NUM division - Publication Highlights
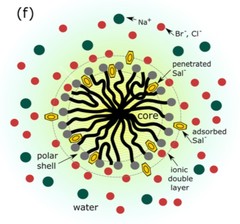
Viscoelasticity Enhancement of Surfactant Solutions Depends on Molecular Conformation: Influence of Surfactant Headgroup Structure and Its Counterion
During the anisotropic growth from globular to wormlike micelles, the basic interactions among distinct parts of the surfactant monomer, its counterion, and additives are fundamental to tune molecular self-assembly. We investigate the addition of sodium salicylate (NaSal) to hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and bromide (CTAC and CTAB), 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride and bromide (CPyCl and CPyBr), and benzyldimethylhexadecylammonium chloride (BDMC), which have the same hydrophobic tail.
Observation of Weyl nodes and Fermi arcs in tantalum phosphide
A Weyl semimetal possesses spin-polarized band-crossings, called Weyl nodes, connected by topological surface arcs. The low-energy excitations near the crossing points behave the same as massless Weyl fermions, leading to exotic properties like chiral anomaly. To have the transport properties dominated by Weyl fermions, Weyl nodes need to locate nearly at the chemical potential and enclosed by pairs of individual Fermi surfaces with non-zero Fermi Chern numbers.
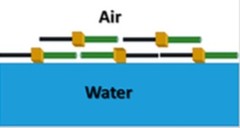
Semifluorinated Alkanes at the Air–Water Interface: Tailoring Structure and Rheology at the Molecular Scale
Semifluorinated alkanes form monolayers with interesting properties at the air–water interface due to their pronounced amphi-solvophobic nature and the stiffness of the fluorocarbons. In the present work, using a combination of structural and dynamic probes, we investigated how small molecular changes can be used to control the properties of such an interface, in particular its organization, rheology, and reversibility during compression–expansion cycles.
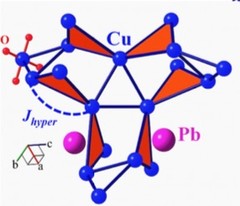
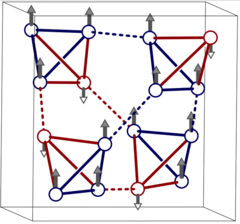
Spin Liquid State in the 3D Frustrated Antiferromagnet PbCuTe2O6: NMR and Muon Spin Relaxation Studies
PbCuTe2O6 is a rare example of a spin liquid candidate featuring a three-dimensional magnetic lattice. Strong geometric frustration arises from the dominant antiferromagnetic interaction that generates a hyperkagome network of Cu2+ ions although additional interactions enhance the magnetic lattice connectivity.
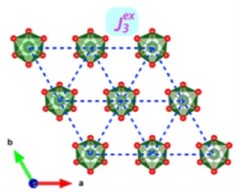
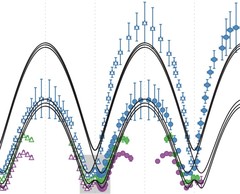
Spin excitations in copper selenate, a skyrmion host material
G.S. Tucker et al., Physical Review B 93, 054401 (2016). Inelastic neutron scattering measurements performed at EIGER and TASP have mapped the magnetic excitation spectrum along high-symmetry directions of the first Brillouin zone for the magnetic skyrmion host copper selenate, Cu2OSeO3.
Giant Controllable Magnetization Changes Induced by Structural Phase Transitions in a Metamagnetic Artificial Multiferroic
The realization of a controllable metamagnetic transition from AFM to FM ordering would open the door to a plethora of new spintronics based devices that, rather than reorienting spins in a ferromagnet, harness direct control of a materials intrinsic magnetic ordering. In this study FeRh films with drastically reduced transition temperatures and a large magneto-thermal hysteresis were produced for magnetocaloric and spintronics applications.
Stratified Micellar Multilayers - Toward Nanostructured Photoreactors
Polyelectrolyte multilayers (PEMs) with stratification of the internal structure were assembled from statistical amphiphilic copolyelectrolytes of opposite charges. These polyelectrolytes organize in aqueous solutions into micellar structures with fluoroalkyl and aromatic nanodomains, respectively, that were also preserved after deposition as thin films via layer-by-layer (LbL) electrostatic self-assembly.
Origin of the Spin-Orbital Liquid State in a Nearly J=0 Iridate Ba3ZnIr2O9
We show using detailed magnetic and thermodynamic studies and theoretical calculations that the ground state of Ba3ZnIr2O9 is a realization of a novel spin-orbital liquid state. Our results reveal that Ba3ZnIr2O9 with Ir5+ (5d4) ions and strong spin-orbit coupling (SOC) arrives very close to the elusive J 1⁄4 0 state but each Ir ion still possesses a weak moment.
Quasiparticle-continuum level repulsion in a quantum magnet
When the energy eigenvalues of two coupled quantum states approach each other in a certain parameter space, their energy levels repel each other and level crossing is avoided. Such level repulsion, or avoided level crossing, is commonly used to describe the dispersion relation of quasiparticles in solids.