3+ Pyrochlore Stannate Ce2Sn2O7
We report the low-temperature magnetic properties of Ce2Sn2O7, a rare-earth pyrochlore. Our suscep- tibility and magnetization measurements show that due to the thermal isolation of a Kramers doublet ground state, Ce2Sn2O7 has Ising-like magnetic moments of ∼1.18 μB. The magnetic moments are confined to the local trigonal axes, as in a spin ice, but the exchange interactions are antiferromagnetic.
Beating the Stoner criterion using molecular interfaces
Only three elements are ferromagnetic at room temperature: the transition metals iron, cobalt and nickel. The Stoner criterion explains why iron is ferromagnetic but manganese, for example, is not, even though both elements have an unfilled 3d shell and are adjacent in the periodic table: according to this criterion, the product of the density of states and the exchange integral must be greater than unity for spontaneous spin ordering to emerge.
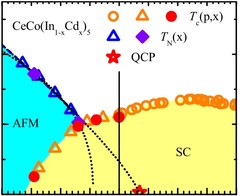
Evidence for Coexistence of Bulk Superconductivity and Itinerant Antiferromagnetism in the Heavy Fermion System CeCo(In1−xCdx)5
In the generic phase diagram of heavy fermion systems, tuning an external parameter such as hydrostatic or chemical pressure modifies the superconducting transition temperature. The superconducting phase forms a dome in the temperature-tuning parameter phase diagram, which is associated with a maximum of the superconducting pairing interaction. Proximity to antiferromagnetism suggests a relation between the disappearance of antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity.
A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
Skyrmions, topologically protected vortex-like nanometric spin textures in magnets, have been attracting increasing attention for emergent electromagnetic responses and possible technological applications for spintronics. In particular, metallic magnets with chiral and cubic/tetragonal crystal structure may have high potential to host skyrmions that can be driven by low electrical current excitation.
Interplay between magnetic order at Mn and Tm sites alongside the structural distortion in multiferroic films of o-TmMnO3
We employ resonant soft x-ray diffraction to individually study the magnetic ordering of the Mn and the Tm sublattices in single-crystalline films of orthorhombic (o−)TmMnO3. The same magnetic ordering wave vector of (0q0) with q≈0.46 is found for both ionic species, suggesting that the familiar antiferromagnetic order of the Mn ions induces a magnetic order on the Tm unpaired 4f electrons.
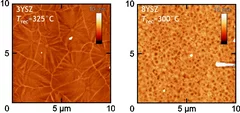
Crystallization of zirconia based thin films
In pulsed laser deposition the use of a rectangular or elliptical beam spot with a non 1:1 aspect ratio leads to the so called flip-over effect. Here, the longest dimension of the laser spot results in the shortest direction of plasma plume expansion.