NUM division - Publication Highlights
Nanostructure surveys of macroscopic specimens by small-angle scattering tensor tomography
The mechanical properties of many materials are based on the macroscopic arrangement and orientation of their nanostructure. This nanostructure can be ordered over a range of length scales. In biology, the principle of hierarchical ordering is often used to maximize functionality, such as strength and robustness of the material, while minimizing weight and energy cost.
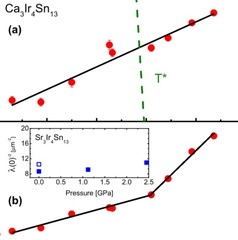
Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
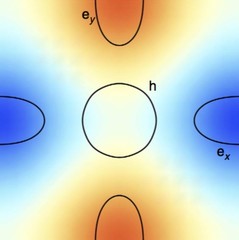
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
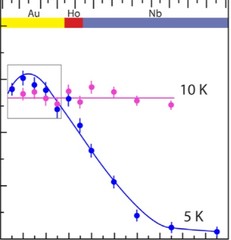
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
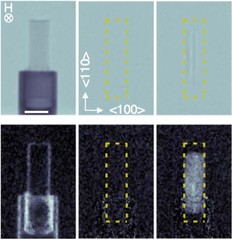
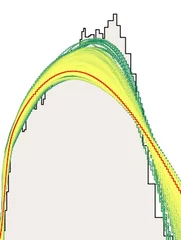
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Observation of Gravitationally Induced Vertical Striation of Polarized Ultracold Neutrons by Spin-Echo Spectroscopy
We describe a spin-echo method for ultracold neutrons (UCNs) confined in a precession chamber and exposed to a |B0| = 1μT magnetic field. We have demonstrated that the analysis of UCN spin-echo resonance signals in combination with knowledge of the ambient magnetic field provides an excellent method by which to reconstruct the energy spectrum of a confined ensemble of neutrons.
Response of Plasma-Polymerized Hexamethyldisiloxane Films to Aqueous Environments
Thin plasma polymer films were deposited in hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and HMDSO/O2 low-pressure discharges and their chemical structures analyzed using infrared (IR) spectroscopy and neutron reflectometry (NR). The (plasma-polymerized) ppHMDSO film exhibits hydrophobic, poly(dimethylsiloxane)-like properties, while the retention of carbon groups is reduced by O2 addition, yielding a more inorganic, hydrophilic ppSiOx film.
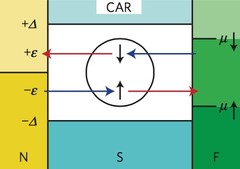
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
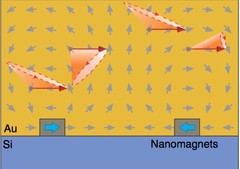
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.