Recherche
Publications 2019
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
Publications 2017
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
Publications
NRES Publications
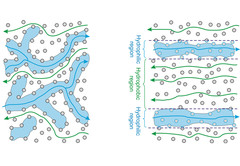
Gas Diffusion Layers with Patterned Wettability
During PEFC’s operation the reactant gas is fed to the cell through the gas diffusion layer (GDL) and through the same material the product water is removed. Water accumulation near the catalyst can block the gas access causing an increase of the mass transport losses. On the other hand, PEFC’s work with a solid electrolyte membrane that needs to be hydrated in order to be proton conductive. In order to obtain the maximum performance PEFC’s require a well-balanced water management.
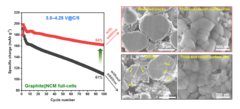
Improved Interfacial Stability of Ni-rich Oxide Full-Cells
PSI researchers have identified a novel electrolyte additive, allowing extended voltage range of Ni-rich oxide full-cells, while keeping excellent performance. The instability of cathode–electrolyte interface causes the structural degradation of cathode active material and the electrolyte consumption, resulting in a rapid capacity fading and shortening battery life-time. The PSI-identified additive help to alleviate these problems and extend battery life-time.
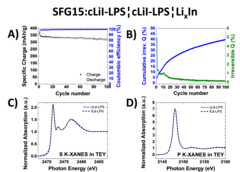
Study of Graphite Cycling in Sulfide Solid Electrolytes
Nowadays, most of the commercial Li-ion batteries employ graphite as the active material in negative electrodes. In the race for the next-generation Li-ion batteries, tremendous research efforts in academia and industry are carried out to replace the current flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid electrolyte, which could improve both, the batteries safety and energy density. Our study investigates two different sulfide-based solid electrolytes, 0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5 (LPS) and 0.3LiI-0.7(0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5), in combination with graphite and discloses the stability of the graphite-solid electrolyte interface. Optimizing the electrode morphology is the key to enhance the rate capability of all-solid-state cells. Using the special tender X-ray range allows chemical characterization of sulfur, phosphor and iodine.
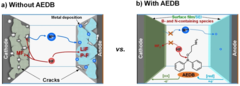
Cross-Talk–Suppressing Electrolyte Additive for Li-ion Batteries
Control of interfacial reactivity at high-voltage is a key to high-energy-density Li-ion batteries. 2-aminoethyldiphenyl borate was investigated as an electrolyte additive to stabilize surface and bulk of both NCM851005 and graphite in the cell with upper cut-off voltage of 4.4 V vs Li+/Li. AEDB almost completely eliminated the “cross-talk” in the cell, by significantly reducing metal leaching from the cathode, preventing their deposition at the anode, and further electrolyte decomposition.