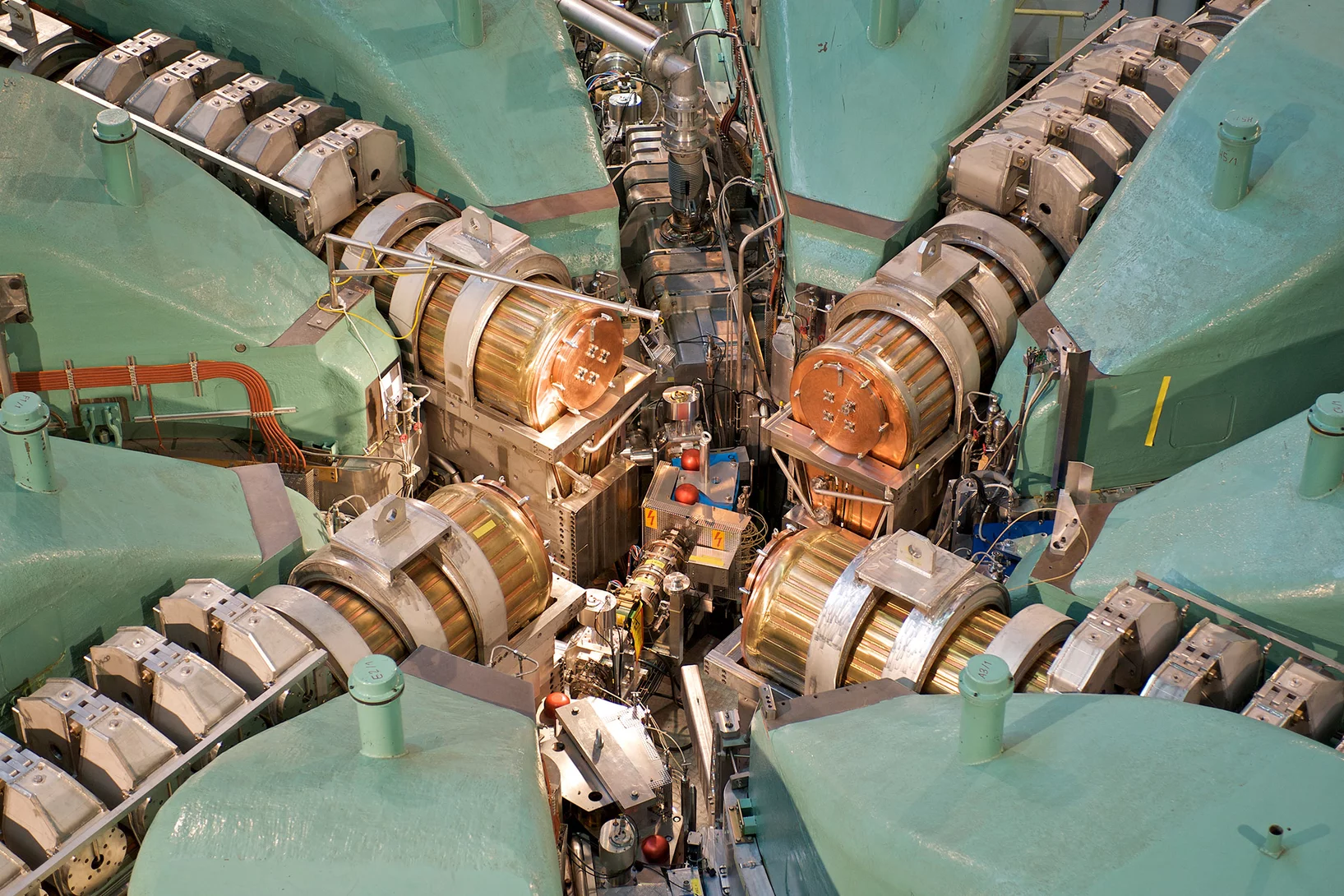
Neutron scattering techniques are highly versatile and powerful tools for studying the structure and dynamics of condensed matter. A wide scope of problems, ranging from fundamental to solid state physics and chemistry, and from materials science to biology, medicine and environmental science, can be investigated with neutrons. In addition to scattering, non-diffractive methods like imaging techniques allows for non-destructive inspection of materials and components, providing information on their internal structure, composition, and integrity with growing relevance also for industrial applications.
The spallation neutron source SINQ is a continuous source - the first and only one of its kind in the world - with a flux of about 1014 n/cm2/s. Beside thermal neutrons, a cold moderator of liquid deuterium (cold source) slows neutrons down and shifts their spectrum to lower energies. These neutrons have proved to be particularly valuable in materials research and in the investigation of biological substances.
SINQ operates as a user facility, meaning that scientists and research groups from around the world can apply for beamtime to conduct experiments using its various neutron instruments.
Latest News
The call for proposals I-26 is closed now. The next proposal submission deadline is planned for 15 May 2026. Please find more detailed information following the link below.
Latest Scientific Highlights and News
Low-frequency electrochemical pulsing to manage flooding and salt precipitation in zero-gap CO2-to-ethylene electrolyzers
The electrochemical conversion of CO2 to ethylene offers a promising approach to expand manufacturing of commodity chemicals and fuels. Specifically, ethylene is a critical precursor for polyethylene a $240B industry. Expanding productivity ...
Investigating the hidden content of Tibetan bronze statues using modern neutron imaging techniques
Bronze statues hold deep significance in Buddhism and Bon, often containing relics sealed within their hollow interiors. Traditional scholarly methods, such iconographic analysis, cannot access the hidden contents of these statues without risking physical damage. This study proposes ...
Anisotropic Band-Split Magnetism in Magnetostrictive CoFe2O4
Single crystal spinel CoFe₂O₄ exhibits the largest room-temperature saturation magnetostriction among non-rare-earth compounds and a high Curie temperature (T₍c₎ ∼ 780 K), properties that are critical to a wide range of industrial and medical applications. Neutron spectroscopy ...
User Contacts
Office hours
Monday through Friday from 8:00-11:30 and 12:30-17:00
otherwise please contact us per email
User Office
Provides all information about user access to the PSI Large Research Facilities
DUO Login
Direct link to the Digital User Office